

Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions of Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 12 / 12 board
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Electric Charges and Fields to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
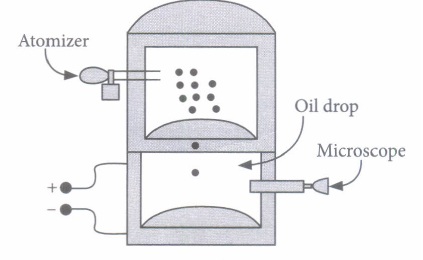
Answer: (a) 6.40 x 10-19 C
(ii) Extra electrons on this particular oil drop (given the presently known charge of the electron) are
Answer: (a) 4
(iii) A negatively charged oil drop is prevented from falling under gravity by applying a vertical electric field 100 V m -1 .If the mass of the drop is 1.6 X 10 -3 g, the number of electrons carried by the drop is (g= 10 m s -2 )
Answer: (c) 1012 .
(iv) The important conclusion given by Millikan’s experiment about the charge is
Answer: (c) charge is quantized
(v) If in Millikan’s oil drop experiment, charges on drops are found to be 8μC,12μC,20μC8μC,12μC,20μC then quanta of charge is
Answer: (d) 4μC
Case Study 2: Surface Charge Density. Surface charge density is defined as the charge per unit surface area the surface (Arial) charge symmetric distribution and follow Gauss law of electrostatics mathematical term of surface charge density σ=ΔQ/ΔS

Two large thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite sign (± s). Having magnitude 8.8 × 10 –12 cm –2 as shown here. The intensity of electrified at a point is E =σ/ε 0 and flux is Φ=E.ΔS, where ΔS = 1 m 2 (unit arial plate)
(i) E in the outer region (I) of the first (A) plate is (a) 1.7 × 10 –22 N/C (b) 1.1 × 10 –12 V/m (c) Zero (d) Insufficient data
Ans. (c) Zero C
(ii) E in the outer region (III) of the second plate (B) is (a) 1 N/C (b) 0.1 V/m (c) 0.5 N/C (d) zero
Ans. (d) Zero
(iii) E between (II) the plate is (a) 1 N/C (b) 0.1 V/m (c) 0.5 N/C (d) None of these
Ans. (d) None of these
(iv) The ratio of E from left side of plate A at distance 1 cm and 2 m respectively is (a) 1 : 2 (b) 10 : 2 (c) 1 : 1 (d) 20 : 1
Ans. (c) 1 : 1
(v) In order to estimate the electric field due to a thin finite plane metal plate the Gaussian surface considered is (a) Spherical (b) Linear (c) Cylindrical (d) Cybic
Ans. (c) Cylindrical
Case Study 3: Electric Charges and Fields, focuses on the basic properties of electric charges, the concept of electric fields, and the forces acting within these fields. The chapter introduces the idea that like charges repel, and unlike charges attract, a fundamental law of electrostatics. It also discusses the principle of superposition, which states that the net electrostatic force experienced by a charge due to multiple charges is simply the vector sum of the individual forces exerted by each charge independently. Further, the chapter introduces the concept of an electric field, defined as the electric force experienced by a unit positive charge at a point in space, and illustrates the way these fields are represented using field lines.
What is the basic property of electric charges?
A) Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract.
B) Like charges attract, and unlike charges repel.
C) All charges repel.
D) All charges attract.
Ans. A) Like charges repel, and unlike charges attract.
What does the principle of superposition state in terms of electrostatic forces?
A) The net electrostatic force is equal to the sum of the individual forces.
B) The net electrostatic force is equal to the difference of the individual forces.
C) The net electrostatic force is independent of the individual forces.
D) The net electrostatic force is inversely proportional to the individual forces.
Ans. A) The net electrostatic force is equal to the sum of the individual forces.
What is an electric field?
A) The region around a charge where magnetic force is experienced.
B) The region around a charge where gravitational force is experienced.
C) The region around a charge where electrostatic force is experienced.
D) The region around a charge where nuclear force is experienced.
Ans. C) The region around a charge where electrostatic force is experienced.
How is the electric field defined?
A) As the electric force experienced by a unit negative charge.
B) As the electric force experienced by a unit positive charge.
C) As the gravitational force experienced by a unit positive charge.
D) As the magnetic force experienced by a unit positive charge.
Ans. B) As the electric force experienced by a unit positive charge.
How are electric fields represented?
A) By field lines.
B) By electric charges.
C) By vectors.
D) By matrices.
Ans. A) By field lines.
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Class 12 biology case study questions chapter 13 organisms and populations, class 12 biology case study of chapter 6 molecular basis of inheritance, class 12 physics case study questions chapter 3 current electricity, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- Competency Based Questions
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- LPU Mock Test
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- NEET Toppers Notes
- NEET Formula
- NEET Important Question
- NEET Assertion Reason Question
- NEET Study Planner
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics PDF
Better preparation of Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics can help students score good marks in the CBSE Class 12 Board examination. Additionally, it helps build confidence and enables students to deepen their knowledge of Electric Charges and Fields. Because case-based questions are equally important for learning and board exam preparation, our team has prepared Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics in a PDF file for free distribution among students.
Links to download the PDF file of the Electric Charges and Fields Case Study for Class 12 Physics free of cost are mentioned on this page.
Electric Charges and Fields Case Study for Class 12 Physics with Solutions in PDF
The PDF file of the Electric Charges and Fields Case Study for Class 12 Physics with Solutions is a very important study resource that can help students better prepare for the exam and boost conceptual learning.
The solutions are in the hint manner as well as contain full examples too, refer to the link to access the Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics with Solutions in PDF - it’s free.
Features of Class 12 Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions
Certain features of Class 12 Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions are -
- Available for free 24×7
- Based on CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- Case Study Questions on Electric Charges and Fields with Answers are given
Step-wise Method to Download Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics
The below-given steps are helpful for students wanting to download Electric Charges and Fields Case Study for Class 12 Physics with Solutions in a PDF file.
- Search Selfstudys.com using the internet browser
- After loading the website, click on the navigation button
- Click on CBSE from the list of categories
- Find and Click on Case Study
- Select Class 12 and Click on Physics to download the Electric Charges and Fields case study questions in PDF.
4 Tips to Answer Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions?
There are 4 solid tips to answer Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields Case Study questions that we are discussing in this section.
- Read the Case Carefully: To start gathering insights from the given case-based questions, it is vital to read the Electric Charges and Fields case carefully and identify the key facts, figures, and units of measurement. Pay attention to any diagrams or graphs related to Electric Charges and Fields provided, as they may contain important information.
- Identify the Problem: While reading the Electric Charges and Fields case it is essential to consider the possible causes and effects. This will help you determine the appropriate approach to solving the problem in Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields.
- Use Elimination Methods Too: Since case study questions of Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields, are often framed in Multiple choice questions, students should have the knowledge of elimination methods in MCQs to better answer the questions.
- Before All, Master the Concept of Electric Charges and Fields: If the above two methods are not working for you to answer Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics then you need to revisit the lesson and master the concepts explained in the Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics.

What is the Benefit of Practising Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions?
When a student decides to practise Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields case study questions before the board examination they generally get these 3 benefits:
- Quick Conceptual Revision: Nothing is better for revision than solving relevant questions and therefore, those who involve in solving the Electric Charges and Fields Case study questions before the Class 12 Physics exam are able to better revise their conceptual learnings from the lesson.
- Better Board Exam Preparation: No doubt, the more you practise Electric Charges and Fields case study questions the better your exam preparation will be so, solving Case-based questions prior to the board examination helps a lot in the preparation. It also enables the students to know what are the Electric Charges and Fields questions which have the possibility to be asked in the board examination.
- Confident in Using Analytical or Critical Thinking Skills: The Case-based questions on Electric Charges and Fields are all about using analytical or critical thinking skills where students are required to solve problems based on the situations or data given. Thus, practising Case Study on Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics benefits students to feel confident and comfortable in using analytical skills.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields
Case study questions class 12 physics chapter 1 electric charges and fields.
CBSE Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Electric Charges and Fields. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Electric Charges and Fields.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.

1.) Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions from 1.1 to 1.4 :
Charge is a property of matter that can be in two forms: positive charge and negative charge. If two objects which are having the same sign of charge repel to each other, and on the other hand objects which have opposite sign charges attract to each other. Electric field concept comes from
The concept of an electric field arises from the effect of a charge body in the space around the body. When a charged particle is placed in a space and it feels some electric force we can say there is an electric field.
Electric field is a vector quantity that means it has magnitude and direction both.
Electric field at any point can be defined as a force on a unit charge particle.
This unit charge is called a test charge, and the direction of the electric field is defined as a force direction on a positive test charge , and force on a charge particle in an electric field is given by F=qE.
1.1 Define electric field and how we can find direction of electric field ?
1.2 Choose the correct options from the following given below.
If two bodies have like charges and opposite charges how will they behave ?
A.) In both cases they will repel.
B.) In both cases they will attract.
C.) They will repel when both have the same charge and attract each other when both have opposite charges.
D.) They will attract when both have the same charge and repel each other when both have opposite charges.
1.3 If Force acting on a test charge of 5C , is 25 N along north direction then what will be electric field intensity at that point.
Electric field or electric field intensity at any point can be defined as a force on a unit charge particle. And we know that force on a charge particle is given by F=qE
From them we can wright E = F/q
And the direction of the electric field will be along the force on the positive charge particle or on the negative charge particle opposite to the force direction.
(C) They will repel when both have the same charge and attract each other when both have opposite charges.
When both bodies have the same charges they will repel each other and on the other hand they will attract each other when both bodies have different charges.
Given test charge value = 5C
And force on the test charge is 25N
We know that electric field intensity is defined as the force on per unit test charge.
So E = F/q = 25/5 = 5 N/C
And Direction of the electric field intensity is along the force direction that is along the north.
2.) Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions from 2.1 to 2.3
E lectric field is a basic property of a charge particle. When a charge particle is placed in a space it will create an electric field around it in all possible directions and that will be inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the point charge.
As we know electric field is a vector quantity so due to more than one point charges electric field intensity can be calculated at any point as a vector sum of due to all point charges intensity and direction will be along the resultant vector direction.If at any point electric field is uniform can be drawn as a parallel line and if electric field is non- uniform it can be drawn non-parallel line but when then electric field line near to each other we can say there is a strong electric field compare to other point, where electric field line is little bit far away that means we can say electric field line density is directly proportional to electric field strength.And this electric field lines never intersect to each other. The electric field strength measure in V/m
2.1 How can electric field strength be measured ? And what is its SI unit ?
2.2 Why electric field lines never intersect with each other?
2.3 Let there be two point charges in space. Charge Q1= +3 μC is at coordinates (0, 0), and charge Q2 = -1 μC is at coordinates (6m, 0). Calculate the resultant electric field at a point P, which is at (3m, 0m), and also calculate force by this electric field on a +2 μC test charge which is placed at the same point P(3m,0).
Electric field can be measure by two ways:
1.) By placing a test charge on that point we can measure the electric field strength, first we calculate the force on test charge and we divide test charge value to force by this method we can calculate the electric field.
2.) Or if we know the field pattern we can say where the electric field is high in magnitude and where is low but by this method we can not determine magnitude of electric electric field strength.
And It’s SI unit is defined is a Volt/meter
Electric field lines never intersect with each other , because if electric field vector quantity means it has both magnitude and direction as well , if electric field lines intersect to each other we can be drawn to tangents on intersecting points which show its two directions at the same point which is impossible. Means electric field lines never intersect to each other.

3.) Read the following paragraph and answer the following questions from 3.1 to 3.3
When two charge or more charged particle placed at a distance then they will create a magnetic field due to this electric field they will exert an electric force on each other, this force can be calculated by Coulomb’s law, which states that force between two charge particles is directly proportional to magnitude of the charge particle and inversely proportional to square distance between them.Coulomb’s force between two charged particle depends on medium between them , when a medium of dielectric constant K is placed between two charged particle electric force decrease by K times

3.1 when two charges, q_1and q_2 are brought closer to each other without changing their magnitude, what will be the effect on electrostatic force between them?
A.) Decrease
B.) Increase
C.) Remain same
D.) Data is not sufficient
3.2 Two charge values of +2 μC and -4 μC are placed at 2m distance. Find the electrostatic force between these two charge particles?
3.3 Choose the correct statement from the given below.
Assertion(A): Electric force between two point charges depends upon the magnitudes of the two charges and also depends upon the distance between them.
Reason(R): Coulomb’s law defines the electrostatic force (F) is directly proportional to the product of magnitude of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between two charges.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of reason.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is NOT the correct explanation of Assertion.
C. Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
D. Assertion is false, but Reason is true
when two charges, and are brought closer to each other without changing their magnitude, electrostatic force between them will increase because force is inversely proportional to distance square.
By Coulomb’s law electrostatic force (F) between two point charges can be

A. Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of reason. By Coulomb’s law we can explain it.
Others Chapter Case Study Questions:
- Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Case Study
- Chapter 10 Wave Optics Case Study
- Chapter 11 Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Case Study
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Ncert joyful mathematics class 1 worksheet 3 – mango treat, new trends civics class 6 solutions chapter 1 rural local self – government, new trends civics class 6 solutions chapter 2 urban local self-government, new trends in history and civics class 6 solutions chapter 4 the rise of kingdoms and republicans.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
