- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Persuasive Speech
Types Of Persuasive Speeches

3 Basic Types of Persuasive Speeches
People also read
Making Persuasive Speech Writing Easy: Steps and Tips
Good Persuasive Speech Topics & Ideas for Debaters
200+ Motivational Speech Topics and Ideas To Inspire You (2024)
16 Best Persuasive Speech Examples for Students
Persuasive Speech Outline - Samples, Format, and Writing Tips
If the question, “How many types of persuasive speeches are there?” is bothering you, worry not, we’ll answer all your questions!
In this guide, you will learn these three types of persuasive speeches in detail, and with comprehensive examples for each kind, we’ll clear all your doubts.
So let’s begin!
- 1. Types of Persuasive Speeches
- 2. Persuasive Speech Topics for Different Types
Types of Persuasive Speeches
Persuasive speeches work with evaluative statements that can be supported by data and reasoning. The subject and the content of the speech determine what kind of persuasive speech it is.
To list the types of persuasive speeches, they are:
Factual Persuasive Speech
- Value Persuasive Speech
Policy Persuasive Speech
Backed with strong evidence, a factual persuasive speech is based on whether a belief or statement is true or false. In simple words, a speaker is attempting to convince the audience about the occurrence or existence of something.
Some factual claims are simple to answer and easy to handle. For example, a speaker is talking about Neil Armstrong's landing on the moon in 1969. This example is well documented and has concrete evidence that supports the fact that Neil Armstrong did land on the moon.
In contrast, some facts are hard to establish, and they can’t be answered in a definite way.
For example, It's hard to say for sure if a stock will go up by 20% next year. Although historical data and expert analysis may suggest this possibility, unforeseen market dynamics always have an uncertain influence on the future.
Your job as a speaker is to persuade your audience, which acts as both opposition attorneys and judges.
Here are some examples of factual claims in a persuasive speech:
- "The global temperature has risen by 1.2 degrees Celsius over the past century due to human activities."
- "The Great Wall of China was constructed primarily to protect against invasions from nomadic tribes."
See this comprehensive factual persuasive speech example:
Value Persuasive Speech
Value persuasive speech states whether something is right or wrong, beautiful or ugly, moral or immoral, or good or bad. It questions the ethical and moral aspects of a particular topic or defines the truth or falsity of an assertion.
For example , can you prove that capital punishment is moral or immoral? The government has added extra tax on gas-guzzling monstrosities, etc. These are some value persuasive speech examples, where you can’t prove whether it is moral or immoral, right or wrong.
The audience might agree or disagree with your point of view. In value persuasive speaking, it is hard to determine why the speaker has chosen a specific stance on a particular topic without listening to his criteria for making a certain evaluation statement.
Let’s say that a speaker claims that all social media sites are immoral. Then they need to provide a strong basis for their evaluation. For the audience to understand the reasoning, the speaker should elaborate on the criteria leading to their conclusion.
These are some examples of value claims:
- "Modern art is more valuable and thought-provoking than classical art."
- "It is our ethical duty to reduce plastic use to protect marine life and the environment."
For a deeper insight, take a look at this comprehensive example of a value persuasive speech:
3. Policy Persuasive Speech
The other most common claim in persuasive speech is a policy claim. This claim is used to convince the audience to either accept or reject a certain policy, candidate, or rule. It argues the nature of the problem and the solution that should be taken.
Probably, this is the most common type of persuasive speech because we live in a society surrounded by policies, rules, and laws.
For instance , when a spokesperson calls for a revision of the legal definition of prostitution, they are urging immediate action and agreement. This type of claim presents a clear opinion about the necessary changes and the expected outcome.
Here are examples of policy claims:
- "The minimum wage should be increased to a living wage to help reduce poverty and improve living standards."
- "Companies should be required to offer paid parental leave to support working families."
Below is a detailed example of a policy persuasive speech:
You can learn how to perfectly outline your persuasive speech with the help of our guide!
The policy claim has two persuasive goals: immediate action and passive agreement.
- Immediate Action
The immediate action persuades the audience to start engaging in certain behaviors. It requires the speaker to convince the audience to act upon his proposal quickly.
For example , the speaker delivers a speech at a school and wants to persuade the student audience to eat more fruits. He would say that an apple a day keeps the doctor away, so he’s encouraging them to either bring apples with their lunch or eat them at their home.
This action of the speaker makes the audience act immediately on his proposal. Remember that the more quickly you make your audience members act upon your proposal, the more likely they will adopt it.
- Passive Agreement
Passive agreement only requires the audience to agree with the speaker. When the speaker tries to gain a passive agreement, he attempts to make the audience agree with what he is saying or accept the policy without practically doing anything.
For instance , the speaker argues that the LGBT community should have equal human rights. The speaker attempts to reach the audience’s agreement by presenting encouraging and strong facts without demanding any action from the audience.
The passive agreement’s main goal is to encourage the audience to adopt a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior, but not necessarily to get the audience members to enact any specific behavior.
Want to know what are examples of persuasive speeches ? Head over to our detailed blog!
Persuasive Speech Topics for Different Types
Different types of persuasive speeches focus on distinct themes and have unique objectives. Whether you're aiming to establish facts, evaluate values, or advocate for policies, choosing the right topic is essential. Below are the different persuasive speech topics:
Policy Persuasive Speech Topics
This kind of persuasive speech advocates for a specific course of action or a change in policy. These topics aim to convince the audience to support or enact certain measures:
- Implementing Universal Healthcare Coverage in the United States
- Enacting Stricter Gun Control Laws to Reduce Mass Shootings
- Implementing Comprehensive Immigration Reform to Address Undocumented Immigration
- Adopting Mandatory Paid Parental Leave Policies for Working Parents
- Reforming the Criminal Justice System to Reduce Racial Disparities in Sentencing
- Enforcing Stricter Regulations on Carbon Emissions to Combat Climate Change
- Establishing Free College Tuition Programs to Increase Access to Higher Education
- Implementing Affirmative Action Policies to Promote Diversity in the Workplace and Education
- Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures to Protect Personal Data and Privacy Online
- Introducing Mandatory Voting Laws to Increase Voter Turnout and Political Participation
Fact Persuasive Speech Topics
Factual persuasive speeches aim to establish the truth or falsehood of a statement by presenting evidence and logical reasoning. These topics often involve empirical data and scientific research:
- The Impact of Climate Change on Polar Ice Caps
- The Link Between Smoking and Lung Cancer
- The Benefits of Regular Exercise on Heart Health
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Function
- The Role of Renewable Energy Sources in Reducing Carbon Emissions
- The Importance of Early Childhood Education in Academic Success
- The Relationship Between Diet and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- The Impact of Deforestation on Biodiversity Loss
- The Effectiveness of Vaccines in Preventing Infectious Diseases
- The Influence of Technology on Human Behavior and Social Interaction
Value Persuasive Speech Topics
Value persuasive speeches focus on the worth, morality, or rightness of an issue. These topics involve ethical considerations and personal beliefs:
- The Ethics of Animal Testing
- The Importance of Preserving Cultural Heritage
- The Value of Digital Privacy
- The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- The Importance of Fair Trade Practices
- The Value of Higher Education
- The Moral Responsibility of Ethical Consumption
- The Necessity of Work-Life Balance
- The Benefits of Gender Equality in the Workplace
- The Role of Art in Society
Need more topics? Explore our extensive list of persuasive speech topics to get ideas!
To wrap it up,
This guide has made the 3 types of persuasive speeches clear, so you should be able to write an effective one now.
Writing any type of persuasive speech can be tricky, but with some good examples, you can craft a strong speech.
Still finding it challenging? If you need help, ask us " Just do my essay !" MyPerfectWords.com offers a quality and 100% unique speechess at affordable prices.
Order your speech from our speech writing service and make a lasting impact on your listeners. Our expert writers are here to meet your expectations and deliver top-notch results!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Cathy has been been working as an author on our platform for over five years now. She has a Masters degree in mass communication and is well-versed in the art of writing. Cathy is a professional who takes her work seriously and is widely appreciated by clients for her excellent writing skills.
Struggling With Your Paper?
Get a custom paper written at
With a FREE Turnitin report, and a 100% money-back guarantee
LIMITED TIME ONLY!
Keep reading


15 Powerful Persuasive Speech Examples to Inspire Your Next Talk
- The Speaker Lab
- June 24, 2024
Table of Contents
Crafting a persuasive speech that captivates your audience and drives them to action is no easy feat. If you’re hitting the books, climbing the corporate ladder, or just dreaming of rocking the stage with your speeches, having a killer set of persuasive speech examples can totally change your game. In this post, we’ve curated some of the most compelling and inspiring persuasive speech examples to help you elevate your own speaking skills. So buckle up and grab your pen, because we’re diving into the secrets behind these unforgettable speeches.
What is a Persuasive Speech?
When we talk about a persuasive speech , we refer to a form of communication that seeks to influence the audience’s beliefs or actions. In the course of a persuasive speech, a person will present compelling arguments—backed by evidence and persuasive techniques—in order to convince listeners to embrace a specific viewpoint or take a particular course of action. Persuasive speeches are used in many different areas of life, such as in a school or university setting, in a job, or in a social setting.
When preparing to give a persuasive speech, always choose a topic or cause you’re interested in and passionate about. If you want to convince other people to agree with your stance, you must be seen to believe in it yourself. In addition, it helps to choose a topic that people care about and hasn’t been overdone.
Funny Persuasive Speech Examples
Looking for some funny persuasive speech examples to inspire your next presentation? You’ve come to the right place. Humor is a powerful tool when it comes to persuasion. It can help you connect with your audience, make your message more memorable, and even diffuse tension around controversial topics.
One classic example comes from David McCullough, Jr.’s high school commencement speech entitled “You Are Not Special.” While the title might not sound funny, McCullough delivers a hilarious reality check to graduates, poking fun at the coddling and praise they’ve received growing up. His ultimate message—that true success comes from hard work and taking risks—is made all the more powerful by his humorous approach.
But what makes funny persuasive speeches so effective? For one, humor helps the speakers build rapport with their audiences. Laughter is a shared experience that brings people together and makes them more open to new ideas. Additionally, injecting some levity into a speech can make the overall message more palatable and less preachy.
Of course, using humor in a persuasive speech requires some finesse. The jokes should be tasteful, relevant to your overall message, and not offensive to your audience. When in doubt, err on the side of caution. After all, a flat joke is better than one that leaves listeners cringing.
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a FREE call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
Persuasive Speech Examples About Public Policy
Policy persuasive speeches advocate for a particular course of action on a public policy issue. These speeches go beyond simply raising awareness about a problem – they propose concrete solutions and try to sway the audience to support a specific plan.
One powerful policy persuasive speech example comes from Greta Thunberg’s address to the UN Climate Action Summit in 2019 . Thunberg doesn’t mince words when lambasting world leaders for their inaction on climate change. But she also lays out clear policy demands, like immediately halting fossil fuel subsidies and drastically reducing carbon emissions. Her message is clear: we know what needs to be done and we need to do it.
When crafting your own policy persuasive speech, it’s important to back up your arguments with solid evidence. Use statistics, expert testimony, and real-world examples to show why your proposed solution is feasible and necessary. Anticipate counterarguments and address them head-on. And most importantly, make a clear call to action. Ask yourself: what exactly do you want your audience to do to support your policy goals?
Value Persuasive Speech Examples
Value persuasive speeches aim to change people’s beliefs or attitudes about a particular issue. Rather than advocating for a specific policy, these speeches try to shift the audience’s underlying values and assumptions.
A classic example of a value persuasive speech is Mary McLeod Bethune’s “ What Does American Democracy Mean to Me? ” address. As an African American woman born into poverty, Bethune faced countless obstacles and injustices throughout her life. But in this speech, she reframes the narrative around American democracy, arguing that our nation’s highest ideals are worth fighting for, even if we haven’t yet lived up to them. By appealing to shared values like freedom, justice, and equality, Bethune inspires her audience to keep pushing for change.
The key to a successful value persuasive speech is tapping into your audience’s existing beliefs and values. Use vivid language and storytelling to paint a picture of the world you want to see. Make your case in moral and ethical terms, not just practical ones. And don’t be afraid to show some vulnerability. By sharing your own experiences and struggles, you can create an emotional connection with your listeners.
Persuasive Speech Examples About Social Issues
Social issues make for compelling persuasive speech topics because they touch on deeply held beliefs and affect people’s everyday lives. Whether you’re talking about racial justice, gender equality, or income inequality, these speeches require a deft touch and a willingness to engage with complex, often controversial ideas.
Talking About Mental Health
One powerful example of a persuasive speech about mental health is Kevin Breel’s “ Confessions of a Depressed Comic ” from TEDxKids@Ambleside. As a stand-up comedian, Breel knows how to get laughs, but he also knows the pain of living with depression. In this speech, he shares his own story of struggling with mental illness and calls on society to break the stigma around talking about mental health. By speaking vulnerably, Breel makes a compelling case for why we need to take depression seriously and support those who are struggling.
Addressing Physical Health
Another great example of a persuasive speech about health is Jamie Oliver’s TED Talk “ Teach Every Child About Food .” As a celebrity chef, Oliver has seen firsthand the impact of poor nutrition on people’s health. In this speech, he makes a passionate plea for better food education in schools, arguing that it’s a matter of life and death. With shocking statistics and personal anecdotes, Oliver paints a grim picture of the obesity epidemic and calls on parents, educators, and policymakers to take action.
Persuasive Speech Examples About the Environment
Environmental issues are some of the most pressing challenges we face as a society. From climate change to pollution to habitat destruction, the stakes couldn’t be higher. That’s why persuasive speeches about the environment are so important. By inspiring people to take action, they make a true difference.
One of the most famous environmental speeches of all time is Al Gore’s “An Inconvenient Truth” lecture, which was later turned into an Academy Award-winning documentary. In this speech, Gore lays out the scientific evidence for climate change and argues that we have a moral imperative to act. With compelling visuals and a sense of urgency, Gore makes a powerful case for why we need to reduce our carbon footprint and transition to renewable energy sources.
Another great example of an environmental persuasive speech is Severn Suzuki’s address to the UN Earth Summit in 1992. At just 12 years old, Suzuki delivered a heartfelt plea for action on behalf of her generation, arguing that adults were stealing children’s future by destroying the planet. Her speech went viral and helped galvanize the youth environmental movement. By speaking from the heart and calling out the hypocrisy of world leaders, Suzuki showed that you’re never too young to make a difference.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
FAQs on Persuasive Speech Examples
What are some examples of a persuasive speech.
Think climate change action, voting rights, or the importance of mental health awareness. They push for change.
What are 5 examples of persuasive essay?
Gun control laws, school uniforms debate, death penalty perspectives, animal testing ethics, and social media impacts make the list.
What’s an easy persuasive speech topic?
“Why recycling matters” is straightforward and impactful. It connects with everyday actions and broader environmental goals.
What is an example of a persuasive statement?
“Switching to renewable energy sources can significantly reduce our carbon footprint.” This urges action towards sustainability.
Persuasive speech examples show us how to inspire, motivate, and transform the way we communicate our ideas to the world. By studying these remarkable speeches, you’ve gained valuable insights into the art of persuasion and the techniques that make a speech truly unforgettable.
Remember, winning people over with your words takes more than just knowing the right things to say. It’s about practice, caring deeply, and tuning into the folks listening. Take the lessons you’ve learned from these examples and apply them to your own unique style and message. Pouring your soul into your speech can truly move an audience emotionally, altering their thinking for good.
Now your moment in the spotlight is here, so show off those persuasive speech skills. Go forth and create a speech that not only informs and entertains but also inspires and empowers your audience to take meaningful action. The world is waiting to hear your voice, so make it count!
- Last Updated: June 21, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples
What is a persuasive speech.
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
| Benefits of healthy foods | Animal testing | Affirmative action |
| Cell phone use while driving | Arts in education | Credit cards |
| Climate change | Capital punishment/death penalty | Fossil fuels |
| Extinction of the dinosaurs | Community service | Fracking |
| Extraterrestrial life | Fast food & obesity | Global warming |
| Gun violence | Human cloning | Gun control |
| Increase in poverty | Influence of social media | Mental health/health care |
| Moon landing | Paying college athletes | Minimum wage |
| Pandemics | Screen time for young children | Renewable energy |
| Voting rights | Violent video games | School choice/private vs. public schools vs. homeschooling |
| World hunger | Zoos & exotic animals | School uniforms |
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.
Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?

Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Forgot your Password?
First, please create an account
Persuasive speeches on questions of value.
- Introduction
- Questions to Ask Yourself
- Creating a Persuasive Speech on Questions of Value
1. Introduction
There are three types of persuasive speeches:
- Persuasive speeches of fact
- Persuasive speeches of value
- Persuasive speeches of policy
In this unit, our focus will be on persuasive speeches of value. Here is where we argue something is right or wrong, moral or immoral, or better or worse than another thing. The appeals are made on value judgements .
Examples include speeches that attempt to persuade the audience that it is wrong to drive over the speed limit, that Pepsi is better than Coke, that it is better to live together before marriage, that swimming is the best form of exercise, or that bikes are the best form of transportation to get around town.
Persuasive speeches on questions of value imply certain actions, but they are not a call to action.
term to know Policy A principle of behavior, conduct, etc., thought to be desirable or necessary, especially as formally expressed by a government or other authoritative body.
2. Questions to Ask Yourself
When analyzing any type of persuasive speech, you should ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the speaker's goal?
- What are the main points?
- How does the structure of the speech help the speaker to make the argument?
- How does the speaker try to make you care?
- How does the speaker use evidence?
- What kinds of sources does the speaker use?
3. Creating a Persuasive Speech on Questions of Value
How should you go about creating such a speech?
1. Introduce appeals, information, and criteria.
2. Provide evidence that makes your audience arrive at your conclusion. (Your claims should agree with the current beliefs and feeling of your audience.)
3. Use facts to justify your claims.
4. Consider your audience's feeling and values.

summary Persuasive speeches on questions of value imply certain actions, but they are not a call to action. Persuasive speeches of value depend on a judgement that something is right or wrong, moral or immoral, or better or worse than another thing. The speech should include an appeal, criteria for judgement, and facts that support the appeal using the judgement criteria. When analyzing any type of persuasive speech, there are several questions you should ask yourself regarding the speaker's goal, main points, speech structure, and use of evidence.
Source: Boundless. "Persuasive Speeches on Questions of Value." Boundless Communications Boundless, 23 Feb. 2017. Retrieved 22 May. 2017 from https://www.boundless.com/communications/textbooks/boundless-communications-textbook/persuasive-speaking-14/types-of-persuasive-speeches-73/persuasive-speeches-on-questions-of-value-288-1083/
A principle of behavior, conduct, etc., thought to be desirable or necessary, especially as formally expressed by a government or other authoritative body.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
© 2024 SOPHIA Learning, LLC. SOPHIA is a registered trademark of SOPHIA Learning, LLC.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Persuasive Speaking
Introduction, 11.1 foundation of persuasion.
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members (Poggi, 2005). Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant.
The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis (Nordquist, 2020). Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim (McCroskey, 1969). The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence (McCroskey, 1966). One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the U.S. Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people should not do things they know are unsafe.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence (McCroskey, 1966). If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.
11.2 Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to influence directly the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important (Hamm, 2006).
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to reinforce further their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment, so they are more likely to follow through on the action (Hamm, 2006).
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral about your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they do not see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement (Williams, 2018).
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To persuade effectively, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who does not appear prepared or does not present well-researched and supported information. Do not give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience. Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives (Williams, 2018).
11.3 Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that content relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy (Mackay, 2012). A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done (Mackay, 2012). Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
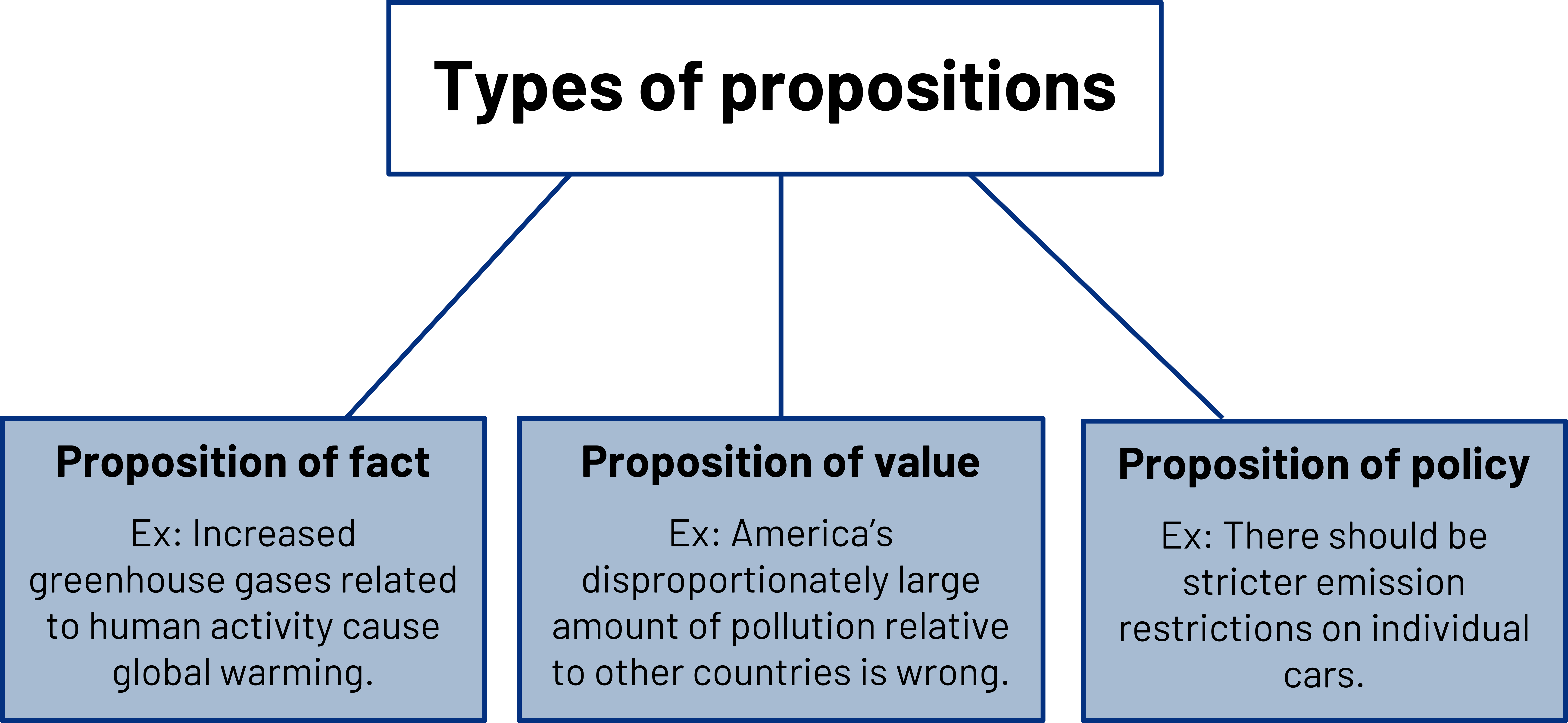
- Proposition of fact. Increased greenhouse gases related to human activity cause global warming.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong.
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered (Barton & Tucker, 2021).
11.4 Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Recency and primacy, as well as adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first. It is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action (Morrison, 2015).
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action (Macasieb, 2018). One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
The cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that leads to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that should not be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore, we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s motivated sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action (Watt & Barnett, 2021). If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. Here is an example of that pattern:
Step 1: Attention
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older, you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
Step 2: Need
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
Step 3: Satisfaction
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
Step 4: Visualization
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
Step 5: Action
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
11.5 Persuasive Reasoning and Fallacies
Persuasive speakers should be concerned with what strengthens and weakens an argument. Knowing different types of reasoning can help you put claims and evidence together in persuasive ways and help you evaluate the quality of arguments that you encounter. Further, being able to identify common fallacies of reasoning can help you be a more critical consumer of persuasive messages.
Reasoning refers to the process of making sense of things around us. In order to understand our experiences, draw conclusions from information, and present new ideas, we must use reasoning. We often reason without being aware of it, however, becoming more aware of how we think can empower us to be better producers and consumers of communicative messages. The three types of reasoning we will explore are inductive, deductive, and causal.
Inductive Reasoning

Inductive reasoning reaches conclusions through the citation of examples and is the most frequently used form of logical reasoning (Walter, 1966). While introductory speakers are initially attracted to inductive reasoning because it seems easy, it can be difficult to employ well. Inductive reasoning, unlike deductive reasoning, does not result in true or false conclusions. Instead, since conclusions are generalized based on observations or examples, conclusions are “more likely” or “less likely.” Despite the fact that this type of reasoning is not definitive, it can still be valid and persuasive.
Some arguments based on inductive reasoning will be more cogent, or convincing and relevant, than others. For example, inductive reasoning can be weak when claims are made too generally. An argument that fraternities should be abolished from campus because they contribute to underage drinking and do not uphold high academic standards could be countered by providing examples of fraternities that sponsor alcohol education programming for the campus and have members that have excelled academically (Walter, 1966). In this case, one overly general claim is countered by another general claim, and both of them have some merit. It would be more effective to present a series of facts and reasons and then share the conclusion or generalization that you have reached from them.
You can see inductive reasoning used in the following speech excerpt from President George W. Bush’s address to the nation on the evening of September 11, 2001. Notice how he lists a series of events from the day, which builds to his conclusion that the terrorist attacks failed in their attempt to shake the foundation of America.
“Today, our fellow citizens, our way of life, our very freedom came under attack in a series of deliberate and deadly terrorist acts. The victims were in airplanes or in their offices: secretaries, business men and women, military and federal workers, moms and dads, friends, and neighbors. Thousands of lives were suddenly ended by evil, despicable acts of terror. The pictures of airplanes flying into building, fires burning, huge—huge structures collapsing have filled us with disbelief, terrible sadness, and a quiet unyielding anger. These acts of mass murder were intended to frighten our nation into chaos and retreat. But they have failed. Our country is strong. A great people has been moved to defend a great nation. Terrorist attacks can shake the foundations of our biggest buildings, but they cannot touch the foundation of America.”
If a speaker is able to provide examples that are concrete, proxemic, and relevant to the audience, as Bush did in this example, audience members are prompted to think of additional examples that connect to their own lives. Inductive reasoning can be useful when an audience disagrees with your proposition. As you present logically connected examples as evidence that build to a conclusion, the audience may be persuaded by your evidence before they realize that the coming conclusion will counter what they previously thought. This also sets up cognitive dissonance, which is a persuasive strategy we will discuss later.
Reasoning by analogy is a type of inductive reasoning that argues that what is true in one set of circumstances will be true in another (Walter, 1966). Reasoning by analogy has been criticized and questioned by logicians, since two sets of circumstances are never exactly the same. While this is true, our goal when using reasoning by analogy in persuasive speaking is not to create absolutely certain conclusions but to cite cases and supporting evidence that can influence an audience. For example, let’s say you are trying to persuade a university to adopt an alcohol education program by citing the program’s success at other institutions. Since two universities are never exactly the same, the argument cannot be airtight. To better support this argument, you could first show that the program was actually successful using various types of supporting material such as statistics from campus offices and testimony from students and staff. Second, you could show how the cases relate by highlighting similarities in the campus setting, culture, demographics, and previous mission. Since you cannot argue that the schools are similar in all ways, choose to highlight significant similarities. In addition, it is better to acknowledge significant limitations of the analogy and provide additional supporting material to address them than it is to ignore or hide such limitations.
So how do we evaluate inductive reasoning? When inductive reasoning is used to test scientific arguments, there is rigorous testing and high standards that must be met for a conclusion to be considered valid. Inductive reasoning in persuasive speaking is employed differently. A speaker cannot cite every example that exists to build to a conclusion, so to evaluate inductive reasoning you must examine the examples that are cited in ways other than quantity. First, the examples should be sufficient, meaning that enough are cited to support the conclusion. If not, you risk committing the hasty generalization fallacy. A speaker can expect that the audience will be able to think of some examples as well, so there is no set number on how many examples is sufficient. If the audience is familiar with the topic, then fewer examples are probably sufficient, while more may be needed for unfamiliar topics. A speaker can make his or her use of reasoning by example more powerful by showing that the examples correspond to the average case, which may require additional supporting evidence in the form of statistics. Arguing that teacher salaries should be increased by providing an example of a teacher who works side jobs and pays for his or her own school supplies could be effectively supported by showing that this teacher’s salary corresponds to the national average (Walter, 1966).
Second, the examples should be typical, meaning they were not cherry-picked to match the point being argued. A speaker who argues to defund the National Endowment for the Arts (NEA) because the organization supports art that is “pornographic and offensive” may cite five examples of grants given for projects that caused such controversy. Failing to mention that these examples were pulled from the more than 128,000 grants issued by the NEA would be an inappropriate use of inductive reasoning since the examples are not sufficient or typical enough to warrant the argument. Another way to support inductive arguments is to show that the examples are a fair sample, meaning they are representative of the larger whole. Arguing that college athletes should not receive scholarships because they do not have the scholastic merit of other students and have less academic achievement could be supported by sharing several examples. However, if those examples were not representative, then they are biased, and the reasoning faulty. A speaker would need to show that the athletes used in the example are representative, in terms of their race, gender, sport, and background, of the population of athletes at the university.
Deductive Reasoning

Deductive reasoning derives specifics from what is already known. It was the preferred form of reasoning used by ancient rhetoricians like Aristotle to make logical arguments (Cooper & Nothstine, 1996).
A syllogism is an example of deductive reasoning that is commonly used when teaching logic. A syllogism is an example of deductive reasoning in which a conclusion is supported by major and minor premises. The conclusion of a valid argument can be deduced from the major and minor premises. A commonly used example of a syllogism is “All humans are mortal. Socrates is a human. Socrates is mortal.” In this case, the conclusion, “Socrates is mortal,” is derived from the major premise, “All humans are mortal,” and the minor premise, “Socrates is a human.” In some cases, the major and minor premises of a syllogism may be taken for granted as true. In the previous example, the major premise is presumed true because we have no knowledge of an immortal person to disprove the statement. The minor premise is presumed true because Socrates looks and acts like other individuals we know to be human. Detectives or scientists using such logic would want to test their conclusion. We could test our conclusion by stabbing Socrates to see if he dies, but since the logic of the syllogism is sound, it may be better to cut Socrates a break and deem the argument valid. Since most arguments are more sophisticated than the previous example, speakers need to support their premises with research and evidence to establish their validity before deducing their conclusion.
A syllogism can lead to incorrect conclusions if one of the premises is not true, as in the following example:
- All presidents have lived in the White House. (Major premise)
- George Washington was president. (Minor premise)
- George Washington lived in the White House. (Conclusion)
In the previous example, the major premise was untrue, since John Adams, our second president, was the first president to live in the White House. This causes the conclusion to be false. A syllogism can also exhibit faulty logic even if the premises are both true but are unrelated, as in the following example:
- Penguins are black and white. (Major premise)
- Some old television shows are black and white. (Minor premise)
- Some penguins are old television shows. (Conclusion)
Causal Reasoning
Causal reasoning argues to establish a relationship between a cause and an effect. When speakers attempt to argue for a particular course of action based on potential positive or negative consequences that may result, they are using causal reasoning. Such reasoning is evident in the following example: Eating more local foods will boost the local economy and make you healthier. The “if/then” relationship that is set up in causal reasoning can be persuasive, but the reasoning is not always sound. Rather than establishing a true cause-effect relationship, speakers more often set up a correlation, which means there is a relationship between two things but there are other contextual influences.
To use causal reasoning effectively and ethically, speakers should avoid claiming a direct relationship between a cause and an effect when such a connection cannot be proven. Instead of arguing “x caused y,” it is more accurate for a speaker to say “x influenced y.” Causal thinking is often used when looking to blame something or someone, as can be seen in the following example: It’s the president’s fault that the economy has not recovered more. While such a statement may garner a speaker some political capital, it is not based on solid reasoning.
Economic and political processes are too complex to distill to such a simple cause-effect relationship. A speaker would need to use more solid reasoning, perhaps inductive reasoning through examples, to build up enough evidence to support that a correlation exists and a causal relationship is likely. When using causal reasoning, present evidence that shows the following: (1) the cause occurred before the effect, (2) the cause led to the effect, and (3) it is unlikely that other causes produced the effect.
11.6 Persuasive Strategies
Do you think you are easily persuaded? If you are like most people, you are not swayed easily to change your mind about something. Persuasion is difficult because changing views often makes people feel like they were either not informed or ill informed, which also means they have to admit they were wrong about something. We will learn about nine persuasive strategies that you can use to influence more effectively audience members’ beliefs, attitudes, and values. They are ethos, logos, pathos, positive motivation, negative motivation, cognitive dissonance, appeal to safety needs, appeal to social needs, and appeal to self-esteem needs.
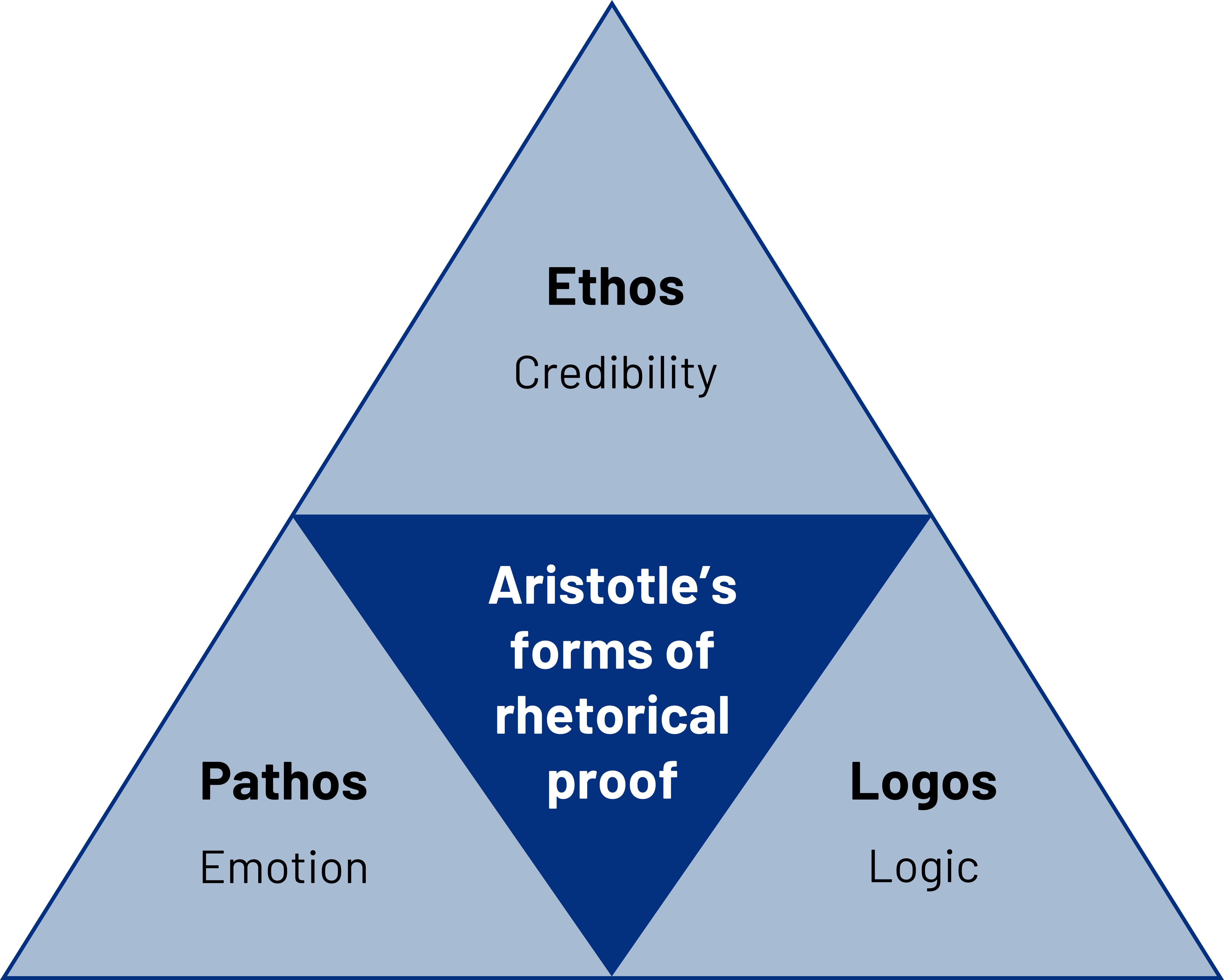
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
Ethos, logos, and pathos were Aristotle’s three forms of rhetorical proof, meaning they were primary to his theories of persuasion. Ethos refers to the credibility of a speaker and includes three dimensions: competence, trustworthiness, and dynamism. The two most researched dimensions of credibility are competence and trustworthiness (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003).
Competence refers to the perception of a speaker’s expertise in relation to the topic being discussed. A speaker can enhance their perceived competence by presenting a speech based in solid research and that is well organized and practiced. Competent speakers must know the content of their speech and be able to deliver that content. Trustworthiness refers to the degree that audience members perceive a speaker to be presenting accurate, credible information in a non-manipulative way. Perceptions of trustworthiness come from the content of the speech and the personality of the speaker. In terms of content, trustworthy speakers consider the audience throughout the speech-making process, present information in a balanced way, do not coerce the audience, cite credible sources, and follow the general principles of communication ethics. In terms of personality, trustworthy speakers are also friendly and warm (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003).
Dynamism refers to the degree to which audience members perceive a speaker to be outgoing and animated (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003). Two components of dynamism are charisma and energy. Charisma refers to a mixture of abstract and concrete qualities that make a speaker attractive to an audience. Charismatic people usually know they are charismatic because they have been told that in their lives, and people have been attracted to them.
Unfortunately, charisma is difficult to develop intentionally, and some people seem to have a naturally charismatic personality, while others do not. Even though not everyone can embody the charismatic aspect of dynamism, the other component of dynamism, energy, is something that everyone can fathom. Communicating enthusiasm for your topic and audience by presenting relevant content and using engaging delivery strategies such as vocal variety and eye contact can increase your dynamism.
Logos refers to the reasoning or logic of an argument. The presence of fallacies would obviously undermine a speaker’s appeal to logos. Speakers employ logos by presenting credible information as supporting material and verbally citing their sources during their speech. Using the guidelines from our earlier discussion of reasoning will also help a speaker create a rational appeal. Research shows that messages are more persuasive when arguments and their warrants are made explicit (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003). Carefully choosing supporting material that is verifiable, specific, and unbiased can help a speaker appeal to logos. Speakers can also appeal to logos by citing personal experience and providing the credentials and/or qualifications of sources of information (Cooper & Nothstine, 1996). Presenting a rational and logical argument is important, but speakers can be more effective if they bring in and refute counterarguments. The most effective persuasive messages are those that present two sides of an argument and refute the opposing side, followed by single argument messages, followed by messages that present counterarguments but do not refute them (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003). In short, by clearly showing an audience why one position is superior to another, speakers do not leave an audience to fill in the blanks of an argument, which could diminish the persuasive opportunity.
Pathos refers to emotional appeals. Aristotle was suspicious of too much emotional appeal, yet this appears to have become more acceptable in public speaking. Stirring emotions in an audience is a way to get them involved in the speech, and involvement can create more opportunities for persuasion and action. Reading in the paper that a house was burglarized may get your attention but think about how different your reaction would be if you found out it was your own home. Intentionally stirring someone’s emotions to get them involved in a message that has little substance would be unethical. Yet such spellbinding speakers have taken advantage of people’s emotions to get them to support causes, buy products, or engage in behaviors that they might not otherwise, if given the chance to see the faulty logic of a message.
Effective speakers should use emotional appeals that are also logically convincing, since audiences may be suspicious of a speech that is solely based on emotion. Emotional appeals are effective when you are trying to influence a behavior or you want your audience to take immediate action (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003). Emotions lose their persuasive effect more quickly than other types of persuasive appeals. Since emotions are often reactionary, they fade relatively quickly when a person is removed from the provoking situation (Fletcher, 2001).
Emotional appeals are also difficult for some because they require honed delivery skills and the ability to use words powerfully and dramatically. The ability to use vocal variety, cadence, and repetition to rouse an audience’s emotion is not easily attained. Think of how stirring Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech was due to his ability to evoke the emotions of the audience. Dr. King used powerful and creative language in conjunction with his vocalics to deliver one of the most famous speeches in our history. Using concrete and descriptive examples can paint a picture in your audience member’s minds. Speakers can also use literal images, displayed using visual aids, to appeal to pathos.
Speakers should strive to appeal to ethos, logos, and pathos within a speech. A speech built primarily on ethos might lead an audience to think that a speaker is full of himself or herself. A speech full of facts and statistics appealing to logos would result in information overload. Speakers who rely primarily on appeals to pathos may be seen as overly passionate, biased, or unable to see other viewpoints.
Dissonance, Motivation, and Needs
Aristotle’s three rhetorical proofs—ethos, logos, and pathos—have been employed as persuasive strategies for thousands of years. More recently, persuasive strategies have been identified based on theories and evidence related to human psychology. Although based in psychology, such persuasive strategies are regularly employed and researched in communication due to their role in advertising, marketing, politics, and interpersonal relationships. The psychologically based persuasive appeals we will discuss are cognitive dissonance, positive and negative motivation, and appeals to needs.
Cognitive Dissonance
If you have studied music, you probably know what dissonance is. Some notes, when played together on a piano, produce a sound that is pleasing to our ears. When dissonant combinations of notes are played, we react by wincing or cringing because the sound is unpleasant to our ears. So dissonance is that unpleasant feeling we get when two sounds clash. The same principle applies to cognitive dissonance , which refers to the mental discomfort that results when new information clashes with or contradicts currently held beliefs, attitudes, or values. Using cognitive dissonance as a persuasive strategy relies on three assumptions: (1) people have a need for consistency in their thinking; (2) when inconsistency exists, people experience psychological discomfort; and (3) this discomfort motivates people to address the inconsistency to restore balance (Stiff & Mongeau, 2003). In short, when new information clashes with previously held information, an unpleasantness results, and we have to try to reconcile the difference.
Cognitive dissonance is not a single-shot persuasive strategy. As we have learned, people are resistant to change and not easy to persuade. While we might think that exposure to conflicting information would lead a rational person to change his or her mind, humans are not as rational as we think.
There are many different mental and logical acrobatics that people do to get themselves out of dissonance. Some frequently used strategies to resolve cognitive dissonance include discrediting the speaker or source of information, viewing yourself as an exception, seeking selective information that supports your originally held belief, or intentionally avoiding or ignoring sources of cognitive dissonance (Cooper & Nothstine, 1996). As you can see, none of those actually results in a person modifying their thinking, which means persuasive speech goals are not met. Of course, people cannot avoid dissonant information forever, so multiple attempts at creating cognitive dissonance can actually result in thought or behavior modification.
Positive and Negative Motivation
Positive and negative motivation are common persuasive strategies used by teachers, parents, and public speakers. Rewards can be used for positive motivation, and the threat of punishment or negative consequences can be used for negative motivation. We have already learned the importance of motivating an audience to listen to your message by making your content relevant and showing how it relates to their lives. We also learned an organizational pattern based on theories of motivation: Monroe’s Motivated Sequence. When using positive motivation , speakers implicitly or explicitly convey to the audience that listening to their message or following their advice will lead to positive results. Conversely, negative motivation implies or states that failure to follow a speaker’s advice will result in negative consequences. Positive and negative motivation as persuasive strategies match well with appeals to needs.
Appeals to Needs
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs states that there are several layers of needs that human beings pursue. They include physiological, safety, social, self-esteem, and self-actualization needs (Maslow, 1943). Since these needs are fundamental to human survival and happiness, tapping into needs is a common persuasive strategy. Appeals to needs are often paired with positive or negative motivation, which can increase the persuasiveness of the message.
Physiological needs form the base of the hierarchy of needs. The closer the needs are to the base, the more important they are for human survival. Speakers do not appeal to physiological needs. After all, a person who does not have food, air, or water is not very likely to want to engage in persuasion, and it would not be ethical to deny or promise these things to someone for persuasive gain. Some speakers attempt to appeal to self-actualization needs, but I argue that this is difficult to do ethically. Self-actualization refers to our need to achieve our highest potential, and these needs are much more intrapersonal than the others are. We achieve our highest potential through things that are individual to us, and these are often things that we protect from outsiders. Some examples include pursuing higher education and intellectual fulfillment, pursuing art or music, or pursuing religious or spiritual fulfillment. These are often things we do by ourselves and for ourselves, so I like to think of this as sacred ground that should be left alone. Speakers are more likely to be successful at focusing on safety, social, and self-esteem needs.
We satisfy our safety needs when we work to preserve our safety and the safety of our loved ones. Speakers can combine appeals to safety with positive motivation by presenting information that will result in increased safety and security. Combining safety needs and negative motivation, a speaker may convey that audience members’ safety and security will be put at risk if the speaker’s message is not followed. Combining negative motivation and safety needs depends on using some degree of fear as a motivator. Think of how the insurance industry relies on appeals to safety needs for their business. While this is not necessarily a bad strategy, it can be done more or less ethically.
Our social needs relate to our desire to belong to supportive and caring groups. We meet social needs through interpersonal relationships ranging from acquaintances to intimate partnerships. We also become part of interest groups or social or political groups that help create our sense of identity. The existence and power of peer pressure is a testament to the motivating power of social needs. People go to great lengths and sometimes make poor decisions they later regret to be a part of the “in-group.” Advertisers often rely on creating a sense of exclusivity to appeal to people’s social needs. Positive and negative motivation can be combined with social appeals. Positive motivation is present in messages that promise the receiver “in-group” status or belonging, and negative motivation can be seen in messages that persuade by saying, “Don’t be left out.” Although these arguments may rely on the bandwagon fallacy to varying degrees, they draw out insecurities people have about being in the “out-group.”
We all have a need to think well of ourselves and have others think well of us, which ties to our self-esteem needs . Messages that combine appeals to self-esteem needs and positive motivation often promise increases in respect and status. A financial planner may persuade by inviting a receiver to imagine prosperity that will result from accepting his or her message. A publicly supported radio station may persuade listeners to donate money to the station by highlighting a potential contribution to society. The health and beauty industries may persuade consumers to buy their products by promising increased attractiveness. While it may seem shallow to entertain such ego needs, they are an important part of our psychological makeup. Unfortunately, some sources of persuasive messages are more concerned with their own gain than the well-being of others and may take advantage of people’s insecurities in order to advance their persuasive message. Instead, ethical speakers should use appeals to self-esteem that focus on prosperity, contribution, and attractiveness in ways that empower listeners.
11.7 Sample Persuasive Speech
Title: Education behind Bars Is the Key to Rehabilitation
General purpose: To persuade
Specific purpose : By the end of my speech, my audience will believe that prisoners should have the right to an education.
Thesis statement: There should be education in all prisons, because denying prisoners an education has negative consequences for the prisoner and society, while providing them with an education provides benefits for the prisoner and society.
Attention getter: “We must accept the reality that to confine offenders behind walls without trying to change them is an expensive folly with short-term benefits—winning battles while losing the war.” Supreme Court Justice Warren Burger spoke these words more than thirty years ago, and they support my argument today that prisoners should have access to education.
Introduction of topic: While we value education as an important part of our society, we do not value it equally for all. Many people do not believe that prisoners should have access to an education, but I believe they do.
Credibility and relevance: While researching this topic, my eyes were opened up to how much an education can truly affect a prisoner, and given my desire to be a teacher, I am invested in preserving the right to learn for everyone, even if they are behind bars. While I know from our audience analysis activity that some of you do not agree with me, you never know when this issue may hit close to home. Someday, someone you love might make a mistake in their life and end up in prison, and while they are there, I know you all would want them to receive an education so that when they get out, they will be better prepared to contribute to society.
Preview: Today, I invite you listen with an open mind as I discuss the need for prisoner education, a curriculum that will satisfy that need, and some benefits of prisoner education.
Transition: First, I will explain why prisoners need access to education.
1. According to a 2012 article in the journal Corrections Today on correctional education programs, most states have experienced an increase in incarceration rates and budgetary constraints over the past ten years, which has led many to examine best practices for reducing prison populations.
a. In that same article, criminologist and former research director of the Federal Bureau of Prisons states that providing correctional education is one of the most productive and important reentry services that our prisons offer.
b. His claim is supported by data collected directly from prisoners, 94 percent of whom identify education as a personal reentry need—ranking it above other needs such as financial assistance, housing, or employment.
c. Despite the fact that this need is clearly documented, funding for adult and vocational education in correctional education has decreased.
1. Many prisoners have levels of educational attainment that are far below those in the general population.
2. According to statistics from 2010, as cited in the Corrections Today article, approximately 40 percent of state prison inmates did not complete high school, as compared to 19 percent of the general population.
3. Additionally, while about 48 percent of the public have taken college classes, only about 11 percent of state prisoners have.
d. At the skill level, research from the United Kingdom, cited in the 2003 article from Studies in the Education of Adults titled “Learning behind Bars: Time to Liberate Prison Education,” rates of illiteracy are much higher among the prison population than the general population, and there is a link between poor reading skills and social exclusion that may lead people to antisocial behavior.
1. Prisoner education is also needed to break a cycle of negativity and stigma to which many prisoners have grown accustomed.
2. The article from Studies in the Education of Adults that I just cited states that prisoners are often treated as objects or subjected to objectifying labels like “ addict , sexual offender , and deviant .”
3. While these labels may be accurate in many cases, they do not do much to move the prisoner toward rehabilitation.
4. The label student , however, has the potential to do so because it has positive associations and can empower the prisoner to make better choices to enhance his or her confidence and self-worth.
Transition: Now that I have established the need for prisoner education, let’s examine how we can meet that need.
2. In order to meet the need for prisoner education that I have just explained, it is important to have a curriculum that is varied and tailored to various prisoner populations and needs.
a. The article from Corrections Today notes that education is offered to varying degrees in most US prisons, but its presence is often debated and comes under increased scrutiny during times of budgetary stress.
b. Some states have implemented programs that require inmates to attend school for a certain amount of time if they do not meet minimum standards for skills such as reading or math.
c. While these are useful programs, prisoner education should not be limited to or focused on those with the least amount of skills.
d. The article notes that even prisoners who have attended or even graduated from college may benefit from education, as they can pursue specialized courses or certifications.
e. Based on my research, I would propose that the prison curriculum have four tiers: one that addresses basic skills that prisoners may lack, one that prepares prisoners for a GED, one that prepares prisoners for college-level work, and one that focuses on life and social skills.
1. The first tier of the education program should focus on remediation and basic skills, which is the most common form of prisoner education as noted by Foley and Gao in their 2004 article from the Journal of Correctional Education that studied educational practices at several institutions.
a. These courses will teach prisoners basic reading, writing, and math skills that may be lacking.
b. Since there is a stigma associated with a lack of these basic skills, early instruction should be one-one-one or in small groups.
2. The second tier should prepare prisoners who have not completed the equivalent of high school to progress on to a curriculum modeled after that of most high schools, which will prepare them for a GED.
3. The third tier should include a curriculum based on the general education learning goals found at most colleges and universities and/or vocational training.
a. Basic general education goals include speaking, writing, listening, reading, and math.
b. Once these general education requirements have been met, prisoners should be able to pursue specialized vocational training or upper-level college courses in a major of study, which may need to be taken online through distance learning, since instructors may not be available to come to the actual prisons to teach.
4. The fourth tier includes training in social and life skills that most people learn through family and peer connections, which many prisoners may not have had.
a. Some population-specific areas of study that would not be covered in a typical classroom include drug treatment and anger management.
b. Life skills such as budgeting, money management, and healthy living can increase confidence.
c. Classes that focus on social skills, parenting, or relational communication can also improve communication skills and relational satisfaction; for example, workshops teaching parenting skills have been piloted to give fathers the skills needed to communicate effectively with their children, which can increase feelings of self-worth.
f. According to a 2007 article by Behan in the Journal of Correctional Education , prisons should also have extracurricular programs that enhance the educational experience.
1. Under the supervision of faculty and/or staff, prisoners could be given the task of organizing an outside speaker to come to the prison or put together a workshop.
2. Students could also organize a debate against students on the outside, which could allow the prisoners to interact (face-to-face or virtually) with other students and allow them to be recognized for their academic abilities.
3. Even within the prison, debates, trivia contests, paper contests, or speech contests could be organized between prisoners or between prisoners and prison staff as a means of healthy competition.
4. Finally, prisoners who are successful students should be recognized and put into peer-mentoring roles, because, as Behan states in the article, “a prisoner who…has had an inspirational learning experience acts as a more positive advocate for the school than any [other method].”
Transition: The model for prisoner education that I have just outlined will have many benefits.
3. Educating prisoners can benefit inmates, those who work in prisons, and society.
a. The article I just cited from the Journal of Correctional Education states that the self-reflection and critical thinking that are fostered in an educational setting can help prisoners reflect on how their actions affected them, their victims, and/or their communities, which may increase self-awareness and help them better reconnect with a civil society and reestablish stronger community bonds.
1. The Corrections Today article I cited earlier notes that a federally funded three-state survey provided the strongest evidence to date that prisoner education reduces the recidivism rate and increases public safety.
2. The Corrections Today article also notes that prisoners who completed a GED reoffended at a rate 20 percent lower than the general prison population, and those that completed a college degree reoffended at a rate 44 percent lower than the general prison population.
b. So why does prisoner education help reduce recidivism rates?
1. Simply put, according to the article in the Studies in the Education of Adults I cited earlier, the skills gained through good prison education programs make released prisoners more desirable employees, which increases their wages and helps remove them from a negative cycles of stigma and poverty that led many of them to crime in the first place.
2. Further, the ability to maintain consistent employment has been shown to reduce the rate of reoffending.
3. Education does not just improve the lives of the prisoners; it also positively affects the people who work in prisons.
c. An entry on eHow.com by Kinney about the benefits of prisoners getting GEDs notes that a successful educational program in a prison can create a more humane environment that will positively affect the officers and staff as well.
1. Such programs also allow prisoners to do more productive things with their time, which lessens violent and destructive behavior and makes prison workers’ jobs safer.
2. Prisoner education can also save cash-strapped states money.
3. Giving prisoners time-off-sentence credits for educational attainment can help reduce the prison population, as eligible inmates are released earlier because of their educational successes.
4. As noted by the Corrections Today article, during the 2008–9 school year the credits earned by prisoners in the Indiana system led to more than $68 million dollars in avoided costs.
Transition to conclusion and summary of importance: In closing, it is easy to see how beneficial a good education can be to a prisoner. Education may be something the average teenager or adult takes for granted, but for a prisoner it could be the start of a new life.
Review of main points: There is a clear need for prisoner education that can be met with a sound curriculum that will benefit prisoners, those who work in prisons, and society.
Closing statement: While education in prisons is still a controversial topic, I hope you all agree with me and Supreme Court Justice Burger, whose words opened this speech, when we say that locking a criminal away may offer a short-term solution in that it gets the criminal out of regular society, but it doesn’t better the prisoner and it doesn’t better us in the long run as a society.
Figure 11.1: Types of propositions with examples. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 11.2: Inductive reasoning. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 . Includes Lightbulb by Maxim Kulikov from NounProject , Magnifying Glass by Pedro Santos from NounProject , and Brain by Bernar Novalyi from NounProject (all Noun Project license ).
Figure 11.3: Deductive reasoning. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 . Includes Lightbulb by Maxim Kulikov from NounProject , Magnifying Glass by Pedro Santos from NounProject , and Paper by AdbA Icons ❤️ from NounProject (all Noun Project license ).
Figure 11.4: Aristotle’s modes of persuassion. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 11.5: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Section 11. 1-11.4
Barton, K., & Tucker, B. G. (2021, February 20). Constructing a persuasive speech . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Exploring_Public_Speaking_(Barton_and_Tucker)/13%3A_Persuasive_Speaking/13.05%3A_Constructing_a_Persuasive_Speech
Hamm, P. H. (2006). Teaching and persuasive communication: Class presentation skills . Harriet W. Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning at Brown University.
Macasieb, D. (2018, June 13). Speech patterns: The proposition-to-proof versus the problem-solution method . https://drumac.com/2018/06/13/speech-patterns-the-proposition-to-proof-versus-the-problem-solution-method/
McCroskey, J. C. (1966). Toward an understanding of the importance of ‘evidence’ in persuasive communication. The Pennsylvania Speech Annual , 23 , 65–71.
McCroskey, J. C. (1969). A summary of experimental research on the effects of evidence in persuasive communication. Quarterly Journal of Speech , 55 (2), 169-176. https://doi.org/10.1080/00335636909382942
Nordquist, R. (2020, December 3). What does it mean to make a claim during an argument? https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-claim-argument-1689845
Poggi, I. (2005). The goals of persuasion. Pragmatics and Cognition , 13 (2), 297-335. https://doi.org/10.1075/pc.13.2.04pog
Watt, S. S., & Barnett, J. T. (2021, January 4). Organizing persuasive messages . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Public_Speaking_(The_Public_Speaking_Project)/16%3A_Persuasive_Speaking/16.09%3A_Organizing_Persuasive_Messages
Williams, E. (2018, October 19). Effective persuasive communication . https://smallbusiness.chron.com/effective-persuasive-communication-56248.html
Section 11.5
ReferencesCooper, M. D., & Nothstine, W. L. (1996). Power persuasion: Moving an ancient art into the media age. Educational Video Group.
Walter, O. M., Speaking to inform and persuade . Macmillan.
Section 11.6
Cooper, M. D., & Nothstine, W. L. (1996). Power persuasion: Moving an ancient art into the media age . Educational Video Group.
Fletcher, L. (2001). How to design and deliver speeches (7th ed.). Longman.
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50 (4), 370–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054346
Stiff, J. B., & Mongeau, P. A. (2003). Persuasive communication (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
Sample Persuasive Speech
Bayliss, P. (2003). Learning behind bars: Time to liberate prison education. Studies in the Education of Adults, 35 (2), 157–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/02660830.2003.11661480
Behan, C. (2007). Context, creativity and critical reflection: Education in correctional institutions. Journal of Correctional Education, 58 (2), 157–169. https://www.jstor.org/stable/23282734
Foley, R. M., & Gao, J. (2004). Correctional education: Characteristics of academic programs serving incarcerated adults. Journal of Correctional Education, 55 (1), 6–21. https://www.jstor.org/stable/23292120
Kinney, A. (2011). What are the benefits of inmates getting GEDs? Ehow.com . Retrieved from https://ehow.com/list_6018033_benefits-inmates-getting-geds_.html
Steurer, S. J., Linton, J., Nally, J., & Lockwood, S. (2010). The top-nine reasons to increase correctional education programs. Corrections Today, 72 (4), 40–43.
The statement that will be supported by evidence
Also called grounds, it supports the claim
The underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence
A five step organizational pattern to help persuade an audience. 1. Attention Step: Grab the audience’s attention in the introduction. 2. Need Step: Establish the reason that your topic needs to be addressed. Satisfaction Step: Present a solution to the problem that you are addressing. 4. Visualization Step: Incorporate a positive/negative motivation to support the relationship you have set up between the need and your proposal. 5. Action Step: Include a call to action that tells people what they can do about the situation.
Reaches conclusions through citation of examples and is the most frequently used form of logical reasoning
Derives specifics from what is already known
Argues to establish a relationship between a cause and effect
Refers to the credibility of the speaker and includes dimensions: competence, trustworthiness, and dynamism
Refers to the perception of a speaker’s expertise in relation to the topic being discussed
The second component of ethos and is the degree that audience members perceive a speaker to be presenting accurate, credible information in a non-manipulative way
Refers to the degree to which audience members perceive a speaker to be outgoing and animated
The reasoning or logic of an argument
The emotional appeal
Refers to the mental discomfort that results when new information clashes with or contradicts currently held beliefs, attitudes, or values
Communication in the Real World Copyright © by Faculty members in the School of Communication Studies, James Madison University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Persuasive Speaking
Learning objectives.
- Explain how claims, evidence, and warrants function to create an argument.
- Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic.
- Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience’s orientation to the proposition.
- Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy.
- Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don’t often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we’ll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Foundation of Persuasion
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis. Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim. The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence. One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the US Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people shouldn’t do things they know are unsafe.
Figure 11.2 Components of an Argument
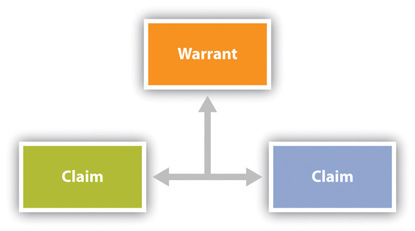
The quality of your evidence often impacts the strength of your warrant, and some warrants are stronger than others. A speaker could also provide evidence to support their claim advocating for a national ban on texting and driving by saying, “I have personally seen people almost wreck while trying to text.” While this type of evidence can also be persuasive, it provides a different type and strength of warrant since it is based on personal experience. In general, the anecdotal evidence from personal experience would be given a weaker warrant than the evidence from the national research report. The same process works in our legal system when a judge evaluates the connection between a claim and evidence. If someone steals my car, I could say to the police, “I’m pretty sure Mario did it because when I said hi to him on campus the other day, he didn’t say hi back, which proves he’s mad at me.” A judge faced with that evidence is unlikely to issue a warrant for Mario’s arrest. Fingerprint evidence from the steering wheel that has been matched with a suspect is much more likely to warrant arrest.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence. If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.
Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
As with any speech, topic selection is important and is influenced by many factors. Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial, and have important implications for society. If your topic is currently being discussed on television, in newspapers, in the lounges in your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it’s a current topic. A persuasive speech aimed at getting audience members to wear seat belts in cars wouldn’t have much current relevance, given that statistics consistently show that most people wear seat belts. Giving the same speech would have been much more timely in the 1970s when there was a huge movement to increase seat-belt use.
Many topics that are current are also controversial, which is what gets them attention by the media and citizens. Current and controversial topics will be more engaging for your audience. A persuasive speech to encourage audience members to donate blood or recycle wouldn’t be very controversial, since the benefits of both practices are widely agreed on. However, arguing that the restrictions on blood donation by men who have had sexual relations with men be lifted would be controversial. I must caution here that controversial is not the same as inflammatory. An inflammatory topic is one that evokes strong reactions from an audience for the sake of provoking a reaction. Being provocative for no good reason or choosing a topic that is extremist will damage your credibility and prevent you from achieving your speech goals.
You should also choose a topic that is important to you and to society as a whole. As we have already discussed in this book, our voices are powerful, as it is through communication that we participate and make change in society. Therefore we should take seriously opportunities to use our voices to speak publicly. Choosing a speech topic that has implications for society is probably a better application of your public speaking skills than choosing to persuade the audience that Lebron James is the best basketball player in the world or that Superman is a better hero than Spiderman. Although those topics may be very important to you, they don’t carry the same social weight as many other topics you could choose to discuss. Remember that speakers have ethical obligations to the audience and should take the opportunity to speak seriously.
You will also want to choose a topic that connects to your own interests and passions. If you are an education major, it might make more sense to do a persuasive speech about funding for public education than the death penalty. If there are hot-button issues for you that make you get fired up and veins bulge out in your neck, then it may be a good idea to avoid those when speaking in an academic or professional context.

Choose a persuasive speech topic that you’re passionate about but still able to approach and deliver in an ethical manner.
Michael Vadon – Nigel Farage – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Choosing such topics may interfere with your ability to deliver a speech in a competent and ethical manner. You want to care about your topic, but you also want to be able to approach it in a way that’s going to make people want to listen to you. Most people tune out speakers they perceive to be too ideologically entrenched and write them off as extremists or zealots.
You also want to ensure that your topic is actually persuasive. Draft your thesis statement as an “I believe” statement so your stance on an issue is clear. Also, think of your main points as reasons to support your thesis. Students end up with speeches that aren’t very persuasive in nature if they don’t think of their main points as reasons. Identifying arguments that counter your thesis is also a good exercise to help ensure your topic is persuasive. If you can clearly and easily identify a competing thesis statement and supporting reasons, then your topic and approach are arguable.
Review of Tips for Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
- Not current. People should use seat belts.
- Current. People should not text while driving.
- Not controversial. People should recycle.
- Controversial. Recycling should be mandatory by law.
- Not as impactful. Superman is the best superhero.
- Impactful. Colleges and universities should adopt zero-tolerance bullying policies.
- Unclear thesis. Homeschooling is common in the United States.
- Clear, argumentative thesis with stance. Homeschooling does not provide the same benefits of traditional education and should be strictly monitored and limited.
Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to directly influence the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important. If possible, poll your audience to find out their orientation toward your thesis. I read my students’ thesis statements aloud and have the class indicate whether they agree with, disagree with, or are neutral in regards to the proposition. It is unlikely that you will have a homogenous audience, meaning that there will probably be some who agree, some who disagree, and some who are neutral. So you may employ all of the following strategies, in varying degrees, in your persuasive speech.
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to further reinforce their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment so they are more likely to follow through on the action.
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral in regards to your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they don’t see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement.
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To effectively persuade, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who doesn’t appear prepared or doesn’t present well-researched and supported information. Don’t give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely, but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience.

Build common ground with disagreeable audiences and acknowledge areas of disagreement.
Chris-Havard Berge – Shaking Hands – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives.
Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy. A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done. Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
- Proposition of fact. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases related to human activity.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong .
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered.
“Getting Critical”
Persuasion and Masculinity
The traditional view of rhetoric that started in ancient Greece and still informs much of our views on persuasion today has been critiqued for containing Western and masculine biases. Traditional persuasion has been linked to Western and masculine values of domination, competition, and change, which have been critiqued as coercive and violent (Gearhart, 1979).
Communication scholars proposed an alternative to traditional persuasive rhetoric in the form of invitational rhetoric. Invitational rhetoric differs from a traditional view of persuasive rhetoric that “attempts to win over an opponent, or to advocate the correctness of a single position in a very complex issue” (Bone et al., 2008). Instead, invitational rhetoric proposes a model of reaching consensus through dialogue. The goal is to create a climate in which growth and change can occur but isn’t required for one person to “win” an argument over another. Each person in a communication situation is acknowledged to have a standpoint that is valid but can still be influenced through the offering of alternative perspectives and the invitation to engage with and discuss these standpoints (Ryan & Natalle, 2001). Safety, value, and freedom are three important parts of invitational rhetoric. Safety involves a feeling of security in which audience members and speakers feel like their ideas and contributions will not be denigrated. Value refers to the notion that each person in a communication encounter is worthy of recognition and that people are willing to step outside their own perspectives to better understand others. Last, freedom is present in communication when communicators do not limit the thinking or decisions of others, allowing all participants to speak up (Bone et al., 2008).
Invitational rhetoric doesn’t claim that all persuasive rhetoric is violent. Instead, it acknowledges that some persuasion is violent and that the connection between persuasion and violence is worth exploring. Invitational rhetoric has the potential to contribute to the civility of communication in our society. When we are civil, we are capable of engaging with and appreciating different perspectives while still understanding our own. People aren’t attacked or reviled because their views diverge from ours. Rather than reducing the world to “us against them, black or white, and right or wrong,” invitational rhetoric encourages us to acknowledge human perspectives in all their complexity (Bone et al., 2008).
- What is your reaction to the claim that persuasion includes Western and masculine biases?
- What are some strengths and weaknesses of the proposed alternatives to traditional persuasion?
- In what situations might an invitational approach to persuasion be useful? In what situations might you want to rely on traditional models of persuasion?
Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Earlier, in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , we discussed recency and primacy, and in this chapter we discussed adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition. These concepts can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first and is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action.

Putting your strongest argument last can help motivate an audience to action.
Celestine Chua – The Change – CC BY 2.0.
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
As was mentioned in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , the cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that lead to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
Persuasive Speech Thesis Statements by Organizational Pattern
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that shouldn’t be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action. If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. We already learned about the five steps of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but we will review them here with an example:
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly US Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
Key Takeaways
- Arguments are formed by making claims that are supported by evidence. The underlying justification that connects the claim and evidence is the warrant. Arguments can have strong or weak warrants, which will make them more or less persuasive.
- Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial (but not inflammatory), and important to the speaker and society.
- When audience members agree with the proposal, focus on intensifying their agreement and moving them to action.
- When audience members are neutral in regards to the proposition, provide background information to better inform them about the issue and present information that demonstrates the relevance of the topic to the audience.
- When audience members disagree with the proposal, focus on establishing your credibility, build common ground with the audience, and incorporate counterarguments and refute them.
- Propositions of fact focus on establishing that something “is or isn’t” or is “true or false.”
- Propositions of value focus on persuading an audience that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.”
- Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done.
- Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic. Then do the same thing for persuasive messages you may receive.
- To help ensure that your persuasive speech topic is persuasive and not informative, identify the claims, evidence, and warrants you may use in your argument. In addition, write a thesis statement that refutes your topic idea and identify evidence and warrants that could support that counterargument.
- Determine if your speech is primarily a proposition of fact, value, or policy. How can you tell? Identify an organizational pattern that you think will work well for your speech topic, draft one sentence for each of your main points, and arrange them according to the pattern you chose.
Bone, J. E., Cindy L. Griffin, and T. M. Linda Scholz, “Beyond Traditional Conceptualizations of Rhetoric: Invitational Rhetoric and a Move toward Civility,” Western Journal of Communication 72 (2008): 436.
Gearhart, S. M., “The Womanization of Rhetoric,” Women’s Studies International Quarterly 2 (1979): 195–201.
Ryan, K. J., and Elizabeth J. Natalle, “Fusing Horizons: Standpoint Hermenutics and Invitational Rhetoric,” Rhetoric Society Quarterly 31 (2001): 69–90.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Resources ›
- For Students and Parents ›
- Homework Help ›
- Homework Tips ›
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- 10 Tips for the SAT Essay
- Basic Tips for Memorizing Speeches, Skits, and Plays
- Mock Election Ideas For Students
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- How to Write an Interesting Biography
- The Difference Between Liberals and Conservatives
- How to Run for Student Council
- Tips to Write a Great Letter to the Editor
- How to Write a Film Review
- Writing the Parts of a Stage Play Script
- 18 Ways to Practice Spelling Words

COMMENTS
Find 110 interesting persuasive speech topics that will impress your audience and learn how to create and deliver a compelling speech. Get expert advice on choosing a topic, organizing your arguments, supporting your claims, and addressing counterarguments.
Value Persuasive Speech. Value persuasive speech states whether something is right or wrong, beautiful or ugly, moral or immoral, or good or bad. It questions the ethical and moral aspects of a particular topic or defines the truth or falsity of an assertion.
The key to a successful value persuasive speech is tapping into your audience’s existing beliefs and values. Use vivid language and storytelling to paint a picture of the world you want to see. Make your case in moral and ethical terms, not just practical ones.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Persuasive speeches of value depend on a judgement that something is right or wrong, moral or immoral, or better or worse than another thing. The speech should include an appeal, criteria for judgement, and facts that support the appeal using the judgement criteria.
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members (Poggi, 2005). Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant.
Learn how to construct arguments that appeal to audience members by using claims, evidence, and warrants. Find out how to choose a persuasive speech topic, adapt to audience orientation, and organize your speech.
Persuasive speeches have one of four types of propositions or claims, which determine your overall approach. Before you move on, you need to determine what type of proposition you should have (based on the audience, context, issues involved in the topic, and assignment for the class). Proposition of Fact.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.