

Apple Orchard Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Solomon O'Chucks
Home » Business ideas » Agriculture Industry » Crop Cultivation » Apple Orchard
An apple orchard business involves the cultivation and management of apple trees for commercial purposes. Orchards are carefully planned and maintained to yield high-quality apples for sale, typically catering to local markets, grocery stores, or other distribution channels.
Successful orchard management requires expertise in horticulture, including knowledge of soil conditions, pest control, and irrigation.
The business involves seasonal activities such as planting, pruning, and harvesting, with a focus on maximizing fruit production and ensuring product quality.
Suggested for You
- Marijuana Cultivation Business Plan [Sample Template]
- CBD Hemp Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Lavender Farm Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Soybean Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Rose Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
Marketing strategies may include direct sales to consumers, participation in farmers’ markets, or supplying larger retailers.
A successful apple orchard business requires a combination of agricultural skills, business acumen, and an understanding of market dynamics.
Steps on How to Write an Apple Orchard Business Plan
Executive summary.
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. is a thriving agricultural enterprise located in Traverse City, Michigan. Specializing in the cultivation and sale of high-quality apples, our orchard covers a picturesque expanse where climate and soil conditions are ideal for apple production.
Established in 2010, the orchard has steadily expanded its acreage and product offerings, becoming a prominent local supplier of premium apples.
Situated in the heart of Traverse City, our orchard benefits from the region’s rich agricultural heritage and proximity to urban markets.
The scenic location enhances the overall customer experience, attracting visitors seeking a connection to nature and locally sourced produce.
Our competitive edge lies in the quality and variety of our apples, as well as our dedication to sustainable farming practices. We prioritize customer satisfaction through personalized service, offering a unique and memorable orchard experience.
Moreover, our community engagement initiatives foster strong relationships, further differentiating us from competitors. Daniel Conwell is the founder and CEO of Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc.
Company Profile
A. our products and services.
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. offers a diverse range of apple varieties, carefully selected for flavour and texture. In addition to bulk sales to local markets and grocery stores, we engage in direct-to-consumer sales through on-site visits, farmers’ markets, and online platforms.
b. Nature of the Business
Our apple orchard company will operate with both a business-to-consumer business model and a business-to-business business model for retailers and distributors.
c. The Industry
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will operate in the agriculture industry, specifically the fruit farming sector.
d. Mission Statement
At Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc., our mission is to cultivate nature’s bounty with dedication and care, providing our community with the freshest and highest-quality apples.
Committed to sustainable farming practices, we strive to be a trusted source of wholesome, locally-grown produce. Our mission extends beyond orchard management; we aim to foster a connection between people and the land, promoting healthy living and environmental stewardship.
Through passion, integrity, and community engagement, we aspire to contribute to the well-being of Traverse City and leave a lasting legacy of excellence in the agricultural landscape.
e. Vision Statement
Our vision at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. is to be the premier destination for exceptional apples, embodying the essence of sustainable agriculture and community enrichment.
We envision a future where our orchard stands as a symbol of environmental responsibility, innovation, and a thriving local economy.
Striving for continuous growth and diversification, we aim to expand our product offerings, embrace technological advancements in farming, and create a welcoming agro-tourism destination.
With a commitment to excellence and a deep connection to our roots, we see Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard becoming synonymous with the finest apples and a model for sustainable, community-focused agriculture.
f. Our Tagline (Slogan)
“Harvesting Nature’s Finest: Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Where Quality Meets Tradition.”
g. Legal Structure of the Business (LLC, C Corp, S Corp, LLP)
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will be formed as a Limited Liability Company (LLC). The reason why we are forming an LLC is to protect our assets by limiting the liability to the resources of the business itself. The LLC will protect our CEO’s assets from claims against the business, including lawsuits.
h. Our Organizational Structure
- Orchard Manager
- Sales and Marketing Manager
- Horticulturist/Arborist
- Harvest Supervisor
- Quality Control Inspector
- Farm Equipment Operator
- Delivery Truck Driver.
i. Ownership/Shareholder Structure and Board Members
- Daniel Conwell (Owner and Chairman/Chief Executive Officer) 52 Percent Shares
- Michael Daniels (Board Member) 18 Percent Shares
- Humphery Maxwell (Board Member) 10 Percent Shares
- Justus Billy (Board Member) 10 Percent Shares
- Esther Emmanuel (Board Member and Secretary) 10 Percent Shares.
SWOT Analysis
A. strength.
- Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard is renowned for cultivating high-quality apples, earning a strong reputation for flavour and freshness.
- The orchard is committed to environmentally friendly and sustainable farming methods, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and fostering long-term soil health.
- Strong ties with the local community through farmers’ markets, agro-tourism initiatives, and educational programs, enhancing brand loyalty.
- Situated in Traverse City, the picturesque location provides a unique and appealing setting for visitors, contributing to a positive customer experience.
- Offering a wide range of apple varieties that cater to varied consumer preferences, attracting a broader customer base.
b. Weakness
- Reliance on seasonal sales may result in fluctuating revenue streams, necessitating strategic planning for off-season sustainability.
- Vulnerability to weather conditions, such as late frosts or storms, can impact crop yields and overall productivity.
- While apples are the primary focus, diversifying the product line with complementary products may present growth opportunities.
c. Opportunities
- Expanding and optimizing the orchard’s online presence can tap into a broader market, offering online sales, virtual tours, and educational content.
- Introducing value-added products such as apple-based snacks, juices, or artisanal goods can create new revenue streams and enhance brand recognition.
- Incorporating advanced agricultural technologies for precision farming, irrigation systems, and pest control can optimize operations and increase efficiency.
- Forming partnerships with local businesses, restaurants, or cideries can create mutually beneficial relationships, expanding distribution channels.
i. How Big is the Industry?
The Apple orchard industry is indeed big and this can be supported by the fact that the Fresh Apple Market size is estimated at USD 101.04 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 111.56 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 2%.
ii. Is the Industry Growing or Declining?
The apple orchard industry was generally stable, with growth influenced by consumer demand for fresh, locally sourced produce.
However, industry trends may have evolved since then, and factors such as climate change, market dynamics, and economic conditions can impact its trajectory.
iii. What are the Future Trends in the Industry?
The future trends in the apple orchard industry point towards a combination of sustainability, technological integration, and diversification.
Sustainable farming practices, including organic cultivation and eco-friendly pest control, are gaining prominence as consumers prioritize environmental responsibility.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as precision agriculture, data analytics, and automation, is enhancing orchard efficiency and productivity.
Diversification of product offerings beyond traditional apple varieties to include value-added products like snacks, juices, and artisanal goods is becoming a key trend.
Additionally, the industry is witnessing a rise in agro-tourism, where orchards transform into experiential destinations, attracting visitors with activities like picking events and educational programs.
Staying attuned to consumer preferences, embracing technological advancements, and exploring innovative business models are essential for apple orchards to thrive in the evolving landscape of the agricultural sector.
iv. Are There Existing Niches in the Industry?
Yes, there are existing niches when it comes to the apple orchard business and some of them are:
- Organic Heirloom Apple Orchard
- Artisanal Cider Orchard
- Educational Agritourism Orchard
- Rare or Heritage Apple Varieties Orchard.
v. Can You Sell a Franchise of Your Business in the Future?
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. has no plans to sell franchises soon.
- The orchard is susceptible to pest infestations and diseases, requiring vigilant monitoring and preventive measures.
- Increasing competition from other local orchards or larger commercial producers may pose a challenge, necessitating continuous differentiation.
- Evolving regulations related to agriculture, environmental practices, or food safety standards may impact operations and require adaptation.
- Unpredictable climate patterns can affect growing seasons, leading to potential challenges in maintaining consistent crop yields.
i. Who are the Major Competitors?
- Apple Hill Orchard (New York)
- Honey Pot Hill Orchards (Massachusetts)
- Carter Mountain Orchard (Virginia)
- Sky Top Orchard (North Carolina)
- Eckert’s Orchard (Illinois)
- Riley’s at Los Rios Rancho (California)
- Lyman Orchards (Connecticut)
- Chudleigh’s (Ontario, Canada – near the U.S. border)
- Fishkill Farms (New York)
- Beak & Skiff Apple Orchards (New York)
- Taves Family Farms (British Columbia, Canada – near U.S. border)
- Mercier Orchards (Georgia)
- Royal Oak Farm Orchard (Illinois)
- Stribling Orchard (Virginia)
- Applecrest Farm Orchards (New Hampshire)
- The Apple Barn and Cider Mill (Tennessee)
- Aamodt’s Apple Farm (Minnesota)
- County Line Orchard (Indiana)
- Masker Orchards (New York)
- Terhune Orchards (New Jersey).
ii. Is There a Franchise for Apple Orchard Business?
Apple orchard is typically not structured as a franchise business, as it involves land ownership, crop cultivation, and specialized equipment that are unique to each farm.
iii. Are There Policies, Regulations, or Zoning Laws Affecting Apple Orchard Business?
Yes, there are county and state regulations as well as zoning laws that may apply to apple orchard businesses in the United States.
However, the specific regulations and laws can vary significantly depending on the location, the size of the business, and the activities involved.
Apple orchard businesses that handle, process, or package food products are subject to health and safety regulations to ensure that the products are safe for consumption.
This may include adherence to specific food safety standards and regular inspections by health authorities. Certain zones may be designated for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes.
Apple orchard businesses, particularly those involved in manufacturing or processing, may need to locate their operations in areas zoned for industrial or commercial use.
There may be specific regulations regarding the packaging and labeling of food products , including apple orchards. Businesses need to comply with these regulations to provide accurate information to consumers and meet the required standards.
Apple orchard businesses that handle large quantities of apple orchard may be subject to environmental regulations, especially if they generate waste or discharge wastewater. Compliance with environmental laws is essential to minimize the business’s impact on the environment.
Businesses must comply with federal and state employment laws regarding wages, working hours, employee safety, and other labor-related issues.
If the apple orchard business involves shipping products across state lines or internationally, there may be regulations and requirements related to transportation, labeling, and customs.
Marketing Plan
A. who is your target audience.
i. Age Range
- The primary focus is on families with children, adults aged 25-55, and seniors enjoying an active lifestyle.
- Special engagement initiatives for young adults, creating a dynamic and inclusive orchard experience.
ii. Level of Educational
- Appeals to a diverse range of educational backgrounds, with an emphasis on educating consumers about sustainable farming practices.
iii. Income Level
- Middle to upper-middle-income households with disposable income for premium, locally-grown produce and agro-tourism experiences.
iv. Ethnicity
- No specific ethnic targeting; aims to be inclusive and cater to the diverse demographics of the local community.
v. Language
- English is the primary language for communication.
- Multilingual signage and basic materials to accommodate a broader audience.
vi. Geographical Location
- Residents of Traverse City and nearby communities, with a focus on creating a sense of community involvement.
- Regional marketing to attract tourists interested in agro-tourism experiences.
vii. Lifestyle
- Targets individuals and families who value healthy living, sustainable practices, and enjoy outdoor activities.
- Appeals to consumers with an interest in supporting local agriculture and participating in seasonal events.
b. Advertising and Promotion Strategies
- Build Relationships with players in the agriculture industry.
- Deliberately Brand All Our Vans and Delivery Bikes.
- Develop Your Business Directory Profiles
- Tap Into Text Marketing
- Make Use of Bill Boards.
- Share Your Events in Local Groups and Pages.
- Turn Your Social Media Channels into a Resource
i. Traditional Marketing Strategies
- Marketing through Direct Mail.
- Print Media Marketing – Newspapers & Magazines.
- Broadcast Marketing -Television & Radio Channels.
- Out-of-Home” marketing (OOH marketing) – Public Transits like Buses and Trains, Billboards, Street shows, and Cabs.
- Leverage direct sales, direct mail (postcards, brochures, letters, fliers), tradeshows, print advertising (magazines, newspapers, coupon books, billboards), referral (also known as word-of-mouth marketing), radio, and television.
ii. Digital Marketing Strategies
- Social Media Marketing Platforms.
- Influencer Marketing.
- Email Marketing.
- Content Marketing.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Marketing.
- Affiliate Marketing
- Mobile Marketing.
iii. Social Media Marketing Plan
- Start using chatbots.
- Create a personalized experience for our customers.
- Create an efficient content marketing strategy.
- Create a community for our target market and potential target market.
- Gear up our profiles with a diverse content strategy.
- Use brand advocates.
- Create profiles on the relevant social media channels.
- Run cross-channel campaigns.
c. Pricing Strategy
When working out our pricing strategy, Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will make sure it covers profits, insurance, premium, license, and economy or value and full package. In all our pricing strategy will reflect;
- Penetration Pricing
- Cost-Based Pricing
- Value-Based Pricing
- Competition-Based Pricing.
Sales and Distribution Plan
A. sales channels.
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. employs a multi-faceted sales strategy to reach diverse consumer segments. Our primary channels include direct-to-consumer sales on-site, providing a unique orchard experience for residents and tourists.
Participation in farmers’ markets amplifies community engagement, offering a platform for face-to-face interactions. Online sales through an optimized website will help expand our reach to a broader audience, providing convenience and accessibility.
Collaborations with local grocery stores and businesses will enhance our distribution channels, ensuring a consistent presence in the retail market.
This diversified approach enables Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard to meet consumer demands while fostering strong relationships within the local community and beyond.
b. Inventory Strategy
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. employs a dynamic inventory strategy to ensure freshness and meet customer demand.
We will utilize precise forecasting based on historical data and market trends; the orchard manages optimal stock levels. A seasonal approach guides inventory fluctuations, aligning with peak harvesting times.
We will emphasize offering diverse apple varieties to cater to different consumer preferences. Our storage facilities are equipped with temperature and humidity control, which will help preserve our fruit quality.
Additionally, we will adopt a just-in-time approach which will help us minimize excess inventory, reduce waste, and enhance sustainability.
This strategic inventory management ensures a consistent and varied supply of high-quality apples while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
c. Payment Options for Customers
Here are the payment options that Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Bank Transfers
- Credit or Debit Card
- Electronic Payment Systems such as PayPal or Venmo
d. Return Policy, Incentives and Guarantees
Return policy:.
At Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc., customer satisfaction is our priority. We offer a flexible return policy for any apples that do not meet our quality standards.
Customers may return or exchange products within 7 days of purchase, provided they are in their original condition. Receipts are required for all returns.
Incentives:
To express gratitude to our loyal customers, we offer a rewards program. Frequent buyers enjoy discounts, exclusive access to seasonal events, and special promotions.
Additionally, bulk purchasers benefit from volume discounts, encouraging larger orders and fostering long-term relationships.
Guarantees:
We stand behind the quality of our apples. If customers are dissatisfied with their purchase, we guarantee a replacement or refund.
Our commitment is to provide consistently fresh, flavorful, and premium apples, ensuring customer confidence and trust in Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc.
Note that these incentives and guarantees are subject to certain terms and conditions, which will be communicated at the time of purchase or inquiry. We are committed to ensuring your satisfaction and building long-term relationships with our valued customers.
e. Customer Support Strategy
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. prioritizes a customer-centric support strategy to enhance the overall experience. A dedicated customer support team is available through various channels, including phone, email, and social media, providing prompt assistance and addressing inquiries.
Transparency is maintained in communication, with clear information on product details, promotions, and events. Personalized engagement is fostered through a loyalty program, acknowledging and rewarding customer loyalty. We actively seek and welcome feedback, using it to continually improve our offerings and services.
By prioritizing accessibility, transparency, and customer feedback, our strategy aims to build lasting relationships and ensure unparalleled satisfaction with Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard products.
Operational Plan
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc.’s operational plan centers on sustainable agricultural practices, technological integration, and customer-centricity.
Orchestrating a seasonal approach, our skilled team manages planting, pruning, and harvesting to optimize yield and quality. Advanced technologies, including precision agriculture and climate control in storage, enhance operational efficiency.
Our emphasis on eco-friendly pest control aligns with our commitment to sustainability. To ensure seamless customer experiences, we prioritize a responsive online presence, engaging in e-commerce and agro-tourism initiatives.
We will engage in regular training and empowerment of our staff to contribute to a cohesive and skilled workforce. This comprehensive operational plan underscores our dedication to quality, innovation, and the satisfaction of our valued customers.
a. What Happens During a Typical Day at an Apple Orchard Business?
A typical day at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard involves a harmonious blend of agricultural management and customer engagement.
The day begins with orchard maintenance tasks, including pruning, irrigation checks, and monitoring for pests. Harvesting, a crucial activity, is executed with precision to ensure the freshest apples. Post-harvest, sorting, and packing operations take place, emphasizing quality control.
Simultaneously, the team engages in agro-tourism activities, offering visitors an immersive orchard experience through tours, apple picking, and educational programs. Sales channels, both on-site and online, are actively managed.
Flexibility is maintained to adapt to seasonal demands and unexpected challenges, reflecting the dynamic nature of daily operations at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc.
b. Production Process
Cultivating apples is a meticulous process at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. It begins with a strategic orchard layout and a selection of disease-resistant rootstocks.
Planting, typically in late winter or early spring, involves careful spacing and proper tree placement. Pruning, an essential practice, shapes the trees for optimal sunlight exposure and air circulation.
Throughout the growing season, diligent pest monitoring and eco-friendly control measures are implemented. Watering and nutrient management are fine-tuned to support healthy tree growth.
Harvesting, a highlight, involves skilled picking, sorting, and immediate storage in controlled environments. This comprehensive approach ensures the cultivation of premium-quality apples, reflecting our commitment to excellence and sustainable farming practices.
c. Service Procedure
At Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc., our service procedure is designed for a seamless and enriching customer experience.
Visitors are warmly welcomed by knowledgeable staff who provide informative tours, allowing them to witness the orchard’s cultivation processes. Engaging activities such as apple picking enhance the customer’s connection with the orchard.
During onsite sales, our team ensures a friendly and efficient transaction, offering guidance on apple varieties and providing educational material. For online customers, our website is user-friendly, offering a secure and straightforward purchasing process.
Our commitment extends beyond transactions – we actively seek customer feedback, valuing their input to continually enhance our services and maintain the highest standards at every touchpoint.
d. The Supply Chain
The supply chain at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. is meticulously managed to ensure a consistent and high-quality flow of apples.
It begins with strategic orchard planning, including varietal selection and sustainable farming practices. Harvested apples undergo thorough sorting and quality checks before entering storage equipped with climate control.
Our distribution channels also include direct-to-consumer sales on-site, participation in farmers’ markets, collaboration with local retailers, and an online platform for wider accessibility.
Continuous communication and collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and retailers contribute to a streamlined supply chain.
By prioritizing efficiency, quality control, and sustainability, we ensure that our apples reach consumers with freshness and excellence.
e. Sources of Income
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will generate revenue through the sale of harvested apples. Income sources include direct sales to consumers at the orchard, wholesale distribution to grocery stores and markets, value-added products like cider and sauces, and Agri-tourism activities such as U-Pick experiences, educational tours, and seasonal events.
Financial Plan
A. amount needed to start your apple orchard business.
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. would need an estimate of $350,000 to successfully set up our apple orchard in the United States of America. Note that this amount includes the salaries of all our staff for the first month of operation.
b. What are the Costs Involved?
- Business Registration Fees – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits – $12,300.
- Marketing, Branding, and Promotions – $10,000.
- Business Consultant Fee – $2,500.
- Insurance – $6,400.
- Rent/Lease – $85,000.
- Operational Cost (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $80,000
- Start-up Inventory – $75,000
- Store Equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $3,750
- Website: $600
- Opening party: $5,000
- Miscellaneous: $5,000
c. Do You Need to Build a Facility? If YES, How Much will it cost?
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will not build a new facility for our apple orchard; we intend to start with a long-term lease and after 8 years, we will start the process of acquiring our own warehouse facility.
d. What are the Ongoing Expenses for Running an Apple Orchard Business?
- Salaries and wages for orchard workers.
- Regular upkeep and repair costs for tractors, pruning equipment, and other machinery used in orchard operations.
- Expenses associated with maintaining irrigation systems and paying for water usage
- Costs for pesticides, insecticides, and other methods to manage pests and diseases affecting apple trees.
- Expenditures on fertilizers and soil enhancers
- Ongoing costs for electricity, gas, and other utilities related to operating the orchard.
- Payments for insurance coverage, including property insurance, liability insurance, and crop insurance to protect against potential risks.
- Budget for ongoing marketing efforts, promotions, and advertising.
- Costs associated with packaging materials and labeling for apples, especially if selling products directly to consumers or through retail channels.
- Payments for property taxes, permits, and compliance with agricultural and environmental regulations imposed by local, state, and federal authorities.
e. What is the Average Salary of your Staff?
- Orchard Manager- $75,000 per year
- Sales and Marketing Manager – $60,000 per year
- Horticulturist/Arborist – $55,000 per year
- Harvest Supervisor – $50,000 per year
- Quality Control Inspector – $50,000 per year
- Farm Equipment Operator – $45,000 per year
- Delivery Truck Drivers -$36,000 Per Year.
f. How Do You Get Funding to Start an Apple Orchard Business?
- Raising money from personal savings and sale of personal stocks and properties
- Raising money from investors and business partners
- Sell shares to interested investors
- Applying for a loan from your bank/banks
- Pitching your business idea and applying for business grants and seed funding from the government, donor organizations, and angel investors
- Source for soft loans from your family members and friends.
Financial Projection
A. how much should you charge for your product/service, common varieties (e.g., gala, fuji, granny smith):.
- Conventional: Approximately $1 to $2 per pound.
- Organic: Can range from $2 to $4 per pound.
Specialty or Organic Varieties (e.g., Honeycrisp):
- Conventional: Typically $2 to $4 per pound.
- Organic: Often priced between $3 to $5 per pound or more.
Bulk or Bagged Apples:
- Conventional: Prices may range from $1 to $2 per pound or higher, depending on quantity and packaging.
- Organic: Bulk or bagged organic apples can be priced higher, often ranging from $2.50 to $4 per pound.
b. Sales Forecast?
- First Fiscal Year (FY1): $450,000
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2): $750,000
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3): $1.2 million
c. Estimated Profit You Will Make a Year?
- First Fiscal Year (FY1) (Profit After Tax): 15%
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2) (Profit After Tax): 20%
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3) (Profit After Tax): 25%
d. Profit Margin of an Apple Orchard Business Product/Service
The ideal profit margin we hope to make at Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. will be between 15 and 25 percent depending on the packaging size.
Growth Plan
A. how do you intend to grow and expand by opening more retail outlets/offices or selling a franchise.
To capitalize on market trends and consumer preferences, we plan to expand our product line, implement innovative agricultural technologies, and strengthen partnerships with local businesses. Exploring agro-tourism opportunities and increasing our online presence will further drive growth and brand visibility.
b. Where do you intend to expand to and why?
Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. plans to expand to the following cities.
- Wenatchee, Washington
- Hood River, Oregon
- Charlottesville, Virginia
- Grand Rapids, Michigan
- Rochester, New York
- Winchester, Virginia
- Sebastopol, California
- Yakima, Washington
- Traverse City, Michigan
- Ellijay, Georgia.
We are expanding to these cities because these cities are ideal for apple orchards due to their favourable climate, rich soil conditions, and proximity to bodies of water. These factors create an optimal environment for cultivating high-quality apples.
The founder of Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. plans to exit the business via family succession. We have positioned structures and processes in place that will help us achieve our plan of successfully transferring the business from one family member to another and from one generation to another without difficulties.
The company has successfully developed a detailed transition plan to smoothly hand over responsibilities to the new successor.
This includes transferring ownership, training key personnel, and communicating with employees, customers, and suppliers about the change.
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Back to All Business Ideas
How to Start an Orchard: Cost, Planning and Profit Potential
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on May 24, 2023

Investment range
$95,800 - $262,300
Revenue potential
$800,000 to $1,200,000 p.a.
Time to build
2 – 7 years
Profit potential
$160,000 - $240,000 p.a.
Industry trend
Important elements to think about when starting your orchard:
- Choose a location with optimal growing conditions — Select land with suitable soil, climate, and sunlight for the type of fruit trees you plan to grow. Ensure the location has good drainage and access to water sources.
- Zoning and permits — Ensure the land is zoned for agricultural use and obtain all necessary licenses and permits to operate your orchard legally. This includes water rights, agricultural permits, and any local regulations.
- Niche and type of plants — Decide on the type of fruit trees or plants you will grow. Specialize in a niche market such as organic fruit, heirloom varieties, or a specific type of fruit to attract a dedicated customer base.
- Suppliers — Establish relationships with reliable suppliers for high-quality seeds, saplings, fertilizers, and other necessary materials. Ensure consistent quality and availability to maintain healthy growth.
- Storage solutions — Invest in proper storage solutions to keep your produce fresh after harvest. This includes cold storage facilities, drying areas, or packing sheds to handle your specific crop needs.
- Equipment — Purchase the necessary equipment for planting, maintaining, and harvesting your orchard. This may include tractors, plows, irrigation systems, and harvesting tools.
- Harvesting SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) — Develop efficient and effective harvesting SOPs to ensure the quality and safety of your produce. Train your staff on these procedures to maintain high standards.
- Secure buyers in advance — Establish relationships with buyers before your first harvest. This can include local markets, grocery stores, restaurants, and food processing companies. Securing buyers in advance ensures a steady demand for your produce.
- Register your business — A limited liability company (LLC) is a good legal structure for new businesses because it is fast and simple. Form your business immediately using ZenBusiness LLC formation service or hire one of the best LLC services on the market.
- Legal business aspects — Register for taxes, open a business bank account, and get an EIN .
- Processing and storage facilities — Invest in processing facilities if you plan to create value-added products like jams, juices, or dried fruits. Proper processing and storage facilities help maintain product quality and extend shelf life.
- Logistics — Plan the logistics for planting, maintaining, and harvesting your orchard. Ensure efficient transportation of your produce to buyers and markets.
- Marketing and promotion — Use a mix of online marketing, local advertising, and partnerships with local businesses to promote your orchard. Highlight your unique offerings, sustainable practices, and high-quality produce to attract customers.
Interactive Checklist at your fingertips—begin your orchard today!
You May Also Wonder:
Is an orchard profitable?
An orchard can be profitable, but it depends on various factors such as the type of fruits grown, market demand, operational costs, yield, and effective marketing strategies. However, it takes a significant amount of time for an orchard to get to the point of profitability.
What happens during a typical day at an orchard?
A typical day at an orchard involves a range of activities, including:
- Cultivation and maintenance of fruit trees, such as pruning, irrigating, and fertilizing.
- Monitoring tree health and addressing any pest or disease issues.
- Harvesting ripe fruits and sorting them based on quality standards.
- Packing and packaging fruits for distribution or sale.
- Managing inventory and storage facilities to maintain fruit freshness.
- Marketing and sales activities, such as promoting the orchard’s produce and engaging with customers.
- Managing farm operations, including administration, equipment maintenance, and staffing.
What is the growth potential of an orchard?
The growth potential of an orchard depends on factors such as market demand, expansion opportunities, the ability to diversify fruit varieties, and effective business strategies. Orchards can expand their operations by increasing acreage, introducing new fruit varieties, developing value-added products (e.g., jams, ciders), and exploring direct-to-consumer channels such as farm stands, farmers markets, or online sales.
What type of business is an orchard?
An orchard can be considered an agricultural business, specifically within the fruit production sector. It involves cultivating and harvesting fruit-bearing trees, managing the orchard’s operations, and marketing the fruits to customers. Orchards can be independent family-owned businesses, part of larger farming operations, or even cooperative ventures among multiple growers.

Step 1: Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Pros and cons.
- Provide nutrition to the community
- Peaceful lifestyle
- Multiple sales channel options
- Takes years to start making money
- High startup costs and labor
Orchard industry trends
Industry size and growth.

Orchards are part of the fruit and nut farming industry.
- Industry size and past growth – The U.S. fruit and nut farming industry is worth $22.6 billion in 2023 after declining 4.8% annually for the last five years.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/united-states/market-research-reports/fruit-nut-farming-industry/ ))
- Growth forecast – The U.S. fruit and nut farming industry is projected to decline 9.4% in 2023.
- Number of businesses – In 2023, 79,691 fruit and nut farming businesses are operating in the U.S.
- Number of people employed – In 2023, the U.S. fruit and nut farming industry employs 202,874 people.
Trends and challenges

- Orchards with dense populations of dwarf trees are becoming more prevalent.
- Robot “pickers” have been developed that can select and pick fruits at a much faster pace than humans.
- Orchards often face difficulties finding laborers to pick their harvests.
- Diseases are a continuous challenge for orchard farmers.
Demand hotspots
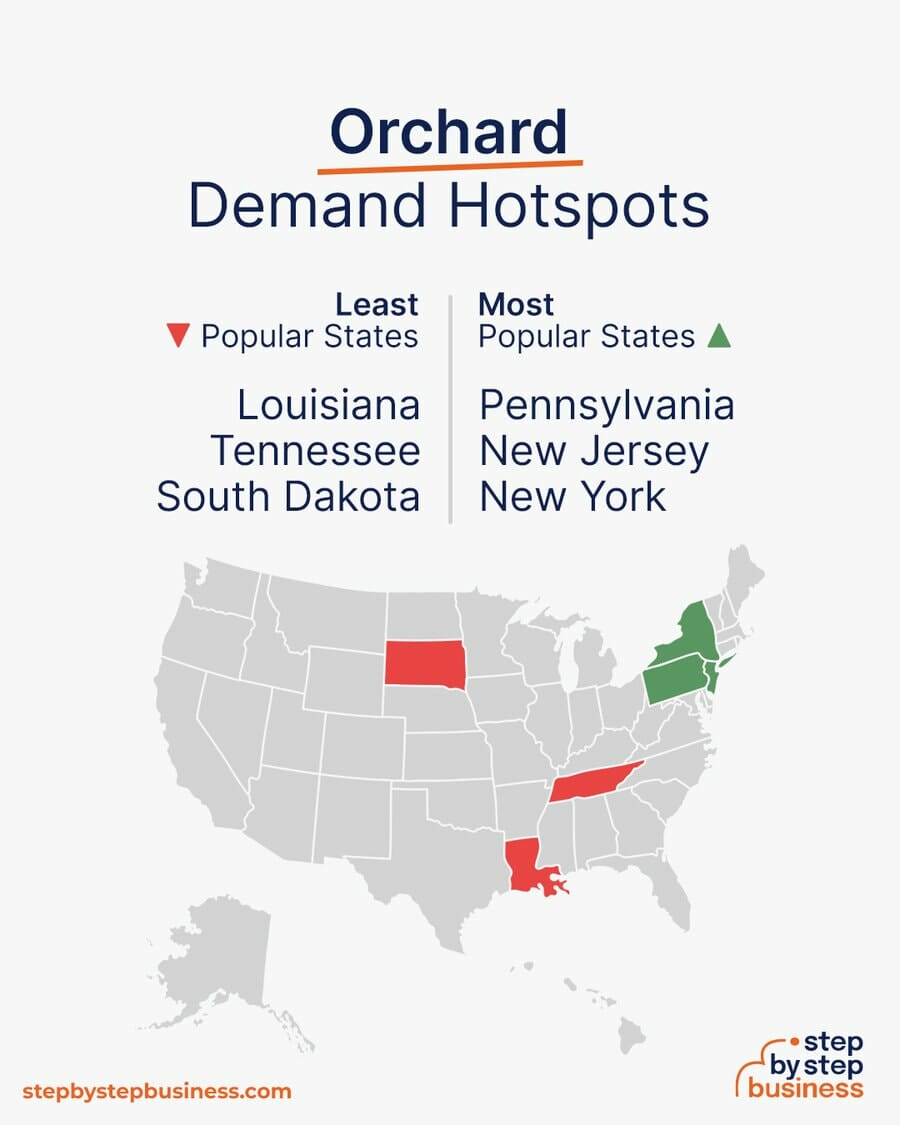
- Most popular states – The most popular states for farmers are Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York. (( https://www.zippia.com/farmer-jobs/best-states/ ))
- Least popular states – The least popular states for farmers are Louisiana, Tennessee, and South Dakota.
What kind of people work in orchards?

- Gender – 26% of farmers are female, while 74% are male. (( https://www.zippia.com/farmer-jobs/demographics/ ))
- Average level of education – The average farmer has a bachelor’s degree.
- Average age – The average farmer in the US is 47.8 years old.
How much does it cost to start an orchard business?
Startup costs for an orchard range from $100,000 to $250,000 or more. Costs include the land, farm equipment, the trees, and a labor budget for planting. Costs will vary based on the size of the orchard.
How much can you earn from an orchard business?
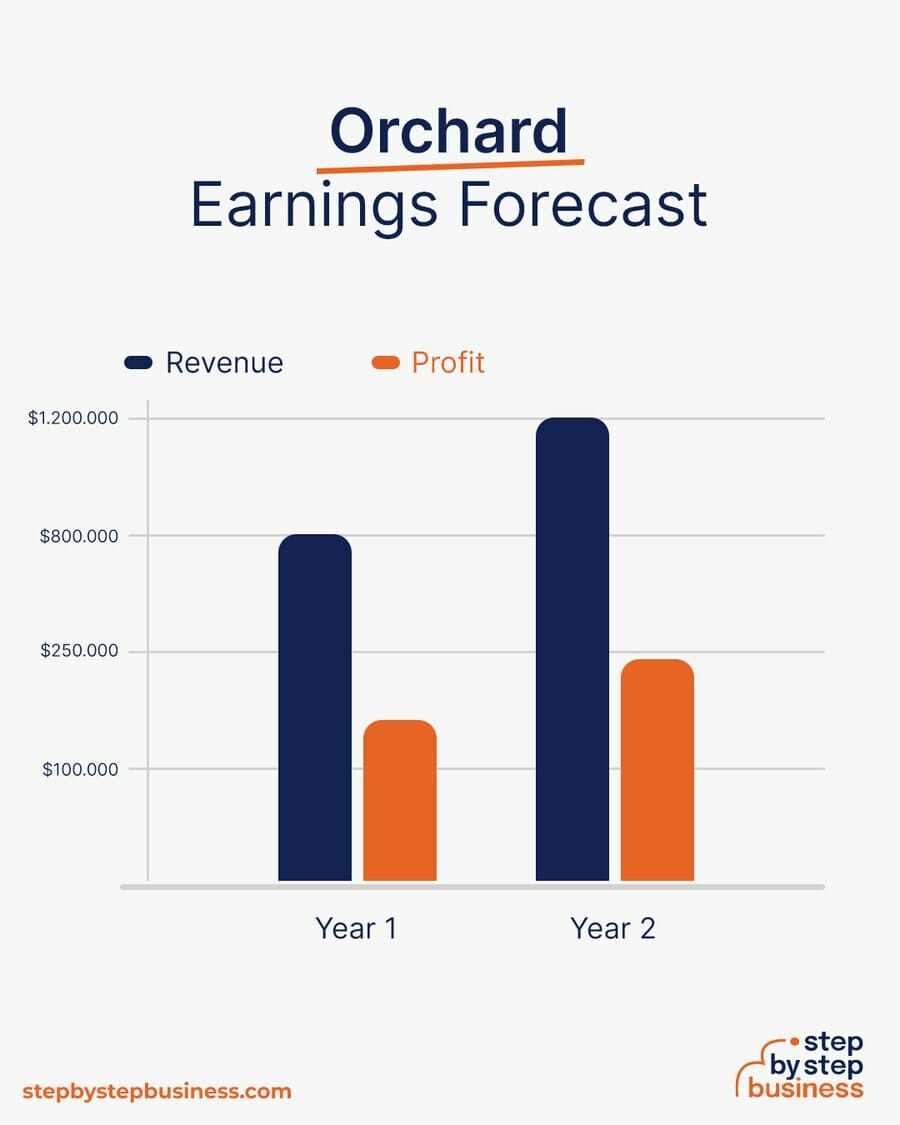
It will take several years to start making money. If you plant dwarf trees, it will take about 2 years. If you plant full size trees, they can take 7 years to mature. Your profit completely depends on the size of your orchard and how many trees you plant.
These calculations will assume that you can charge about $40 per bushel of fruit and have a profit margin after all costs of 20%.
When you start to harvest, you might produce 20,000 bushels a year, bringing in $800,000 in revenue. That would mean $160,000 in profit, assuming that 20% margin.
If you expand your orchard, you might produce 30,000 bushels per year, bringing in $1,200,000 in revenue. That would give you a nice annual profit of $240,000.
What barriers to entry are there?
There are a few barriers to entry for an orchard. Your biggest challenges will be:
- Funding the startup costs
- Finding suitable land for the orchard
Related Business Ideas

How to Open a Smoothie Shop: 13 Key Steps to Success

Squeeze Out Profits: Start a Juice Bar Business

How to Start a Farmer’s Market: Key Factors to Consider
Step 2: hone your idea.
Now that you know what’s involved in starting an orchard, it’s a good idea to hone your concept in preparation to enter a competitive market.
Market research could give you the upper hand even if you’ve got the perfect product. Conducting robust market research is crucial, as it will help you better understand your customers, your competitors, and the broader business landscape.
Plan an orchard location (land)
Choosing an orchard location requires careful consideration and planning, taking into account several important factors:
Climate : Different types of fruit trees have varying temperature and chilling requirements. Some trees, like apple and pear, need a certain number of cold, dormant hours to produce fruit. Others, like citrus, can’t withstand frost and require a warm climate. Check the USDA hardiness zones for your chosen fruit trees and ensure they’re suitable for your location.
Sun Exposure : Fruit trees generally need a lot of sun (at least 6 hours a day) to produce fruit effectively. Therefore, select a location that isn’t shaded by buildings or other trees.
Soil Quality : Fruit trees need well-drained soil to prevent root rot and other diseases. Clay or sandy soil can be improved with organic matter, but avoid planting in areas with consistently soggy soil. The soil’s pH level (how acidic or alkaline it is) can also impact tree health and fruit production, so test it and amend as necessary.
Topography : Ideally, your orchard should be on a gentle slope which helps with air and water drainage. Cold air and frost can settle in low spots, damaging trees, while hilltops can expose trees to wind.
Water Availability : Trees need regular watering, especially when they are young. Make sure your chosen location has a reliable water source for irrigation.
Wind Exposure : Wind can be harmful, particularly for young fruit trees. If your location is in a windy area, consider establishing windbreaks (rows of trees or shrubs) to protect your fruit trees.
Space Requirements : Consider the mature size of the trees when spacing them out. This allows for healthy root growth, reduces disease transmission, and allows for easier care and harvesting.
Pest and Disease Pressure : Check the history of the site. If it has a high incidence of pests or diseases, you may want to consider another site or be prepared to manage those issues.
Access : Think about how you will access the site for maintenance and harvesting. It should be relatively easy to get to with any equipment you need.
Future Growth : Plan for the future. You may want to add more trees or expand your orchard later, so consider how your chosen location will accommodate this.
Once you’ve considered these factors, you can start planning your orchard layout, taking into account pollination needs (some fruit trees need other trees for cross-pollination) and the growth habits of your chosen trees.
Consider working with a local extension service or a horticulture expert to ensure that your plans are suitable for your area and your chosen fruit trees.
Decide what types of trees you want to grow
Choosing apple tree varieties for your orchard can be an exciting process, but it also involves several considerations:
Climate Suitability: Different apple varieties thrive in different climates. Consider your USDA Hardiness Zone and the number of chill hours (hours below 45°F but above freezing) your area receives in the winter. Some apples need more chill hours to produce fruit. Also, if your area is prone to late frosts, choose varieties that bloom later to avoid losing your blossoms.
Disease Resistance: Some apple varieties are more resistant to common diseases like apple scab, fire blight, and cedar apple rust. Choosing disease-resistant varieties can save a lot of time and effort in the long run.
Pollination Requirements: Most apple varieties are not self-pollinating and will require a different apple variety to cross-pollinate. Be sure to select at least two different varieties that bloom at the same time to ensure successful pollination.
Purpose of the Fruit: Are you interested in eating fresh apples, making cider, baking, or preserving? Different apple varieties are better suited for different uses. For instance, ‘Golden Delicious’ is great for eating fresh, ‘Granny Smith’ is favored for baking, while ‘Dabinett’ and ‘Kingston Black’ are popular cider apples.
Harvest Time: Consider when you want to be harvesting your apples. By selecting early, mid, and late-season varieties, you can extend your harvest season.
Tree Size: Apple trees come in standard, semi-dwarf, and dwarf sizes. The tree size affects the amount of space you’ll need, the tree’s lifespan, and when it will start bearing fruit. Dwarf trees take up less space and bear fruit earlier, but they may not live as long as standard trees.
Taste and Texture: Of course, one of the most important factors is whether you enjoy the taste and texture of the apple. If possible, try apples of the varieties you’re considering before making your decision.
Hare some of the most common types of orchards:
- Apple Orchards : Apples are among the most widely grown fruits and are popular due to their high demand and versatility.
- Citrus Orchards : In warmer climates, citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits are common.
- Stone Fruit Orchards : These include fruits like peaches, plums, cherries, apricots, and nectarines.
- Berry Orchards : While not typically grown on trees, berries (like strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries) are often included in orchard discussions due to their similar cultivation methods.
- Nut Orchards : Nut trees like almonds, walnuts, and pecans can also be profitable.
- Pear Orchards : Like apples, there are many different varieties, and they can be used for fresh eating or in processed goods.
- Exotic/Tropical Fruit Orchards : Depending on your climate, you might consider growing more exotic fruits like avocados, mangoes, or figs.
How much should you charge for orchard products?
Your prices should be based on market prices in your area, but also on your ongoing costs like: production costs, quality and variety of products (organically grown orchards are between 10%-20% more expensive than the same items not grown organically), market rates, and volume.
If you’re selling value-added products (like jams, cider, or baked goods made with your produce), consider the cost of the additional ingredients and labor, as well as the price of similar products in your area.
If you’re selling directly to consumers (like at a farm stand or farmers’ market), you can often charge a higher price than if you’re selling wholesale.
Once you know your costs, use this Step By Step profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
Identify your target market
Unless you decide to sell your products at your own farm stand, your target market is likely to be grocery store owners or managers. You can connect with them on LinkedIn or call on them directly.
Step 3: Brainstorm an Orchard Name
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
- Short, unique, and catchy names tend to stand out
- Names that are easy to say and spell tend to do better
- Name should be relevant to your product or service offerings
- Ask around — family, friends, colleagues, social media — for suggestions
- Including keywords, such as “orchard” or “apple orchard”, boosts SEO
- Name should allow for expansion, for ex: “Harvest Haven Orchards” and “Fruitful Fields” over “Applewood Acres” and “Cherry Blossom Groves”
- A location-based name can help establish a strong connection with your local community and help with the SEO but might hinder future expansion
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead and reserve your business name with your state, start the trademark registration process, and complete your domain registration and social media account creation.
Your business name is one of the key differentiators that sets your business apart. Once you pick a name, reserve it and start with the branding, it’s hard to switch to a new name. So be sure to carefully consider your choice before moving forward.
Step 4: Create an Orchard Business Plan
Here are the key components of a business plan:
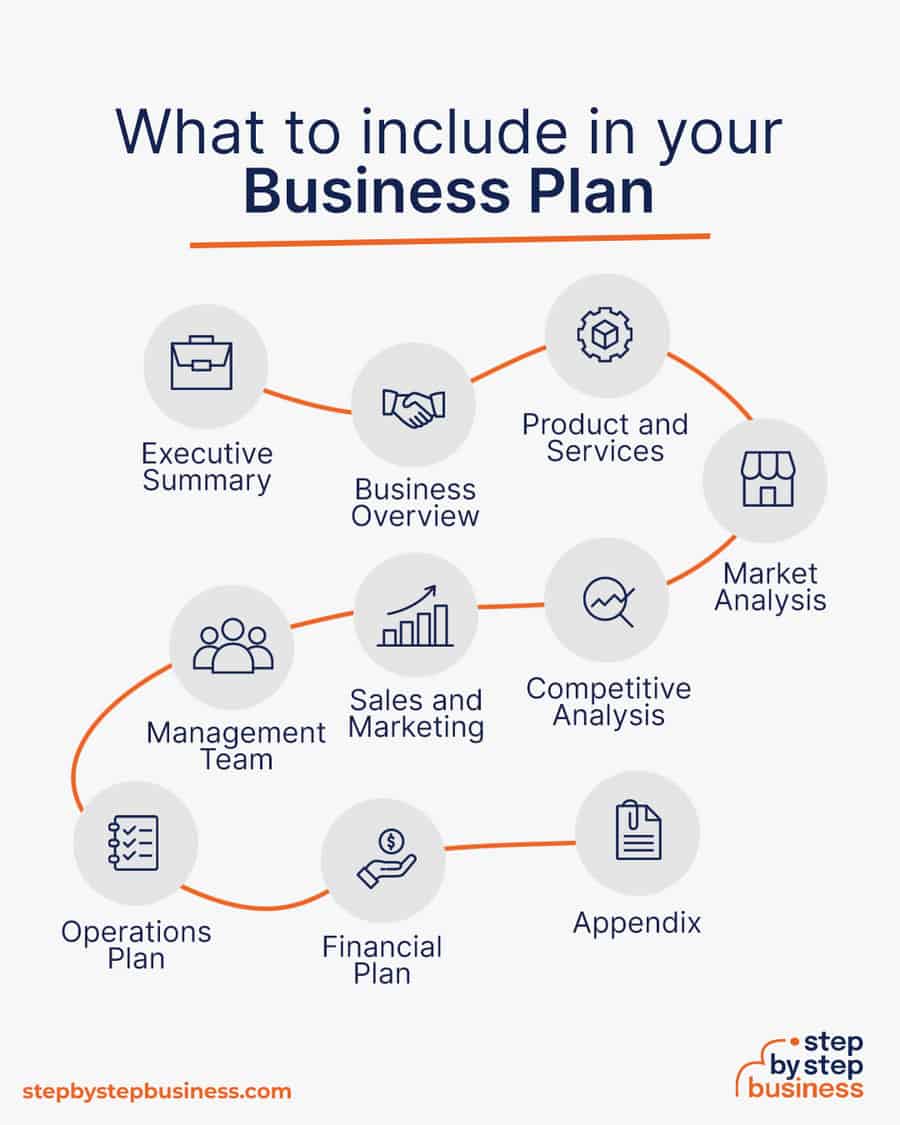
- Executive Summary: Summarize your business plan, outlining your goals, orchard’s location, and the types of fruits you plan to grow.
- Business Overview: Provide an overview of your orchard, including its size, location, and the specific varieties of fruit trees you intend to cultivate.
- Product and Services: Detail the fruits and related products or services you will offer, such as fresh fruit sales, jams, or guided orchard tours.
- Market Analysis: Analyze the demand for locally grown fruits, identify your target customer base, and consider market trends, including preferences for organic produce.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and assess other orchards and fruit suppliers in your area, highlighting what distinguishes your orchard and your competitive advantages.
- Sales and Marketing: Explain how you plan to market your orchard’s products, including branding, farm stand sales, farmers’ markets, and online presence.
- Management Team: Introduce yourself and any key team members involved in running the orchard, emphasizing their relevant experience in agriculture.
- Operations Plan: Describe the day-to-day operations of your orchard, including planting, maintenance, harvesting, and distribution logistics.
- Financial Plan: Present financial projections, including startup costs, revenue forecasts, pricing strategies, and operational expenses, to demonstrate the profitability of your business.
- Appendix: Include supporting documents such as land purchase agreements, crop yield estimates, and marketing materials to provide additional context for your business plan.
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Step 5: Register Your Business
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Choose where to register your company
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you are planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to orchards.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Choose your business structure
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your orchard will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
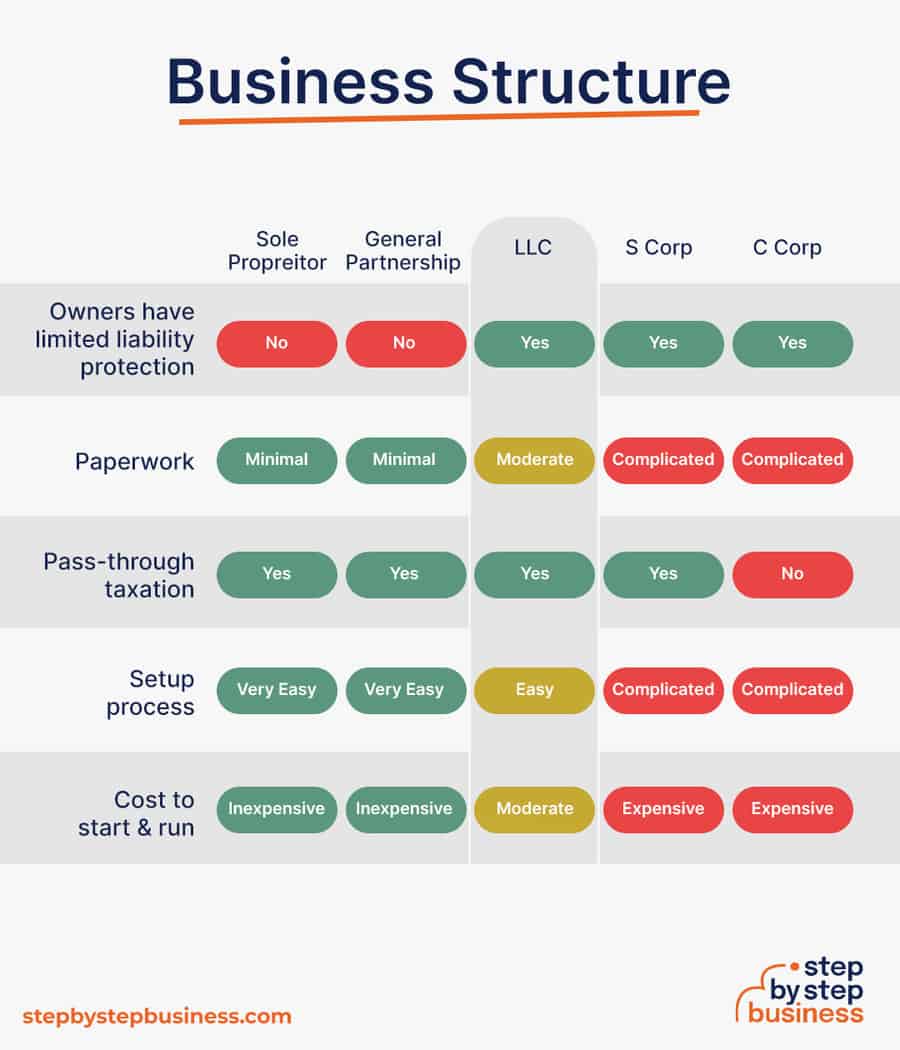
- Sole Proprietorship – The most common structure for small businesses makes no legal distinction between company and owner. All income goes to the owner, who’s also liable for any debts, losses, or liabilities incurred by the business. The owner pays taxes on business income on his or her personal tax return.
- General Partnership – Similar to a sole proprietorship, but for two or more people. Again, owners keep the profits and are liable for losses. The partners pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
- Limited Liability Company ( LLC ) – Combines the characteristics of corporations with those of sole proprietorships or partnerships. Again, the owners are not personally liable for debts. Here’s how to form an LLC .
- C Corp – Under this structure, the business is a distinct legal entity and the owner or owners are not personally liable for its debts. Owners take profits through shareholder dividends, rather than directly. The corporation pays taxes, and owners pay taxes on their dividends, which is sometimes referred to as double taxation. Read how to start a corporation here .
- S Corp – An S-Corporation refers to the tax classification of the business but is not a business entity. An S-Corp can be either a corporation or an LLC , which just need to elect to be an S-Corp for tax status. In an S-Corp, income is passed through directly to shareholders, who pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization , and answer any questions you might have.
Form Your LLC
Choose Your State
We recommend ZenBusiness as the Best LLC Service for 2024

Step 6: Register for Taxes
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number , or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist , and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you are completing them correctly.
Step 7: Fund your Business
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
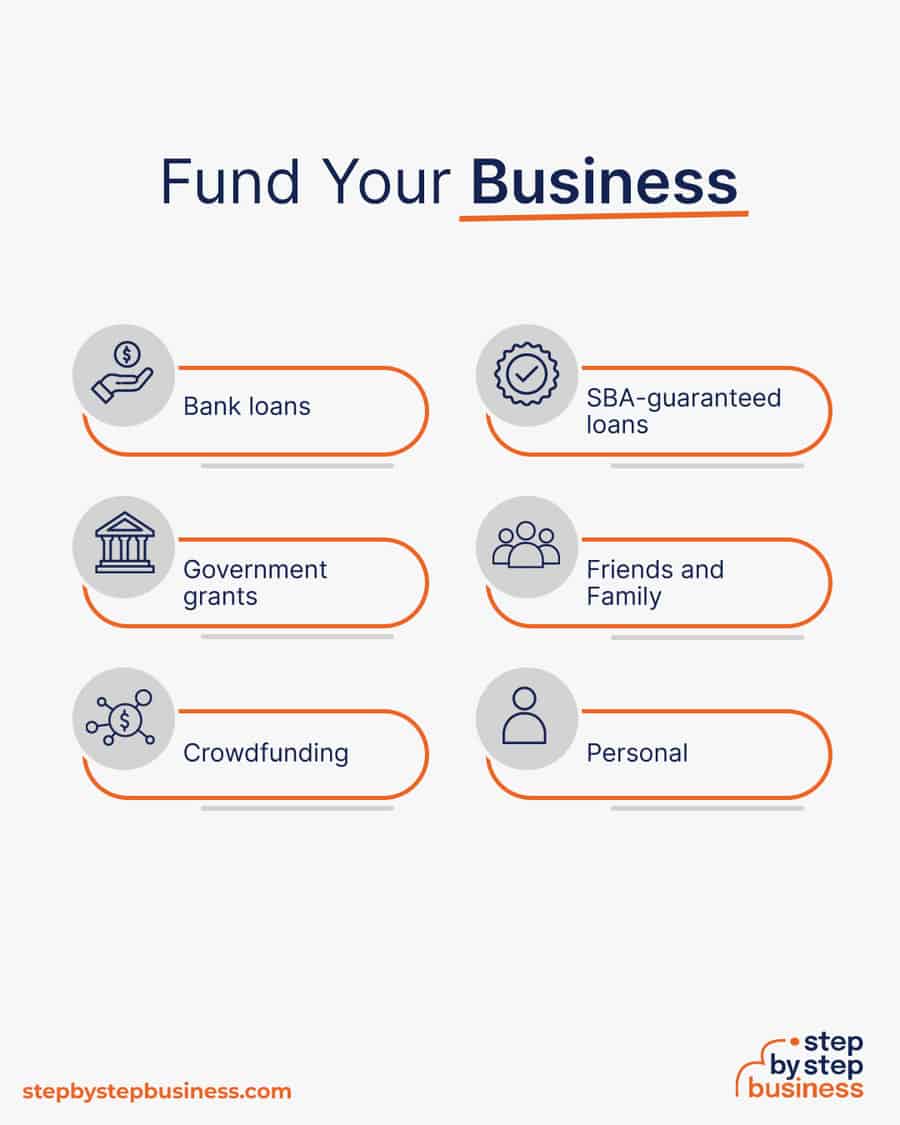
- Bank loans: This is the most common method but getting approved requires a rock-solid business plan and strong credit history.
- SBA-guaranteed loans: The Small Business Administration can act as guarantor, helping gain that elusive bank approval via an SBA-guaranteed loan .
- Government grants: A handful of financial assistance programs help fund entrepreneurs. Visit Grants.gov to learn which might work for you.
- Friends and Family: Reach out to friends and family to provide a business loan or investment in your concept. It’s a good idea to have legal advice when doing so because SEC regulations apply.
- Crowdfunding: Websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo offer an increasingly popular low-risk option, in which donors fund your vision. Entrepreneurial crowdfunding sites like Fundable and WeFunder enable multiple investors to fund your business.
- Personal: Self-fund your business via your savings or the sale of property or other assets.
Bank and SBA loans are probably the best option, other than friends and family, for funding an orchard business.
Step 8: Apply for Licenses/Permits
Starting an orchard business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
Here’s a general list of common permits and licenses that you may need:
- Pesticide Applicator License: If you will be applying any regulated pesticides to your trees, you will likely need to be certified and licensed as a pesticide applicator.
- Food Handler’s Permit: If you plan on selling your produce directly to consumers, you may need a food handler’s permit.
- Seller’s Permit : This permit allows you to collect sales tax on items sold. Requirements can vary by state.
- Health Department Permits: If you plan on selling value-added products made from your fruit, such as jams, jellies, or baked goods, you might need permits from your local health department.
- Weights and Measures Permit: If you’re selling by weight, your scales may need to be inspected and approved by your local department of weights and measures.
- Organic Certification: If you plan on selling your produce as organic, you’ll need to get your orchard certified by a USDA-accredited certifying agent.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package . They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Step 9: Open a Business Bank Account
Before you start making money, you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account .
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your orchard business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
Step 10: Get Business Insurance
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked, yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
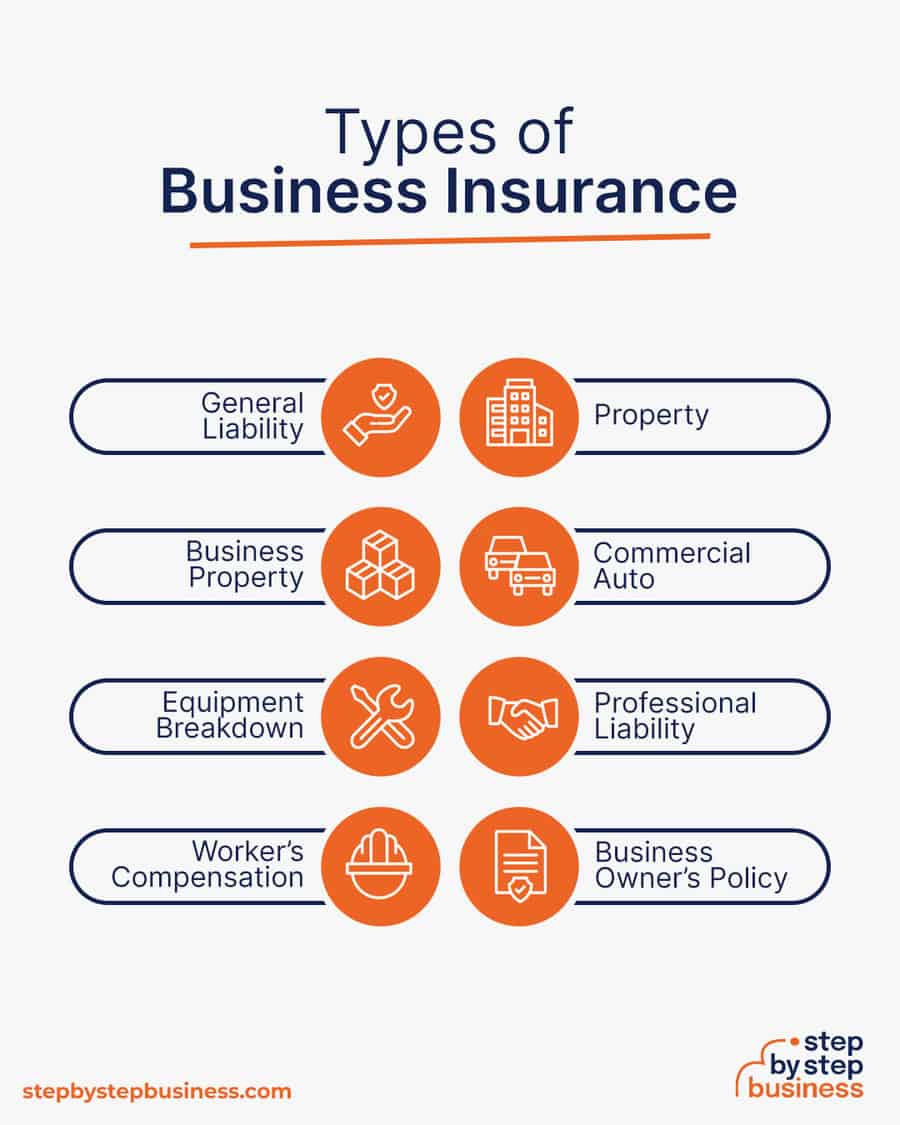
- General liability: The most comprehensive type of insurance, acting as a catch-all for many business elements that require coverage. If you get just one kind of insurance, this is it. It even protects against bodily injury and property damage.
- Business Property: Provides coverage for your equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance: Covers the cost of replacing or repairing equipment that has broken due to mechanical issues.
- Worker’s compensation: Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property: Covers your physical space, whether it is a cart, storefront, or office.
- Commercial auto: Protection for your company-owned vehicle.
- Professional liability: Protects against claims from a client who says they suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP): This is an insurance plan that acts as an all-in-one insurance policy, a combination of the above insurance types.
Step 11: Prepare to Launch
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Essential software and tools
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use industry-specific software, such as Croptracker , or eOrchard , to manage your costs, irrigation, and harvests.
- Popular web-based accounting programs for smaller businesses include Quickbooks , Freshbooks , and Xero .
- If you’re unfamiliar with basic accounting, you may want to hire a professional, especially as you begin. The consequences for filing incorrect tax documents can be harsh, so accuracy is crucial.
Create a website
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism. You can create your own website using services like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace . This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
Your customers are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization (SEO) practices. SEO will help your website appear closer to the top in relevant search results, a crucial element for increasing sales.
Make sure that you optimize calls to action on your website. Experiment with text, color, size, and position of calls to action such as “Buy Now” or “Order”. This can sharply increase purchases.
Here are some powerful marketing strategies for your future business:
- Farm-to-Table Collaborations: Partner with local restaurants, cafes, or farmers’ markets to supply them with fresh, locally grown fruits, emphasizing the farm-to-table concept and the quality of your produce.
- Educational Events: Host workshops, orchard tours, or gardening classes to engage the community, educate them about fruit cultivation, and create a connection between consumers and your orchard.
- Seasonal Promotions: Capitalize on the changing seasons by creating seasonal promotions, such as “U-Pick” events, special discounts during harvest time, or themed fruit baskets for holidays.
- Community Sponsorship: Sponsor local events, sports teams, or community gatherings to increase your orchard’s visibility and build a positive association with your brand among locals.
- Social Media Challenges: Launch social media challenges, like recipe contests or photo competitions featuring your orchard’s fruits, encouraging followers to share their creations and experiences.
- Subscription Boxes: Offer subscription boxes that deliver a variety of fresh fruits directly to customers’ doors, providing a convenient and consistent supply while fostering customer loyalty.
- Mobile Market Stalls: Take your orchard on the road by setting up mobile market stalls at high-traffic locations, giving people a taste of your produce without them having to visit the orchard.
- Collaborate with Influencers: Partner with local influencers or food bloggers to create engaging content showcasing your orchard, reaching a broader audience and leveraging their followers’ trust.
- Community Engagement: Actively engage with your local community through participation in local fairs, parades, or charity events, fostering a sense of community support and loyalty.
- Environmental Sustainability: Highlight your orchard’s commitment to environmentally friendly practices, such as organic farming or sustainable packaging, appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Focus on USPs

Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that sets it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your orchard meets their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Signature USPs for your orchard business could be:
- Experience the juiciest and most flavorful fruits straight from our orchard
- Discover a wide variety of hand-picked fruits grown in our lush orchard
- Enjoy responsibly cultivated fruits nurtured with eco-friendly practices
You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running an orchard business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been working in orchards for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in orchards. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership.
Step 12: Build Your Team
You will need workers to fill various roles. Potential positions for an orchard business include:
- Laborers – care for trees, harvest fruits
- Salesperson – sell fruits to grocery stores
- General Manager – inventory management, accounting
At some point, you may need to hire all of these positions or simply a few, depending on the size and needs of your business. You might also hire multiple workers for a single role or a single worker for multiple roles, again depending on need.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed , Glassdoor , or ZipRecruiter . Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Step 13: Run an Orchard – Start Making Money!
Orchards take time to mature, but once they do, they can be quite profitable. It takes an investment and time to get started, but owning an orchard can be very rewarding. By starting an orchard, you’ll be providing nutritious treats to your community, living the farm lifestyle, and eventually making good money.
Now that you understand the business, you’re ready to start planting and watch your orchard grow into profits!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Decide if the Business Is Right for You
- Hone Your Idea
- Brainstorm an Orchard Name
- Create an Orchard Business Plan
- Register Your Business
- Register for Taxes
- Fund your Business
- Apply for Licenses/Permits
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get Business Insurance
- Prepare to Launch
- Build Your Team
- Run an Orchard - Start Making Money!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.

19 Profitable Farming and Agriculture Ventures
David Lepeska
Published on November 4, 2022
Many young people today think it’s not cool to go into agriculture so they shy away from anything related to farms. Well, they’re missing a lot. ...

49 Small Business Ideas For Rural Areas
Published on July 13, 2022
Rural businesses typically provide value and economic strength to the community and generate income for the owner. If you live in a rural area, then ...
16 Food Truck Business Ideas and Themes
Natalie Fell
Published on June 8, 2022
Food trucks have exploded in popularity in recent years and offer a unique, potentially lucrative alternative to brick-and-mortar restaurants. Foodt ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

How to Start a Fruit Orchard: Comprehensive Steps
Main Sections In This Post Steps To Starting A Fruit Orchard Points to Consider Knowledge Is Power Featured Video
This post offers a clear roadmap for launching a fruit orchard, including a detailed step-by-step guide and an overview of anticipated outcomes. Numerous illustrative examples and templates are provided as initial references.
The links to our “Knowledge Is Power” section ensure access to up-to-date and trending information. These resources are valuable for the initial startup phase and ongoing operations once the business is set up.
Given the comprehensive nature of the content, consider sharing and bookmarking the post for future reference.
Let’s get started with the steps.
The Steps to Take To Start Your Fruit Orchard
Below are the steps to starting a fruit orchard.
Each step is linked to a specific section, allowing you to jump to your desired section or scroll to follow the steps in order.
- An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
- Fruit Orchard Overview
- Researching Your Fruit Orchard
- Looking at Financials
- Choosing A Business Location
- Creating Your Mission Statement
- Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Choose a Fruit Orchard Name
- Register Your Company
- Create Your Corporate Identity
- Writing a Business Plan
- Banking Considerations
- Getting the Funds for Your Operation
- Software Setup
- Business Insurance Considerations
- Supplier and Service Provider Considerations
- Setting Your Prices
- Physical Setup
- Creating a Website
- Create an External Support Team
- Hiring Employees
1. An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
The Power of Passion in Business
The ability to work in a field where you’re doing what you love is a blessing. Passion is crucial for your business success and the driving force you need.
Passion Fuels Problem-Solving
When you’re passionate about your business and problems arise, you look for solutions. On the other hand, without passion, you’ll look for a way out when you see problems coming your way.
Impact of Passion in Orcharding
The amount of passion you have for owning and operating a fruit orchard will greatly influence your success.
Considering Financial Freedom
Here is something important to think about:
Suppose you don’t have to worry about money because you have enough to live comfortably for the rest of your life.
The Ultimate Question
Now, the big question:
With no worries about money, would you start a fruit orchard and run it for free?
Passion as a Guide
If your answer is yes, it shows that you are passionate about owning and operating a fruit orchard and are heading in the right direction.
Exploring Alternatives
However, if your answer is no, it prompts another question:
What would you prefer to do instead? Perhaps you should pursue that path rather than start a fruit orchard.
Key to Success
In summary, you need to be passionate about owning and operating your business to give you a better chance of success.
For More, See How Passion Affects Your Business . Also, see Considerations Before You Start Your Business to identify key points for a new business owner.
2. Gaining an Overview of Owning a Fruit Orchard
Next, let’s spend some time on key issues to give you an overview of what to expect from owning and running your business.
a.) A Quick Overview of Owning a Fruit Orchard
A fruit orchard is an agricultural establishment that cultivates fruit-bearing trees and plants.
Orchards are meticulously planned spaces where fruits, such as apples, pears, peaches, cherries, and citrus fruits, are grown in organized rows or sections.
These orchards are carefully managed to ensure optimal growth, yield, and fruit quality.
Managing a Fruit Orchard: Daily Operations
Running and managing a fruit orchard involves a series of essential day-to-day tasks to ensure healthy growth and successful harvests.
These tasks can vary depending on the specific type of fruit and regional conditions, but generally include:
1. Pruning and Trimming: Regularly trimming and pruning trees is vital for maintaining their shape, controlling growth, and promoting better sunlight exposure and airflow.
2. Irrigation: Providing adequate water to trees is crucial, especially during critical growth phases and dry periods, to prevent water stress and promote fruit development.
3. Pest and Disease Management: Monitoring for pests and diseases and implementing appropriate control measures is essential to protect the orchard’s health and fruit quality.
4. Fertilization: The right nutrients at the right times ensure healthy tree growth and optimal fruit production.
5. Pollination: For certain fruit varieties, ensuring proper pollination is necessary for fruit set. This may involve maintaining beehives or other pollination methods.
6. Thinning: Thinning excess fruit from the trees helps improve the remaining fruits’ size, quality, and overall yield.
7. Harvesting: Timing the harvest correctly is crucial to ensure fruits are picked at their peak ripeness. This task requires careful observation and coordination.
8. Post-Harvest Handling: Sorting, packing, and storing harvested fruits appropriately is essential for maintaining their freshness and extending their shelf life.
9. Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of tasks, treatments, and results helps track the orchard’s performance and aids in future planning.
10. Seasonal Planning: Orchards require ongoing seasonal planning to coordinate activities like pruning, planting new trees, and preparing for winter.
Successful fruit orchard management requires horticultural knowledge, attention to detail, and adaptability to changing conditions.
By consistently tending to these day-to-day tasks, orchard managers can ensure the health and productivity of their fruit-bearing trees and the quality of the harvests they yield.
b.) Fruit Orchard Models
Diverse Types of Fruit Orchard Setups and Business Models
Fruit orchards come in various setups, each with distinct business models catering to different goals and market demands. Here are a few notable types:
1. Traditional Commercial Orchards:
These orchards cultivate various fruits for mass production.
They often supply local markets, grocery stores, and processing industries.
The business model involves high volume and consistent supply.
2. Pick-Your-Own Orchards:
These setups invite customers to pick their own fruits directly from the orchard. It offers a unique experience and direct connection with consumers.
Revenue is generated through entry fees and the sale of harvested fruits.
3. Organic and Specialty Orchards:
Organic orchards prioritize sustainable and chemical-free practices, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Specialty orchards might focus on unique or heirloom fruit varieties, commanding premium prices.
4. Agro-Tourism Orchards:
Combining orchard operations with tourism, these setups offer guided tours, educational activities, and recreational experiences.
The business model diversifies income through entrance fees, product sales, and tourism-related services.
5. Value-Added Processing Orchards:
These orchards produce products like jams, jellies, juices, and dried fruits using their harvest.
Value is added to the produce, allowing for higher profit margins and extended shelf life.
Choosing the Right Business Model
Selecting the appropriate business model from the outset is pivotal. Changing your model later can be complex.
Your decision will be assessed by Assessing your resources, location, target audience, and personal preferences.
Identifying Profitable Niches
To thrive, pinpoint a profitable and high-demand niche: research consumer preferences, market trends, and gaps in the market.
This could involve focusing on organic produce, catering to specific cultural preferences, or targeting health-conscious consumers.
In conclusion, the world of fruit orchards offers diverse setups and business models.
Understanding these options, their pros and cons, and aligning them with your vision will set the course for your orchard’s success.
Choose wisely, as altering your model later presents challenges.
Moreover, identifying a niche that’s both lucrative and in demand is fundamental to ensuring your fruit orchard’s growth and profitability.
c.) Pros and Cons of Owning a Fruit Orchard
Owning and operating a business offers both advantages and drawbacks. While the benefits are appealing, many entrepreneurs overlook the challenges.
It’s essential to acknowledge these potential issues to be prepared.
By anticipating and understanding possible problems, you can proactively plan and avoid surprises in your business journey.
For more, see Pros and Cons of Starting a Small Business.
d.) Challenges You Could Face When Starting and Operating a Fruit Orchard
Challenges When Starting a Fruit Orchard
Starting a fruit orchard comes with its share of challenges that aspiring orchardists should be aware of:
1. Site Selection: Choosing the right location with suitable soil, climate, and water availability is crucial for the orchard’s success.
2. Investment and Resources: Establishing an orchard requires significant upfront investment for land, trees, equipment, and infrastructure.
3. Tree Establishment: Proper planting and early care are vital for healthy tree establishment, which impacts future yields.
4. Pest and Disease Management: Orchards are susceptible to various pests and diseases that can harm trees and reduce yields.
5. Time to First Harvest: Fruit trees take several years to mature and produce a significant harvest, requiring patience and ongoing care.
6. Market Research: Understanding consumer preferences and market demand is essential to ensure profitable fruit sales.
7. Labor and Skill: Orchards demand consistent labor for tasks like pruning, thinning, and harvesting. Skilled labor is essential for effective orchard management.
Challenges During Full Orchard Operation
Once a fruit orchard is operational, new challenges arise:
1. Weather Variability: Unpredictable weather patterns can impact flowering, pollination, and fruit quality.
2. Crop Load Management: Ensuring proper fruit set, size, and quality requires effective thinning and management techniques.
3. Market Fluctuations: Prices and demand for fruits can fluctuate due to market conditions, impacting revenue.
4. Labor Management: Orchards demand seasonal labor for various tasks, requiring efficient workforce coordination.
5. Pest and Disease Control: Continuously monitoring and managing pests and diseases is crucial to maintaining tree health and yield.
6. Post-Harvest Handling: Proper handling, sorting, and storing harvested fruits are essential to prevent losses and maintain quality.
7. Sustainability: Orchards must adopt sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact and resource depletion.
8. Competition: Competing with other orchards and fruit suppliers requires consistent quality and differentiation.
9. Regulations: Navigating agricultural regulations, permits, and certifications can be complex.
10. Succession Planning: Orchards need plans for the next generation to ensure continued operation.
Managing a fruit orchard demands continuous effort, adaptability, and a strategic approach to overcome challenges and ensure long-term success.
e.) Questions You Need to Consider for Your Fruit Orchard
Questions to Consider for Your Fruit Orchard
In preparation for potential challenges when starting a fruit orchard, addressing these key questions is crucial:
- What type of fruit orchard model are you considering?
- Do you have the skills needed to manage and operate a fruit orchard?
- Will you do all the work alone, or will you hire employees?
- Do you intend to manage your business, or are you planning to hire a manager?
- How will you get customers?
- How will you keep customers coming back?
- Are you interested in finding partners or investors?
- How will you finance your startup costs?
- Have you considered how long it will take to become profitable?
- How will you support yourself during the early stage of operation, which can be financially challenging?
- What products and services will you offer?
- How do you know people will want what you have to offer?
- What will you provide that sets you apart from your competition?
Addressing these questions before starting your fruit orchard, you’ll be better equipped to navigate potential obstacles and make informed decisions for a successful orchard venture.
3. Research
Inside information fruit orchard research.
Essential Research Before Starting Your Fruit Orchard
Before embarking on any actions, thorough research is imperative when starting a fruit orchard.
Quality information offers insights into what to expect, preventing unexpected situations.
Engage with Experienced Orchardists
Engaging with experienced orchardists is valuable for obtaining reliable information and insights. Their expertise is invaluable, offering insights gained from years of experience.
Guidance on Finding the Right People
While finding such individuals is beyond this post, an article guides connecting with the right people and approaching them effectively.
Invaluable Insights Await
Their expertise is invaluable, offering insights gained from years of experience.
Read “An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start”
Reading “An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start” via the provided link is strongly recommended.
This resource equips you with the knowledge to understand the journey ahead and make informed decisions.
See An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start for all the details.
Target Audience
Understanding Your Target Audience:
Understanding your target audience offers several advantages.
The more you know about your market, the better you can tailor your products, services, and offers to meet their needs.
This enables you to concentrate on providing items your customers are genuinely interested in rather than attempting to offer an extensive array of options.
Target Market Ideas:
- Health-conscious individuals seeking fresh and organic produce.
- Local farmers’ markets, grocery stores, and restaurants looking for reliable fruit suppliers.
- Families and individuals interested in pick-your-own fruit experiences.
- Small-scale food processors looking for high-quality ingredients.
- Consumers seeking unique or heirloom fruit varieties.
- Eco-conscious buyers supporting sustainable farming practices.
- Agro-tourists seeking farm experiences and educational activities.
- Health and wellness businesses in need of natural ingredients for products.
- Individuals looking to support local agriculture and promote community.
- Culinary enthusiasts and bakers requiring premium fruit for recipes.
For more, see How To Understand Your Target Market.
Product & Service Demand
Strategies to Assess Market Demand:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Conduct surveys in the target area to gauge interest in locally grown fruits and preferences.
- Competitor Analysis: Study existing orchards and their popularity to understand the market’s saturation and potential gaps.
- Local Events and Farmers’ Markets: Attend community and farmers’ markets to engage with potential customers and gather feedback.
- Online Search Trends: Use tools to analyze online search trends related to fruit orchards and fresh produce in the intended location.
- Social Media Engagement: Monitor discussions about local produce and orchards to gauge interest.
- Talk to Local Businesses: Speak with restaurants, markets, and food processors to understand their demand for fresh fruits.
- Pilot Programs: Consider starting with a small-scale pilot program to test the market response.
- Community Meetings: Attend local meetings to understand community interests and needs.
- Collaborate with Agricultural Agencies: Seek insights from agricultural agencies or cooperative extensions about local market trends.
- Seasonal Popularity: Observe the demand for fresh fruits during peak seasons and holidays.
- Lease a Plot with a Mature Orchard: Before investing in your orchard, try leasing a plot of land with a mature orchard for one season.
- This experience provides hands-on insight into operational challenges and potential market response.
By employing these strategies, including leasing a mature orchard plot for a season, you can gain comprehensive insights into the potential demand for your fruit orchard’s offerings in the desired location.
For more, see the Demand for Your Products and Services.
4. Looking at Financials:
Understanding Financial Aspects of Your Fruit Orchard
This section offers insights into vital financial considerations encompassing startup costs, monthly expenses, revenues, and profits for your fruit orchard.
Startup Costs:
Estimating startup costs accurately is essential for a successful launch, ensuring a smooth journey from planning to opening.
Underestimation might lead to inadequate funds, hindering your business launch, while overestimation could appear risky.
Costs hinge on operation size, location, hiring, equipment choices (new or used), and renting versus leasing.
List all necessary items and gather prices, incorporating emerging issues during research.
For more detailed information, refer to my article on Estimating Startup Costs.
Sales and Profit:
Sales are influenced by factors such as customer service, product popularity, demand, and effective marketing to your target audience. For profitability, consider:
- Profit per Sale: Analyze your profit margin per sale.
- Sales Volume: Evaluate your potential sales volume.
- Overhead: Calculate your monthly expenses.
Understanding Profitability:
To illustrate, if you make a $500 profit per sale but have only one monthly sale, it won’t cover expenses.
Conversely, high-volume sales with low-profit margins may also fall short.
To assess your orchard’s profitability, analyze profit per sale, projected sales volume, and overhead costs.
For More, See Estimating Profitability and Revenue.
Gaining insight into these financial aspects equips you with a comprehensive understanding of the financial landscape for your fruit orchard.
Simple Sample: Financial Lists to Consider As a Starting Point
Note: Focus on the list items more than the numbers. The numbers are samples. Your estimates will differ due to how you set up your business, location, expenses, and revenues.
Sample Estimated Startup Costs for a New Fruit Orchard in the USA:
- Land Purchase or Lease: $50,000 – $150,000
- Trees and Planting: $10,000 – $30,000
- Irrigation System: $5,000 – $15,000
- Equipment (Tractors, Tools): $20,000 – $50,000
- Infrastructure (Sheds, Fencing): $10,000 – $20,000
- Initial Marketing and Branding: $5,000 – $10,000
- Professional Services (Legal, Consulting): $3,000 – $8,000
- Permits and Licenses: $2,000 – $5,000
- Initial Inventory (Fertilizers, Pesticides): $2,000 – $5,000
- Contingency Fund: $5,000 – $10,000 Total Startup Costs Range: $112,000 – $293,000
Sample Estimated Monthly Expenses for a Fruit Orchard in the USA:
- Land Lease/Rent: $1,000 – $3,000
- Labor (Employees or Contractors): $3,000 – $7,000
- Utilities (Water, Electricity): $500 – $1,500
- Equipment Maintenance: $300 – $800
- Supplies (Fertilizers, Pesticides): $300 – $800
- Insurance: $200 – $500
- Loan Payments (Equipment, Land): $1,000 – $2,500
- Marketing and Advertising: $300 – $1,000
- Miscellaneous (Repairs, Contingency): $500 – $1,000 Total Monthly Expenses Range: $7,100 – $18,100
Sample Examples of Profit per Sale:
- Sale of 10 Apple Baskets at $15 each: Total Revenue = $150, Profit = $100 (after deducting production costs).
- Sale of 50 Gallons of Fresh Apple Cider at $5 per Gallon: Total Revenue = $250, Profit = $125.
- Pick-Your-Own Entry Fee for 50 Visitors at $10 each: Total Revenue = $500, Profit = $450 (after considering operational costs).
- Sale of 100 Jars of Homemade Fruit Jam at $8 each: Total Revenue = $800, Profit = $550.
- Sale of 20 Fruit Trees at $50 each: Total Revenue = $1,000, Profit = $600.
Note: These sample figures are illustrative and can vary based on location, market conditions, and business practices.
Consider revisiting Step 3. Researching your fruit orchard , where there is a technique to get inside information, will benefit you in this step.

5. Choosing The Right Business Location
Choosing the Right Location for Fruit Orchards: Balancing Factors
For fruit orchards, location holds paramount importance, encompassing various critical factors.
Success or failure pivots on your chosen locale, impacted by demand, competition, affordability, and climate.
Demand and competition must harmonize – excessive competitors hinder progress, while insufficient demand spells failure.
Affordability is crucial; populous areas promise exposure but must not incur costs surpassing profits. Conversely, cheaper locations need adequate customer potential for sustainability.
Climate is pivotal; a fruit orchard thrives in a climate conducive to fruit growth and yield. Ideal conditions – sunlight, temperature, and precipitation – optimize harvests.
In summation, the right location is pivotal for fruit orchards.
Thorough research and analysis, considering demand, competition, affordability, and climate, ensure an informed decision steering your orchard toward prosperity.
For more about business locations, see Choosing The Best Location for Your Business.
6. Create Your Mission Statement
The Significance of a Mission Statement in Defining Your Business:
A mission statement serves as a compass, defining your business’s purpose.
It keeps you focused, reminding you of the primary value you offer to customers and the community.
By articulating your mission, you establish a clear direction for your business, aiding in decision-making and guiding your efforts toward achieving your goals.
Examples of Mission Statements for a Fruit Orchard:
- “Nurturing Nature’s Bounty: We are committed to cultivating premium, organic fruits while fostering sustainable farming practices that nourish both our customers and the environment.”
- “Harvesting Joy, One Bite at a Time: Our mission is to provide families with memorable experiences by offering pick-your-own fruit opportunities, promoting health, community engagement, and a love for nature.”
- “Preserving Heritage, Cultivating Health: Dedicated to preserving heirloom fruit varieties and promoting wellness, we strive to offer locally grown, nutrient-rich fruits that reconnect consumers with traditional flavors and a healthier lifestyle.”
- “Rooted in Quality and Sustainability: Our mission is to deliver the freshest, highest-quality fruits to our community while upholding ethical farming practices that support the land and future generations.”
- “Delighting Senses, Enriching Lives: With a commitment to exceptional taste and nutritional value, our fruit orchard endeavors to enhance the lives of our patrons by providing an array of delectable, homegrown fruit options.”
For more, see How To Create a Mission Statement.
7. Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Harnessing Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) for Distinctiveness:
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) empowers you to pinpoint and craft a distinctive element for your business.
It aids in differentiating your offering from competitors and highlights what makes your venture special.
By identifying a USP, you create a memorable aspect that resonates with customers, setting you apart in the market and fostering customer loyalty.
Examples of USPs for a Fruit Orchard:
- “Farm-to-Table Freshness”: Our orchard’s USP is our commitment to delivering hand-picked, farm-fresh fruits directly to customers, ensuring the ultimate in taste, quality, and nutrition .
- “Heritage Harvests”: Our USP revolves around reviving rare and heirloom fruit varieties, offering a unique array of flavors and fostering a connection with the past.
- “Sustainable Orchard Experience”: Our orchard’s USP is our dedication to sustainable practices, allowing customers to enjoy organic fruits while contributing to environmental well-being.
- “Family-Friendly Farm Fun”: Our USP focuses on providing an enjoyable, family-centric experience through pick-your-own fruit activities, making lasting memories in our orchard.
- “Educational Orchard Journeys”: Our USP centers on offering guided tours and workshops, immersing visitors in fruit cultivation, and enhancing their understanding of the process.
8. Choose a Business Name
Selecting a Catchy and Appropriate Business Name:
Choosing a business name demands thoughtfulness, aiming for a memorable and fitting title within your industry.
Opt for a name that’s easy to pronounce and recall.
Given that business names tend to remain constant, avoid hasty decisions.
Your chosen name will likely stay with you throughout your business journey.
Moreover, securing a matching domain name for your online presence is crucial. Ensure the desired name is unclaimed by other businesses.
Here Is a List of Sample Fruit Orchard Names:
- Orchard Delights
- Blossom Acres Orchard
- FreshHarvest Fruits
- SunKissed Orchards
- Nature’s Bounty Farm
- Juicy Grove Orchard
- Orchard Oasis
- Fruitful Haven
- Golden Harvest Orchards
- GreenLeaf Gardens
- Harvest Haven Orchards
- SweetNectar Farms
- Orchard Elegance
- Serene Fruit Fields
- Blissful Orchard Retreat
- Fruitful Serenity Farms
- Majestic Orchard Views
- Orchard Tranquility
- Fruity Essence Orchards
- Harvest Horizon Gardens
- Orchard Oasis Haven
- Enchanted Fruitland
- Sunny Orchard Meadows
- Orchard Rhapsody
- Eden’s Orchard
- Whispering Breeze Fruits
- Orchard Charm Acres
- Radiant Harvest Gardens
- Orchard Whispers
- Vibrant Orchard Dreams
This compilation can stimulate creativity and inspire an original name that resonates with your fruit orchard’s essence.
For more, see the following articles:
- How To Register a Business Name
- Registering a Domain Name For Your Business
9. Register Your Company
Ensuring Legal Compliance for Your Business:
Legal compliance is paramount when establishing a business.
Seek professional guidance to ensure your business adheres to legal requirements, achieving an optimal setup for tax advantages and liability protection.
Consulting experts streamline the process and mitigate potential pitfalls.
Common Types of Registrations for a Fruit Orchard:
- Business Structure Registration: Choose from sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation, registering as per your chosen structure.
- Fictitious Business Name (DBA): If operating under a name other than your legal name, registering a DBA is necessary.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Obtain an EIN from the IRS for tax purposes.
Permits and Licenses for a Fruit Orchard:
- Agricultural Permits: Often required due to the nature of farming operations.
- Zoning and Land Use Permits: Verify land usage compliance with local zoning regulations.
- Environmental Permits: Adhering to environmental regulations for irrigation and potential chemical use.
- Health and Safety Permits: If selling food products, meet health and safety standards.
- Business License: A general requirement for operating any business.
- Sales Tax Permit: For collecting and remitting sales tax.
- Pesticide and Chemical Application License: If using chemicals, adhere to regulations.
Consulting professionals and obtaining necessary permits and licenses ensure your fruit orchard’s legality, avoiding potential legal issues and enabling smooth operations.
Registration:
- How to Register Your Business
- How To Register a DBA
- How to Register a Trademark
- How to Get a Business License
Business Structures:
- How to Choose a Business Structure
- Pros & Cons of a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Form an LLC
- How To Register a Business Partnership
- How To Form a Corporation
- How To Choose a Business Registration Service
10. Create Your Corporate Identity
Crafting a Strong Corporate Identity:
A Corporate ID encompasses a design that embodies your business.
It comprises your logo, business cards, website, signage, stationery, and promotional materials.
A consistent, professional design establishes a lasting impression on new and existing customers, reinforcing your brand’s credibility and appeal.
You can see our page for an overview of your logo , business cards , website , and business sign , or see A Complete Introduction to Corporate Identity Packages.
11. Writing a Business Plan
The Crucial Role of a Business Plan:
A business plan is an indispensable document used for financing and attracting investors.
It serves as a guide during startup and ongoing operations, ensuring focus and strategic alignment.
Creating a Detailed and Effective Business Plan:
Drafting a business plan demands time and effort as it outlines your business’s future vision.
Thoughtful planning and expression of details are essential, offering a clear roadmap for launch and operation.
Diverse Approaches for Business Plan Creation:
Various options exist for crafting your business plan – from scratch, hiring professionals, utilizing templates, or employing business plan software.
Active involvement in the process, especially when hiring experts, ensures effective communication of your business’s nature and management strategies.
Flexibility and Adaptability:
Business plans can evolve with experience, operational changes, or market shifts.
Regular review and optimization allow for necessary adjustments, ensuring alignment with evolving goals and circumstances.
A well-crafted business plan sets the foundation for a successful venture, offering clarity and adaptability as your business journey unfolds.
Business Plan Template for a Fruit Orchard
Executive Summary:
- Overview of your fruit orchard’s mission, vision, and goals.
- Brief description of products, services, and unique selling proposition (USP).
- Summary of market analysis, target audience, and competitive landscape.
- Financial highlights and funding requirements.
Company Description:
- Detailed explanation of your fruit orchard’s concept and vision.
- Description of your orchard’s location, size, and facilities.
- Explanation of your mission, values, and commitment to sustainability.
- Overview of business structure, ownership, and key personnel.
Market Analysis:
- Comprehensive research on the fruit industry, local market trends, and consumer preferences.
- Identification of your target market, including demographics and psychographics.
- Analysis of competitors, highlighting strengths and weaknesses.
Products and Services:
- Detailed description of the types of fruits you will grow and sell.
- Explanation of any unique or specialty products or services.
- Outline of your quality standards, organic practices, and production methods.
Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Explanation of your branding, logo, and corporate identity.
- Description of marketing channels, such as farmers’ markets, local stores, and online platforms.
- Strategies for customer acquisition, retention, and engagement.
- Marketing budget allocation and tactics for reaching your target audience.
Operational Plan:
- Overview of daily operations, including planting, harvesting, and maintenance routines.
- Explanation of equipment and technology used for cultivation.
- Details about labor requirements, including hiring and training practices.
- Description of your orchard’s management structure and responsibilities.
Financial Plan:
- Detailed startup costs, including land purchase/lease, equipment, and infrastructure.
- Projections for monthly and annual revenue based on sales estimates.
- Breakdown of operational expenses, including labor, utilities, and supplies.
- Cash flow projections, profit and loss statement, and balance sheet.
Funding and Financing:
- Explanation of your funding needs and how you plan to secure financing.
- Overview of personal investment, loans, grants, or investor partnerships.
- Detailed repayment plans for any borrowed funds.
- Supporting documents such as market research data, permits, licenses, and legal documents.
- Resumes of key team members, highlighting their expertise and relevant experience.
- Sample marketing materials, photos of your orchard, and product samples if applicable.
Conclusion:
This comprehensive business plan template is a structured guide to creating a professional and detailed plan for your fruit orchard.
Tailor each section to reflect your unique vision, strategies, and goals for a thriving fruit orchard venture.
See How to Write a Business Plan for information on creating your business plan.
12. Banking Considerations
Strategic Banking for Your Business:
Opt for a local bank with a small business focus for your banking needs.
A dedicated business account ensures a clear separation of personal and business transactions.
This separation facilitates expense tracking and accurate financial reporting during tax filing.
Cultivating a rapport with your banker offers access to advice, financial services, and streamlined applications.
Consider having a merchant account or online service for credit and debit card payments.
This step enhances customer convenience and sales growth.
Establishing a solid banking foundation empowers your fruit orchard’s financial operations.
For more, see How to Open a Business Bank Account. You may also want to look at What Is a Merchant Account and How to Get One.
13. Getting the Funds for Your Operation
Securing Financing for Your Fruit Orchard:
Utilize the insights in this section when seeking a loan for your fruit orchard startup.
Financing options include traditional lenders, private loans, investors, and selling owned assets.
Government grants might also aid your orchard’s inception.
Considerations When Meeting a Loan Officer:
- Prepare by researching different lenders and their terms.
- Have a clear business plan outlining your orchard’s vision and financial projections.
- Be ready to explain how the loan will benefit your orchard’s growth.
- Clarify your repayment strategy and how you intend to manage any risks.
Sample Documents for Applying for a NEW Business Loan:
- Business Plan including mission, market analysis, and financial projections.
- Personal and business tax returns for the past few years.
- Financial statements, including balance sheets and income statements.
- Collateral documentation, if applicable.
- Proof of ownership for any assets.
- Legal documents such as business licenses and permits.
- Personal identification and credit history.
- Letters of reference or recommendation.
- Bank statements and credit history.
Prepare these documents to enhance your loan application process and increase your chances of securing funding for your fruit orchard.
For more, see the following:
- Getting a Small Business Loan
- SBA Small Business Grants
- Fruit Orchard Start-up Loans
- Grants For a Fruit Orchard
14. Software Setup
Selecting Software for Your Fruit Orchard Management:
Prioritize thorough software research as it’s easier to build from scratch than switch systems later.
Opt for established companies to ensure future support. Demos allow trial before purchase, while reviews and forums offer insights from others’ experiences.
Explore software for expense tracking and financial document preparation for tax filing.
Types of Software for Fruit Orchard Management and Operations:
- Farm Management Software: Monitor planting, harvesting, and maintenance schedules.
- Accounting Software: Handle financial transactions, invoicing, and bookkeeping.
- Weather Forecasting Software: Monitor weather conditions for optimal crop management.
- GIS Mapping Software: Map orchard layout and plan irrigation systems.
- Pest and Disease Management Software: Monitor and address potential threats to crops.
- Employee Scheduling Software: Organize work shifts and manage labor.
- Website and E-commerce Platforms: Manage online sales and customer engagement.
Selecting the right software tools streamlines orchard management and enhances operational efficiency.
Check out Google’s latest search results for software packages for a fruit orchard.
15. Get The Right Business Insurance
Preventive action is crucial to safeguarding your orchard against unexpected incidents.
Procure appropriate insurance before commencing any activities on your premises.
Adequate coverage should extend to customers, employees, property, and potential lawsuits.
Professional liability insurance protects against legal claims, while Interruption Insurance is vital to mitigate losses from involuntary shutdowns due to unforeseen events.
Collaborate with a competent insurance broker to secure comprehensive coverage that shields your fruit orchard against various risks.
For more, see What to Know About Business Insurance . You can also browse the latest Google search results for fruit orchard insurance .
16. Suppliers, Service Providers and Inventory
Selecting Suppliers and Service Providers:
A solid relationship with suppliers and service providers is pivotal for a fruit orchard’s success.
Reliability and trustworthiness in suppliers contribute significantly to positive outcomes.
Competitive pricing from suppliers allows cost savings for customers and increased profit margins.
Ensuring a consistent supply of necessary items is crucial for seamless business operations.
Treating suppliers and providers respectfully while ensuring mutual financial benefits enhances the working relationship.
Items and Services from Suppliers and Service Providers:
- Fruit Trees and Seeds: High-quality fruit trees and seeds for planting.
- Irrigation Systems: Equipment and installation for efficient irrigation.
- Fertilizers and Pest Control: Supplies to maintain healthy and pest-free orchards.
- Harvesting Equipment: Tools and machinery for efficient fruit picking.
- Packaging and Labeling: Materials for presenting and branding products.
- Transportation Services: Reliable options for product delivery.
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Services: Professionals to manage financial records.
- Marketing and Branding Services: Support for promoting the orchard and products.
- Legal and Regulatory Consultants: Guidance on compliance and permits.
Effective Inventory Management:
- Focus on customer-demanded products for inventory to enhance value.
- Balancing inventory levels is crucial; excess ties up funds, while insufficient leads to lost sales.
- Managing fruit shelf life is vital; attractive pricing can help move excess stock without spoilage concerns.
A well-managed relationship with suppliers, strategic inventory control, and maintaining fruit freshness balance contribute to a thriving fruit orchard operation.
For More, See How To Choose a Supplier.
17. Setting Prices
Importance of Pricing Research for Your Fruit Orchard:
Thorough pricing research is vital during the inception of a fruit orchard.
Striking the right pricing balance yields several advantages.
Balancing Pricing for Success:
- Setting excessively high prices can deter potential customers, leading to lost sales.
- Extremely low prices might attract customers, but insufficient profit hampers expense coverage.
- Optimal pricing entails aligning with market standards while showcasing the value you offer.
Finding the Sweet Spot:
Researching pricing ensures your orchard finds the sweet spot – a harmonious balance between attracting customers and maintaining profitability.
This equilibrium sustains growth, customer satisfaction, and your orchard’s financial health.
See the following for more:
- Setting the Price of Your Products and Services
- Search Results for Pricing Strategies for a Fruit Orchard.
18. Physical Setup
Orchard Layout and Setup:
Creating an efficient layout is pivotal for your fruit orchard’s functionality. Designate sections for planting, harvesting, and storage.
Arrange pathways for accessibility irrigation systems for efficient watering and consider weather and sunlight factors for optimal growth.
Effective Signage Implementation:
Signage is crucial for smooth orchard operations. Erect a prominent main business sign for easy identification.
Place signs in parking lots, exits, and key areas to guide visitors. Well-designed signage reflects professionalism and aids navigation, enhancing customer experiences.
Streamlined Office Setup:
Managing a fruit orchard requires time and effort. A well-organized office significantly boosts productivity.
Equip your office with essentials such as computers, phones, and relevant software.
Maintain organized files for records and transactions. An efficient set-up office streamlines daily tasks, facilitating smoother management of your orchard business.
See Here are Considerations for The Setup of Your Office for tips and ideas to make your office work for you. Also, have a look at our article About Company Signs.
19. Creating a Website
Essential Website Presence for Your Fruit Orchard:
A website is indispensable for your fruit orchard.
It serves as the primary point of contact and key business information dissemination.
Unlike social media platforms, a website is under your ownership and control when you register a domain name and host it.
Utilize your website as a dynamic marketing tool to engage customers.
Blogging about industry trends and offering tailored tips establishes trust and positions you as an industry expert.
This strengthens your connection with customers and enhances your orchard’s credibility.
For more, see How to Build a Website for Your Business .
20. Create an External Support Team
External Support Team for Your Orchard:
An external support team comprises professionals providing advice and services crucial for your fruit orchard’s success.
Not on your payroll, they offer project-based, contractual, hourly, or retainer services.
Focusing on these individuals highlights their significance and allows for team expansion.
While building professional relationships takes time, it’s a continuous effort.
A robust team includes accountants, lawyers, financial advisors, marketing specialists, technical advisors, and consultants.
This team’s expertise provides invaluable guidance and assistance when needed, enhancing your orchard’s operations and growth prospects.
For more, see Building a Team of Professional Advisors for Your Business.
21. Hiring Employees
Operational Scaling and Hiring for Your Orchard:
Running your orchard solo initially is cost-effective, but managing it alone becomes challenging as your business expands.
Hiring employees becomes essential to meet demands effectively.
Key Considerations in Hiring:
- Ensure new hires have relevant qualifications and strong work ethics .
- Hire individuals who are the right fit for each job role.
- Strive for a well-balanced team with complementary skills.
Jobs Needed to Run a Fruit Orchard:
The following are job positions or outsourced services you may want to consider as your fruit orchard grows:
- Orchard Manager
- Harvesting Crew
- Farm Workers
- Sales and Marketing Specialist
- Accountant or Bookkeeper
- Irrigation Technician
- Pest and Disease Control Expert
- Customer Service Representative
- Equipment Maintenance Personnel
- Packing and Packaging Staff
Scaling your team strategically ensures efficient operations and the continued growth of your fruit orchard.
For more, see How and When to Hire a New Employee.
Points To Consider
Next, let’s review essential points before starting your fruit orchard.
We’ll review sections, including getting customers through the door in the early stages, marketing tips, making your business stand out, looking at established companies, and more.
A List of Equipment and Supplies to Consider for a Fruit Orchard:
- Disc harrow
- Rotary tiller
- Drip irrigation system
- Sprinkler system
- Water pumps
- Hoses and pipes
- Planting auger
- Tree planter
- Pruning shears
- Hand tools (shovels, rakes, hoes)
- Fruit picker
- Harvest bins or crates
- Sprayers (backpack and tractor-mounted)
- Insect traps
- Netting or covers
- Cold storage units
- Packaging materials (boxes, crates, bags)
- Sorting and grading equipment
- Utility vehicles
- Trucks or trailers for transporting produce
- Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- First aid kits
- Maintenance tools (wrenches, screwdrivers)
- Farm management software
- Tablets or computers
- Barcode scanners (for tracking inventory)
- Fertilizer spreader
- Soil testing kits
- Weather station
- Thermometers
- Trellis systems
- Pruning saws
- Warning signs
- Directions and information signs
- Shade structures
- Benches or seating for visitors
- Protective netting (for hail or birds)
- Communication tools (phones, email)
- Perimeter fencing
- Security cameras
- Compost bins or piles
- Turning equipment
- Educational materials for visitors
- Signage explaining orchard practices
Having the right equipment ensures efficient orchard management, enhances productivity, and contributes to the overall success of your fruit orchard business.
Key Points To Succeeding in a Fruit Orchard
Points to Succeed in Operating a Fruit Orchard:
Running a successful fruit orchard demands strategic focus and attention to several crucial factors:
- Niche Focus: Specialize in a particular fruit variety or unique offering to distinguish yourself in the market and attract a dedicated customer base.
- Building Customer Base: Establishing a customer base is challenging at the outset, but focus on quality, consistency, and customer engagement to foster loyalty.
- Relationship Building: Forge strong connections with customers, suppliers, and employees to create a supportive network contributing to the orchard’s growth.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Provide products and services aligned with customer preferences and actively seek and act on valuable feedback.
- Customer Feedback: Leveraging customer feedback to address credible concerns and improve operations gives you a competitive edge.
- Exceptional Service: Elevate customer experiences through high-level service; prioritize value creation for customers.
- Team Building: Assemble a skilled and motivated team that aligns with your orchard’s values; effective teamwork is pivotal.
- Staff Management: Manage staff respectfully, fostering a positive work environment for better retention and enhanced productivity.
- Cash Flow Management: Maintain robust cash flow management to ensure financial stability and growth.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimize costs while maintaining product quality and excellent customer service.
- Adaptability: Embrace change in industry trends, processes, and technology; adapt to stay ahead.
- Fluctuating Revenue: Prepare for revenue fluctuations and implement strategies to handle them effectively.
- Competition Management: Address competition by continuously improving offerings and understanding market dynamics.
- Effective Marketing: Employ impactful marketing, either personally or through professionals, to create awareness and drive customer engagement.
By focusing on these elements, you can establish a thriving fruit orchard that meets customer needs, adapts to challenges, and secures long-term success in the industry.
Making Your Fruit Orchard Stand Out
Ideas to Make a Fruit Orchard Stand Out:
- Diverse Fruit Varieties: Offer a wide range of fruit varieties, including heirloom and exotic options, to attract customers seeking unique flavors and experiences.
- Educational Tours: Provide guided tours that educate visitors about fruit cultivation, harvesting, and the importance of sustainable practices. This adds an interactive element to the orchard visit.
- Pick-Your-Own Experience: Allow visitors to handpick their favorite fruits directly from the orchard. This engaging activity creates lasting memories and a deeper connection to the produce.
- Farm-to-Table Events: Organize farm-to-table events where guests can enjoy meals prepared using fresh fruits harvested from the orchard. This showcases the farm’s produce and culinary potential.
- Seasonal Festivals: Host seasonal festivals celebrating the bounty of each fruit harvest. Offer entertainment, activities, and themed events that attract families and communities.
- Farm Market: Set up an on-site farm market where visitors can purchase not only fresh fruits but also artisanal products, baked goods, jams, and preserves made from the orchard’s produce.
- Picnic Areas: Create inviting picnic areas amid the fruit trees. Visitors can relax, enjoy a meal, and immerse themselves in the tranquil orchard surroundings.
- Children’s Play Area: Design a play area with fruit-themed activities for kids, promoting family-friendly experiences and attracting parents with young children.
- Seasonal Decor: Enhance the orchard’s ambiance with seasonal decorations, creating a picturesque setting that draws visitors for memorable photo opportunities.
- Community Engagement: Partner with local schools, clubs, and organizations for workshops, events, and collaborative projects to foster community engagement and support.
Add on Ideas for a Fruit Orchard
- Cooking Workshops: Offer cooking classes that teach participants how to create delectable dishes using the orchard’s fruits, fostering culinary creativity.
- Fruit-Infused Beverages: Create a beverage station offering freshly made fruit juices, smoothies, and fruit-infused water to refresh and quench thirst.
- Fruit-Centric Spa Products: Develop a line of skincare and spa products using orchard fruits known for their beneficial properties, such as exfoliating scrubs and moisturizers.
- U-Pick Bundles: Package fruits in bundles for customers to pick and take home, making it convenient to enjoy a variety of fruits in one purchase.
- Pet-Friendly Activities: Organize pet-friendly events and activities, such as “bring your dog to the orchard” days, encouraging visitors to enjoy the outdoors with their pets.
- Orchard Photography: Collaborate with photographers to offer picturesque orchard photography sessions for individuals, couples, families, and special occasions.
- Artisan Workshops: Host workshops where participants can learn traditional crafts like jam-making, fruit preserves, and fruit-based crafts.
- Outdoor Movie Nights: Arrange movie nights under the stars, screening family-friendly films against the backdrop of the orchard’s natural beauty.
- Nature Walks: Develop walking trails around the orchard, providing visitors with a serene environment to connect with nature and explore the orchard’s surroundings.
- Fruit Subscription Boxes: Launch subscription services that deliver a selection of fresh fruits to customers’ doorsteps regularly, providing convenience and quality.
By implementing these ideas, a fruit orchard can distinguish itself, create memorable experiences, and offer enticing add-ons that enhance the overall visitor journey.
Marketing Considerations
A fruit orchard’s success hinges on attracting customers. In the early stages, awareness is a challenge due to the newness of your operation.
Over time, a strong reputation and marketing expertise make it easier.
Consistent marketing is key, with increased investment leading to higher revenue.
While not essential, a marketing agency or expert can help when suitable.
Simple Methods to Promote Your Fruit Orchard:
- Social Media: Utilize platforms like Instagram and Facebook to showcase your orchard’s beauty, products, and activities.
- Local Events: Participate in farmers’ markets, food festivals, or community events to connect with locals and raise awareness.
- Word of Mouth: Encourage satisfied customers to spread the word, leveraging the power of personal recommendations.
- Online Presence: Create a website with essential information, including location, offerings, and contact details.
- Blogging: Share insights about fruit growing, recipes, and orchard updates through a blog on your website.
- Collaborations: Partner with local businesses for cross-promotions and joint marketing efforts.
- Google My Business: Set up a profile to appear in local searches and provide accurate information to potential customers.
- Flyers and Brochures: Distribute informational materials at local businesses, community centers, and events.
- Email Marketing: Build a subscriber list and send regular updates about orchard activities, promotions, and events.
- Open House Events: Organize open house days where visitors can tour the orchard and enjoy fruit picking.
- Loyalty Programs: Reward returning customers with special offers to encourage repeat visits.
- Press Releases: Share notable updates or events with local media outlets to gain coverage.
- Networking: Attend local business networking events to establish connections and promote your orchard.
- Online Reviews: Encourage customers to leave positive reviews on platforms like Google and Yelp.
- Direct Mail: Send postcards or mailers to the local community to introduce your orchard.
- Community Engagement: Participate in charitable events or community projects to establish your orchard as a valued local entity.
By employing these straightforward methods, you can create awareness and attract a loyal customer base to your fruit orchard.
See How To Get Customers Through the Door and our marketing section to provide ideas to help you bring awareness to your business.
Sample Ad Ideas:
1. Sample Ad:
“Experience Fresh Delights at Our Orchard!”
Discover the joy of hand-picked, succulent fruits straight from our orchard. Perfect for a healthy snack or creating delicious recipes. Visit us today!
2. Sample Ad:
“Taste Nature’s Bounty at Our Orchard”
Indulge in nature’s sweetness with our assortment of premium fruits. Plucked at peak ripeness for ultimate flavor. Your palate will thank you!
3. Sample Ad:
“Elevate Your Meals with Orchard Freshness”
Upgrade your culinary creations with our farm-fresh fruits. Elevate your dishes from ordinary to extraordinary. Visit us for a flavorful experience.
4. Sample Ad:
“Savor Orchard Bliss in Every Bite”
Rediscover the taste of real fruit—juicy, ripe, and bursting with flavor. Treat yourself to the finest nature has to offer. Come pick your favorites!
5. Sample Ad:
“Nurture Wellness with Orchard Goodness”
Nourish your body and soul with our handcrafted selection of fruits. Elevate your well-being while enjoying natural goodness. Experience it today!
Each display ad emphasizes the orchard’s fresh and flavorful offerings, encouraging customers to explore and enjoy the variety of fruits available.
You can establish strategic partnerships with various businesses to facilitate mutual referrals and create a win-win situation.
Consider these potential partners:
- Local Restaurants and Cafes: Collaborate with eateries to source fresh fruit for their dishes and refer customers seeking local produce.
- Grocery Stores: Partner with grocery stores to supply fresh fruits and cross-promote each other’s offerings.
- Event Planners: Provide fruit arrangements for events they organize, while they refer clients to your orchard for unique décor ideas.
- Health and Wellness Centers: Offer your fruits as part of health programs, and they can direct clients seeking healthy options.
- Tourism Companies: Suggest your orchard as a tourist attraction, and they can send visitors your way.
- Wedding Planners: Offer fruit baskets or favors for weddings they organize, while they recommend your orchard for themed weddings.
- Local Schools: Supply fruits for school events, and they can inform parents about your healthy options.
- Gardening and Landscaping Services: Cross-refer clients seeking gardening supplies and landscaping designs.
- Bakeries: Provide fruits for pastry fillings and receive referrals for customers interested in your produce.
- Online Food Delivery Platforms: Collaborate to offer fresh fruit options for online food orders.
By crafting creative partnerships that benefit both parties, you can establish a network of reliable referrals, attract new customers, and enhance your business’s reputation within the community.
Focusing on your skill set is crucial when considering a fruit orchard venture.
Evaluating your abilities ensures you possess the necessary competencies to manage various aspects of the business effectively.
Owning an orchard demands diverse skills like horticulture, business management, marketing, and customer relations.
Should a vital skill be lacking, you have two options: acquiring it through learning or hiring someone skilled.
This impacts the orchard’s success and your ability to adapt to challenges.
Essential Skills for a Fruit Orchard Owner:
- Horticulture Expertise: Understand planting, growing, and caring for fruit trees.
- Business Management: Knowledge of finances, operations, and strategic planning.
- Marketing: Promoting products and attracting customers.
- Customer Service: Building strong relationships and addressing concerns.
- Problem-Solving: Dealing with pests, diseases, and unexpected issues.
- Time Management: Juggling tasks efficiently and seasonally.
- Adaptability: Responding to changing market trends and climate conditions.
- Negotiation Skills: Interacting with suppliers, partners, and customers.
- Leadership: Managing a team and fostering a positive work environment.
- Salesmanship: Selling fruit and related products effectively.
These skills collectively ensure successful orchard management and growth.
Knowledge Is Power if You Use It!
Examining industry trends and statistics for a fruit orchard informs decision-making during startup and operation phases, enhancing business strategies.
See the latest search results for trends and statistics related to the fruit industry.
Fruit Orchard Associations
Trade associations provide benefits such as industry news updates and networking opportunities for staying informed and connected.
See the search results related to fruit orchard associations and the benefits of Joining the Chamber of Commerce.
The Top Fruit Orchards
Exploring existing orchards sparks ideas, unveils industry gaps for a competitive edge, and reveals overlooked offerings by other businesses.
See the latest search results for the top fruit orchards.
The Future of the Fruit Industry
Researching the industry’s future aids potential orchard owners. Insights inform decisions and align strategies with upcoming trends and demands.
See the search results for the future of the fruit orchard industry.
Find a Fruit Orchard For Sale
There are pros and cons to purchasing an existing business.
Opting for an established fruit orchard over starting anew offers benefits like immediate revenue, avoiding the startup phase, proven success, known financials, an existing customer base, and a built reputation.
Moreover, it saves time since mature trees yield fruit right away.
On the flip side, downsides encompass higher costs due to goodwill, potential customer loss during changes, and inheriting both positive and negative aspects of the business’s reputation.
Though an exact fruit orchard sale might be absent, exploring related industry options through the provided link remains valuable.
The latest search results for a fruit orchard for sale and others in the same category.
Franchise Opportunities Related to a Fruit Orchard
Owning a fruit orchard franchise has pros and cons worth considering.
Pros include a proven model, established reputation, full business knowledge, and corporate support.
However, the cons involve costs, limited autonomy, product restrictions, operational limitations, and ongoing fees.
Exploring franchise opportunities may reveal unforeseen options related to fruit orchards. For related franchises, use the provided link to search within the industry.
See the latest search results for franchise opportunities related to this industry.
Customer Expectations
Reviewing search results on customer fruit preferences offers insights to meet and surpass expectations.
Discover overlooked issues and enhance customer satisfaction by addressing all aspects comprehensively.
See the search results related to customer expectations for eating fruits.
Expert Tips
Expert tips enhance skills for both novices and experts. Fresh perspectives and techniques benefit all levels, fostering growth and improvement in the field.
See the latest search results for fruit orchards to gain tips and insights.
Fruit Orchard Insights
Exploring tips yields innovative ideas, pitfalls to dodge in orchard management, and valuable industry expertise.
See the latest search results about insights into running a fruit orchard.
Fruit Publications
Publications provide essential updates and ideas on fruit-related topics. Stay informed and inspired through reading.
See the search results for fruit orchard publications.
Fruit Forums
Engage in fruit forums for connections and insights. Discussions aid customer understanding and relationships with industry peers.
See the latest search results related to fruit forums.
Online or local courses enhance orchard skills. Learning boosts knowledge and benefits fruit orchard endeavors.
See the latest courses that could benefit a fruit orchard owner . Also, see our management articles for tips and insights for managing your business.
Fruit Orchard Blogs
Subscribe to fruit orchard blogs for ideas and industry updates. Add multiple, then trim based on value and updates. Build a useful collection for consistent insights.
Look at the latest search results for fruit orchard blogs to follow.
News serves as a source to stay updated on fruit-related media coverage, offering current stories and information.
See the latest results for fruit news.
YouTube adds new daily videos. Valuable info on fruit orchards can be found. Spend time browsing for insights if desired.
YouTube videos related to fruit orchards.
Privacy Overview

How to Craft a Business Plan for Apple Farming Success in 2024

Apple Farming Bundle
Embarking on an apple farming venture requires meticulous planning and preparation. Before crafting your business plan, it's essential to conduct thorough market research, analyze local conditions, and explore the necessary certifications and funding options. This 9-step checklist outlines the key considerations to ensure your apple farming endeavor takes root and flourishes.
Steps Prior To Business Plan Writing
Before embarking on the journey of writing a comprehensive business plan for an organic apple farming venture, it is crucial to undertake a series of preparatory steps. These preliminary actions will help you gather crucial information, assess the feasibility of your project, and lay the groundwork for a well-informed and robust business plan.
Conduct Market Research on Organic Apple Demand
Before embarking on your apple farming venture, it is crucial to conduct thorough market research to understand the demand for organic apples in your target market. This step will help you make informed decisions about the scale and scope of your orchard operations, as well as guide your overall business planning process.
The organic food industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, with the global organic food market valued at $187.4 billion in 2021 and projected to reach $380.8 billion by 2027 , growing at a CAGR of 12.2% from 2022 to 2027 . Within this industry, organic fruits and vegetables, including apples, have been driving much of the demand.
According to a recent report by the Organic Trade Association, organic fruit and vegetable sales in the United States reached $20.4 billion in 2021, accounting for 36.3% of total organic food sales . Furthermore, the study found that apples are the second-most purchased organic produce item, with 91% of U.S. households purchasing organic apples in 2021 .
To assess the local demand for organic apples, consider the following:
- Identify your target market and understand their preferences, purchasing habits, and willingness to pay a premium for organic apples.
- Analyze the competitive landscape, including the number of existing organic apple producers, their market share, and pricing strategies.
- Estimate the potential size of the organic apple market in your local or regional area, taking into account population, income levels, and consumer trends.
- Gather data on the current supply of organic apples in your target market, including imports and local production, to identify any gaps or unmet demand.
- Attend local farmers' markets, food co-ops, or organic food stores to observe consumer behavior and gather insights directly from potential customers.
- Conduct surveys or interviews with local residents, chefs, and food retailers to understand their preferences and willingness to purchase organic apples from a local producer.
- Reach out to industry associations, such as your state's apple growers' association or the Organic Trade Association, to access industry reports and market data.
By conducting a thorough market analysis, you can develop a clear understanding of the organic apple demand in your target market, which will inform your business planning and help you make strategic decisions about the size, product offerings, and pricing of your apple farming operation.
Analyze local climate and soil conditions for apple growth
Establishing a successful organic apple orchard requires a thorough understanding of the local climate and soil conditions. These factors play a crucial role in the growth, yield, and overall health of the apple trees. Before embarking on your apple farming venture, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the environmental factors that will impact your operation.
The first step is to assess the local climate. Apples thrive in temperate climates with distinct seasons, adequate rainfall, and moderate temperatures. Evaluate the average annual rainfall, the frequency and intensity of precipitation, the average temperatures throughout the year, and the occurrence of frost or extreme weather events. According to the National Apple Growers Association, the ideal climate for apple cultivation should have an average annual rainfall of 30-40 inches and average temperatures ranging from 45°F to 75°F during the growing season.
Next, analyze the soil composition and quality of the land where you plan to establish your orchard. Apples prefer well-drained, loamy soils with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. The USDA's Natural Resources Conservation Service recommends that apple orchards have a soil depth of at least 3 feet and a clay content of less than 35%. Conduct soil tests to determine the nutrient levels, organic matter content, and any potential deficiencies or imbalances that may need to be addressed.
- Consult with local agricultural extension services or soil and water conservation districts to obtain detailed information about the climate and soil characteristics of your target area.
- Consider the potential impact of climate change and how it may affect the suitability of your orchard location in the long run.
- Explore the possibility of implementing soil-building practices, such as cover cropping or organic matter incorporation, to optimize the soil conditions for apple cultivation.
By thoroughly analyzing the local climate and soil conditions, you can make informed decisions about the viability of your apple farming venture and take the necessary steps to ensure the long-term success of your orchard. This comprehensive assessment will serve as a critical foundation for the development of your business plan and the implementation of your apple farming operation.
Determine Land Requirements and Availability for Orchard
Establishing an organic apple orchard requires careful consideration of the land requirements and availability. The size of the orchard, soil conditions, and access to water are crucial factors that will impact the success of your apple farming business.
To determine the land requirements for your organic apple orchard, you should first consider the desired production capacity. As a general rule, one acre of land can typically support between 100 to 150 apple trees , depending on the variety and planting density. For the Orchard Origins business plan, let's assume a target of 5 acres of land to accommodate 500-750 apple trees .
- Consider the optimal tree spacing for your chosen apple varieties, which can range from 12 to 18 feet between rows and 8 to 15 feet between trees within the row.
- Factor in additional space for access roads, equipment storage, and other infrastructure required for the orchard operations.
Next, you'll need to analyze the local climate and soil conditions to ensure they are suitable for growing organic apples. Apples thrive in temperate climates with annual rainfall between 30-50 inches and average summer temperatures between 70-85°F . The soil should be well-drained, with a pH range of 6.0-6.5 , and be rich in organic matter.
Once you have determined the land requirements, you'll need to assess the availability of suitable land in your target area. This may involve researching local real estate listings, contacting land owners, or exploring opportunities for leasing farmland. Keep in mind that the cost of land can vary significantly based on factors such as location, size, and existing infrastructure.
- Consider the proximity of the land to your target customer base, as well as accessibility for transportation and distribution of your apple products.
- Investigate any zoning or regulatory requirements that may impact the use of the land for an organic apple orchard.
By carefully evaluating the land requirements and availability, you can ensure that your organic apple orchard is established on a suitable site that will support the long-term success of your business.
Investigate Organic Certification Process and Regulations
As an aspiring organic apple farmer, navigating the organic certification process will be a crucial step in establishing your business. Organic certification not only ensures your apples meet strict environmental and sustainability standards, but it also provides a competitive advantage in the marketplace and builds trust with health-conscious consumers.
The first step in the organic certification process is to familiarize yourself with the National Organic Program (NOP) regulations set forth by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). These regulations outline the specific requirements for organic production, handling, and labeling of agricultural products, including apples.
- Understand that the organic certification process can take 12-18 months to complete, so it's essential to start planning well in advance.
Once you have a solid understanding of the NOP regulations, you will need to select an accredited organic certifying agency to work with. These agencies are responsible for inspecting your orchard and operations to ensure compliance with organic standards. Some popular certifying agencies in the United States include the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI), the California Certified Organic Farmers (CCOF), and the Northeast Organic Farming Association (NOFA).
During the certification process, you will need to provide detailed records and documentation demonstrating that your apple farming practices adhere to the organic standards. This may include information about your land use, soil management, pest control methods, and record-keeping systems. The certifying agency will also conduct an on-site inspection of your orchard to verify your compliance.
It's important to note that the cost of organic certification can range from $400 to $3,000 or more, depending on the size of your operation and the certifying agency you choose. Additionally, you may need to budget for annual inspection fees and any necessary changes to your farming practices to meet organic requirements.
- Establish a strong relationship with your certifying agency and be prepared to provide any additional information or documentation they may request during the certification process.
By successfully navigating the organic certification process, you will not only position your apple farming business to meet the growing demand for organic produce, but you will also demonstrate your commitment to sustainable and environmentally-friendly agricultural practices.
Assess Startup Costs for Orchard Establishment and Operations
Establishing an organic apple orchard requires significant upfront investment, and understanding the startup costs is crucial for developing a comprehensive business plan. The primary expenses involved in setting up and maintaining an apple orchard include land acquisition, orchard establishment, equipment and infrastructure, and operational costs.
Land Acquisition and Orchard Establishment
The cost of land for an apple orchard can vary widely depending on the location, size, and quality of the land. According to industry data, the average cost of agricultural land in the U.S. is around $3,160 per acre . However, prime apple-growing regions may command higher prices. Additionally, the cost of preparing the land for orchard planting, including soil amendments, drainage, and fencing, can range from $5,000 to $10,000 per acre .
The next major expense is the cost of apple trees and their planting. Depending on the variety and rootstock, apple trees can cost between $10 and $30 per tree . Assuming a planting density of 100 to 200 trees per acre , the total cost for tree purchase and planting can range from $1,000 to $6,000 per acre .
Equipment and Infrastructure
Establishing the necessary infrastructure and acquiring the required equipment is another significant startup cost. This may include the construction of a storage facility, packing shed, and irrigation system, as well as the purchase of tractors, sprayers, and other specialized farming equipment. These costs can vary widely based on the scale of the operation, but a rough estimate would be $50,000 to $150,000 for a small to medium-sized organic apple orchard.
Operational Costs
Once the orchard is established, ongoing operational costs must be considered. These include labor for pruning, harvesting, and packing; materials such as fertilizers, pesticides, and packaging; and utilities like water and electricity. Based on industry data, the annual operational costs for an organic apple orchard can range from $3,000 to $6,000 per acre .
- Explore government grants and subsidies that may be available for organic or sustainable agriculture projects to help offset startup costs.
- Consider leasing rather than purchasing land and equipment to reduce the initial capital investment required.
- Investigate potential cost-sharing opportunities with local agricultural organizations or cooperatives to leverage economies of scale.
Accurately estimating the startup costs for an organic apple orchard is essential for creating a realistic and viable business plan. By carefully analyzing the various expense categories, growers can develop a comprehensive understanding of the financial resources needed to establish and maintain a successful apple farming operation.
Explore Funding Options, such as Loans or Grants
Establishing an organic apple orchard like Orchard Origins requires significant upfront investment. Securing the necessary funding is a crucial step in the business planning process. Fortunately, there are several options available to aspiring apple farmers looking to finance their operations.
One of the primary funding sources to consider is agricultural loans . These specialized loans, offered by banks, credit unions, and government agencies, are designed to support the unique needs of farmers and agricultural businesses. They often feature favorable interest rates and flexible repayment terms, making them an attractive option for apple farmers.
- Research local and regional banks or credit unions that have experience working with agricultural businesses to find the most suitable loan options.
- Be prepared to provide a detailed business plan, financial projections, and collateral to increase your chances of loan approval.
In addition to loans, government grants can also be a valuable source of funding for organic apple farming ventures. Programs such as the USDA's Organic Agriculture Research and Extension Initiative (OREI) or the Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE) grants offer financial assistance to farmers and researchers working to advance sustainable agriculture practices.
To maximize your chances of securing grant funding, it's important to carefully research and identify the grants that align with your business goals and priorities. This may involve networking with local agricultural extension offices, attending industry events, or consulting with experienced grant writers.
- Start the grant application process well in advance, as the process can be competitive and time-consuming.
- Ensure that your business plan and project proposal clearly demonstrate how your organic apple farming operation will contribute to the grant program's objectives.
Another potential source of funding for Orchard Origins is crowdfunding . This approach allows you to tap into a broader network of supporters, including local community members, environmentally conscious consumers, and investors interested in sustainable agriculture. By leveraging platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo, you can raise funds while also building brand awareness and engaging with your target audience.
Regardless of the funding route you choose, it's essential to thoroughly research and evaluate each option to ensure that it aligns with your business goals and financial needs. By carefully considering these funding sources, you can secure the necessary resources to establish and grow your successful organic apple farming operation.
Identify Potential Suppliers of Organic Apple Seedlings
As you embark on your journey to establish an organic apple orchard, one of the crucial steps is to identify reliable suppliers of organic apple seedlings. These seedlings will form the foundation of your orchard, and sourcing them from reputable providers is essential for the long-term success of your business.
When searching for organic apple seedling suppliers, it's important to consider factors such as the quality of their stock, their commitment to sustainable practices, and their ability to meet your specific needs. According to industry data, the global organic apple seedling market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% between 2021 and 2026, reaching a value of $2.4 billion by 2026 , underscoring the importance of securing high-quality suppliers.
To identify potential suppliers, start by researching local and regional nurseries and orchards that specialize in organic fruit tree cultivation. A recent survey of organic apple growers in the United States found that over 70% source their seedlings from local or regional suppliers, as this helps ensure the seedlings are well-adapted to the local climate and soil conditions .
- Attend local agricultural trade shows and conferences to network with potential suppliers and learn about the latest advancements in organic apple cultivation.
- Check online directories and industry associations for listings of reputable organic apple seedling providers in your area.
- Reach out to your local extension office or agricultural department for recommendations on trusted suppliers they have worked with in the past.
Once you have identified a shortlist of potential suppliers, it's essential to thoroughly vet their credentials and conduct due diligence. Look for suppliers that are certified organic, have a track record of delivering high-quality seedlings, and can provide detailed information on the genetic lineage and cultivation practices of their stock . This will help ensure that the seedlings you acquire are well-suited to your local growing conditions and will thrive in your orchard.
By taking the time to carefully select your organic apple seedling suppliers, you'll be laying the groundwork for a successful and sustainable apple farming venture. With the right suppliers in place, you can confidently move forward with the remaining steps in your business plan, secure in the knowledge that you have a strong foundation for your organic apple orchard.
Network with Local Farmers and Agricultural Experts
Establishing a successful apple farming business requires more than just understanding the technical aspects of apple cultivation. It's essential to build a strong network of local farmers and agricultural experts who can provide invaluable insights and support throughout the process. By tapping into this wealth of knowledge and experience, you can enhance your chances of creating a thriving and sustainable apple farming operation.
One of the primary benefits of networking with local farmers is the opportunity to learn from their real-world experiences. These individuals have navigated the challenges of apple farming in your specific region and can offer guidance on navigating local regulations, addressing climate and soil-related issues, and identifying reliable suppliers of organic apple seedlings. Their firsthand knowledge can be an invaluable resource as you develop your business plan and prepare to launch your apple farming venture.
In addition to local farmers, it's crucial to connect with agricultural experts, such as extension agents, horticulturists, and agronomists. These professionals can provide technical expertise on topics ranging from optimal orchard design and planting techniques to pest management and organic certification requirements. By leveraging their expertise, you can make informed decisions that will help ensure the long-term success of your apple farming business.
- Attend local agricultural events and conferences to network with fellow farmers and industry experts. These gatherings can be excellent opportunities to learn about the latest trends, challenges, and best practices in organic apple farming.
- Reach out to your state's Cooperative Extension Service to connect with agricultural specialists who can provide guidance on everything from soil analysis to disease management.
- Join relevant industry associations , such as the U.S. Apple Association or your state's apple growers' association, to stay informed about regulatory changes, funding opportunities, and other important developments in the apple farming industry.
By actively networking with local farmers and agricultural experts, you can gain a deeper understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities associated with apple farming in your region. This knowledge can inform the development of a comprehensive business plan that addresses the specific needs and requirements of your apple farming operation, ultimately increasing your chances of success.
According to the USDA's 2017 Census of Agriculture , there were 12,444 apple farms in the United States, with a total of 346,989 acres dedicated to apple production. By tapping into the expertise of local farmers and agricultural professionals, you can position your apple farming business to capitalize on the growing demand for organic and locally-sourced apples, which accounted for over 25% of the total apple market in 2020 .
Develop a Preliminary Operational and Management Plan
Establishing a successful organic apple farming business requires a well-thought-out operational and management plan. This preliminary plan will serve as a roadmap for the day-to-day operations, resource allocation, and overall management of the Orchard Origins apple orchard.
One of the key components of the operational plan is the cultivation and production strategy. This involves determining the optimal planting density, selecting the most suitable apple cultivars for the local climate and soil conditions, and implementing sustainable farming practices to ensure the long-term health and productivity of the orchard.
- Consider planting a diverse array of apple varieties to cater to different customer preferences and extend the harvesting season.
- Explore the use of integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to minimize the reliance on synthetic pesticides and promote a balanced ecosystem.
- Implement water-efficient irrigation systems and mulching practices to conserve water and maintain soil moisture levels.
The management plan should also address the organizational structure and staffing requirements. This includes identifying key roles and responsibilities, such as orchard manager, harvest coordinator, and marketing specialist, as well as determining the necessary skill sets and labor needs for each position.
Additionally, the preliminary plan should outline the financial management strategies, including budgeting, cash flow projections, and pricing models. This will help ensure the financial viability of the Orchard Origins business and guide the decision-making process for investments and operational expenditures.
To develop a comprehensive operational and management plan, it is crucial to consult with local agricultural experts, experienced organic apple farmers, and industry associations. These resources can provide valuable insights, best practices, and recommendations to optimize the efficiency and sustainability of the Orchard Origins apple farming operations.
By investing time and effort into creating a well-structured preliminary operational and management plan, Orchard Origins can establish a solid foundation for the successful launch and long-term growth of its organic apple farming business.
Related Blogs
- 7 Mistakes to Avoid When Starting a Apple Farming in the US?
- What Are The Top 9 Business Benefits Of Starting A Apple Farming Business?
- What Are The Nine Best Ways To Boost A Apple Farming Business?
- What Are Nine Methods To Effectively Brand A Apple Farming Business?
- Apple Farming Business Idea Description in 5 W’s and 1 H Format
- Unlocking Apple Farm Success: Your Ultimate Acquisition Checklist
- What Are The Reasons For The Failure Of Apple Farming Businesses?
- How To Fund Or Get Money To Start A Apple Farming Business?
- How To Name A Apple Farming Business?
- The Earnings of Apple Farming Owners
- How to Start an Apple Farm: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- 7 Key KPIs for Successful Apple Farming Operations
- How to Manage Apple Farming Costs Efficiently
- What Are The Top Nine Pain Points Of Running A Apple Farming Business?
- Boost Your Apple Farming Business with a Stellar Pitch Deck. Get Started Today!
- Expert Tips for Increasing Profits on Your Apple Farm
- What Are Nine Strategies To Effectively Promote And Advertise A Apple Farming Business?
- The Complete Guide To Apple Farming Business Financing And Raising Capital
- Strategies To Increase Your Apple Farming Sales & Profitability
- What Are The Best Nine Strategies For Scaling And Growing A Apple Farming Business?
- How To Sell Apple Farming Business in 9 Steps: Checklist
- How Much Does It Cost To Set Up An Apple Farm?
- What Are The Key Factors For Success In A Apple Farming Business?
- Appraising an Apple Farm Business: Guidelines.
- How to Start Apple Farming with No Money: A Step-by-Step Guide
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
Essential Steps to Prepare for Writing a Business Plan for Apple Farms

- 5-Year Excel
- MAC & PC Compatible
- Immediate Download
Related Blogs
- How to Boost Your Apple Orchard Profits: 9 Methods
- Essential Startup Costs for an Apple Farming Business
- Top 7 KPIs for Monitoring Your Apple Farm Business
- How to Start an Apple Farm: Checklist for the Aspiring Grower
- Must-Know Operating Costs for Apple Farmers
Are you ready to embark on your apple farming venture? Before you dive into writing your business plan, it's essential to understand the critical steps that will set you on the path to success. From conducting a thorough market analysis to identifying funding sources, this 9-step checklist will guide you in crafting a comprehensive and effective business plan tailored for apple farming. Discover more and start planning your future by visiting this link .
Why Is It Important To Prepare Before Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
Preparing before writing a business plan for apple farming is crucial for several reasons. A well-thought-out plan not only serves as a roadmap for your venture but also helps in identifying potential challenges and opportunities in the apple farming industry. With the global organic apple market projected to reach $4.5 billion by 2027 , understanding the landscape is vital for success.
Furthermore, a comprehensive preparation phase allows you to refine your apple farming business strategy . This includes conducting market research for apple farming , understanding the target market , and analyzing competitors. In fact, studies show that businesses that conduct thorough market analysis are 30% more likely to succeed than those that do not.
Another key aspect of preparation is compliance with agricultural regulations. Knowing the compliance and regulations in your area can save you from costly mistakes and legal issues down the line. For example, understanding water usage regulations and organic certification processes can significantly impact your operational plans.
Tips for Effective Preparation
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to identify your position in the market.
- Engage with local agricultural extension services for insights into best practices and compliance.
- Network with other apple farmers to gain insights into their challenges and successes.
Lastly, preparing adequately sets the stage for crafting a detailed apple orchard business plan . This includes gathering essential financial projections for apple farming, which are critical for attracting investors and securing funding. A well-prepared plan can highlight your unique selling proposition, making it easier to differentiate your apple farming business in a competitive market.
What Research Is Needed Prior To Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
Before embarking on the journey of writing a business plan for apple farming , it is crucial to conduct thorough research. This foundational research sets the stage for your apple farming business strategy and ensures that you are well-informed about market dynamics, regulatory requirements, and operational challenges specific to apple cultivation.
Here are key areas to focus on while conducting your research:
- Market Research: Analyze current trends in the apple farming market. According to the USDA , the apple production in the United States is around 10 billion pounds annually, indicating a robust market. Understand consumer preferences for organic versus conventional apples.
- Target Market Identification: Determine who your potential customers are. This includes local grocery stores, farmers' markets, and direct consumers. Assess demographic data to identify your apple farming target market —for instance, focusing on health-conscious consumers who prefer organic produce.
- Regulatory Compliance: Investigate local and federal regulations affecting apple farming. This includes understanding pesticides' regulations, food safety requirements, and certifications necessary for organic farming. Non-compliance can lead to fines and delays in farming operations.
- Competitive Analysis: Study your competitors in the apple farming sector. Evaluate their pricing strategies, product varieties, and marketing approaches. You should also consider their strengths and weaknesses, which can inform your apple farming market analysis .
- Financial Assessment: Gather data on the financial aspects of apple farming. This includes understanding start-up costs—for example, establishing an orchard can range from $5,000 to $10,000 per acre . Create projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the short and long term.
Research Tips:
- Utilize online databases and agricultural reports to gather up-to-date statistics on apple farming.
- Network with local farmers and agricultural experts to gain insights into best practices and market trends.
In your research, also consider leveraging existing resources such as the apple farm startup guide available online, which can provide valuable insights into practical steps and checklists needed when starting your apple farming venture.
The more comprehensive your research is, the greater the likelihood your apple orchard business plan will succeed, supported by data-driven decisions and strategic positioning in the marketplace.
How Do You Identify Your Target Market Before Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
Identifying your target market is a critical step in crafting an effective business plan for apple farming . Knowing who your customers are not only shapes your marketing strategies but also influences your production decisions and overall apple farming business strategy .
To determine your apple farming target market , start by conducting comprehensive market research for apple farming . This research will help you understand consumer preferences, demographics, and purchasing behaviors. Key factors to consider include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level, and location of potential customers.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, values, and buying motivations, especially focusing on health-conscious consumers.
- Market Trends: Awareness of shifts towards organic and sustainably sourced products, as your business, Apple Orchard Innovations, aims to meet this demand.
Utilizing statistical data can offer valuable insights. For instance, the organic food segment is projected to grow by 10.5% annually, highlighting a significant opportunity for producers of organic apples. Additionally, increasing consumer awareness of sustainable practices is driving demand for locally-sourced foods.
Tips for Identifying Your Target Market:
- Conduct surveys and interviews to gather direct feedback from potential customers.
- Analyze competitors to understand their target audience and positioning.
- Stay abreast of market trends through industry reports and research publications.
Don’t overlook the importance of competitive analysis in agriculture . Identify who your competitors are targeting and assess their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you refine your own market focus and potentially find underserved niches in the market.
In summary, identifying your target market for an apple orchard business plan involves thorough market research and an understanding of consumer needs. Investing time in this crucial step can lead to a more successful written business plan for apple farm and ultimately, a thriving apple farming venture.
What Are The Key Regulations And Compliance Issues To Consider Before Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
When embarking on the journey of apple farming, understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for crafting a successful business plan for apple farming . Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations can significantly impact operational efficiency and sustainability. Here are some of the key areas to consider:
- Land Use Regulations: Depending on your location, zoning laws may dictate how land can be used. Ensure that the land designated for your apple orchard business is compliant with agricultural zoning.
- Environmental Regulations: Familiarize yourself with regulations governing water usage, pesticide application, and waste management. Regulations such as the Clean Water Act may apply, particularly if you are near water bodies.
- Food Safety Standards: Compliance with the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) is essential. This includes adopting practices that minimize the risk of contamination and ensuring product traceability.
- Organic Certification: If you aim to produce organic apples, you'll need to adhere to specific organic farming standards set by the USDA, which includes maintaining records and proving compliance with organic practices.
- Labor Laws: Understand labor laws related to hiring seasonal workers. This includes adhering to wage laws, work hour regulations, and safety standards under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Additionally, consider any state-specific agricultural compliance laws that may affect your operations. For instance, California has specific regulations regarding pesticide use that must be strictly followed.
Tips for Navigating Regulations
- Consult with an agricultural attorney to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
- Regularly review and update your practices to align with changing regulations, especially in areas like food safety and environmental compliance.
Staying informed about regulatory changes and best practices will not only enhance your apple farming business strategy but also help in avoiding potential legal pitfalls that could derail your plans and investments. Resources such as the National Organic Program and local agricultural extension offices can provide valuable information and assistance.
As you prepare your apple farming business plan steps , ensure that you dedicate a section to regulatory compliance. This will demonstrate due diligence and can also be attractive to potential investors who are focused on sustainability and legality.
Understanding these regulations early in your planning process will aid in crafting a comprehensive apple farming plan checklist , promoting a smoother startup and operational experience. To delve deeper into financial projections and metrics related to apple farming, consider visiting resources like this link .
How Do You Analyze Your Competition Prior To Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
Analyzing your competition is a crucial step in crafting a successful business plan for apple farming . Understanding the landscape of your market can help you to position your apple farming business effectively. With the rise of premium organic products, the apple farming sector has seen a significant increase in competition, making it essential to conduct a thorough competitive analysis in agriculture .
Begin your analysis by identifying the key players in your target market. Research local, regional, and national apple producers to gather insights on their business strategies. Consider the following:
- Market Share: Determine which companies dominate the market and what percentage of the market they hold.
- Pricing Strategies: Investigate how your competitors price their apples and other products.
- Product Offerings: Identify the types of apples they sell and any unique varieties or value-added products.
- Distribution Channels: Understand where and how competitors sell their products, such as farmers' markets, grocery stores, or online.
- Marketing Tactics: Analyze their promotional strategies and how they engage with consumers.
Utilizing tools such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis can help you gain a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape. For instance, if you find that your competitors are lacking in sustainable practices , this could represent an opportunity for your business, Apple Orchard Innovations , to stand out by emphasizing your commitment to environmental responsibility.
Tips for Effective Competitive Analysis
- Use market research for apple farming to gather data on competitors’ sales performance and customer satisfaction.
- Visit local orchards and markets to see firsthand how competitors operate and connect with customers.
- Stay updated with industry reports and trends, which can provide benchmarks to measure your performance against competitors.
According to recent statistics, the organic apple market has grown by 20% annually . Understanding who contributes to this growth and how can provide valuable insights into your own apple farming business plan steps .
Finally, it’s advantageous to continuously monitor your competition even after your written business plan for apple farming is complete. The market is dynamic, and staying informed allows you to adapt your strategies effectively and remain competitive in this thriving market.
What Resources And Tools Are Necessary Before Writing A Business Plan For Apple Farming?
Before embarking on the journey of crafting a business plan for apple farming , it is essential to identify and gather the right resources and tools that will support your venture. A well-prepared apple farming business plan not only guides your operations but also helps in securing funding and establishing partnerships. Here are some critical resources and tools you may need:
- Market Research Tools: Utilize platforms such as Statista and IBISWorld to gather market research for apple farming . These tools provide insights into consumer trends, market size, and competitive landscape.
- Financial Planning Software: Invest in financial management tools like QuickBooks or Xero for accurate financial projections for apple farming . This ensures you can effectively budget and manage your finances.
- Regulatory Guidelines: Access resources that outline relevant compliance and regulations specific to apple farming. The USDA and local agricultural departments provide valuable information on legal requirements.
- Networking Platforms: Join online forums or local agricultural associations to establish connections. These can offer insights and potential apple farming partnerships .
- Production Management Tools: Use agricultural management software like AgriWebb to create efficient production plans. This tool assists in tracking crop health and optimizing yield.
Tips for Gathering Resources
- Connect with local farmers to share insights on resources and techniques that work.
- Attend agricultural expos and workshops to learn about the latest tools and technologies in the industry.
Additionally, consider using templates for crafting a business plan for farmers which can streamline the writing process. These templates can provide structured sections on goals, strategies, and financial projections, ensuring that you cover all necessary aspects of your apple farming plan checklist . You may refer to resources like this guide for more specific instructions and templates.
Lastly, don't overlook the importance of establishing a clear apple farming business strategy . This includes identifying your unique selling proposition, production practices, and sustainability measures. These elements are vital for attracting the right investors and partners while positioning your orchard in a competitive market.
How Do You Develop A Clear Vision And Mission For Your Apple Farming Business Before Writing A Business Plan?
Developing a clear vision and mission for your apple farming business is essential to guiding your decisions and strategies throughout the planning process. A compelling vision will not only inspire your team but also resonate with your target market, helping to establish a brand identity. For Apple Orchard Innovations , this means articulating a future where sustainable practices and advanced technology coexist to produce premium organic apples.
To start, consider these critical components when defining your vision and mission:
- Vision Statement : Create a concise and aspirational statement that reflects your long-term goals. For instance, “To become a leader in sustainable apple farming, providing healthy, organic produce while nurturing the environment.”
- Mission Statement : Outline the purpose of your business. It should communicate what you do, who you serve, and how you do it. For example, “At Apple Orchard Innovations, we aim to revolutionize apple farming through sustainability and technology, ensuring transparency and quality for health-conscious consumers.”
- Core Values : Identify the principles that will drive your business operations. This might include sustainability, innovation, transparency, and community engagement.
- Long-Term Goals : Specify measurable goals that align with your vision and mission, such as achieving a 30% market share in organic apple sales within five years.
Conducting a thorough market analysis is pivotal to shaping your mission and vision. Research the apple farming market to identify trends, such as the increasing demand for organic products, which is growing at a rate of 10% annually according to industry reports. This data can help you align your mission with market expectations.
Tips for Developing Your Vision and Mission
- Engage stakeholders, including employees and potential customers, in discussions about your core values to ensure alignment.
- Regularly revisit and refine your vision and mission statements as your business evolves, especially as you gather feedback from market research.
- Utilize tools such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to better understand where your apple farming business fits within the competitive landscape.
Finally, ensure that your vision and mission are not just statements but are integrated into your apple farming business plan . This ensures that all strategies, from marketing to operations, remain aligned with your foundational goals. As you move forward, remember that clarity in your vision and mission will significantly enhance your ability to execute the rest of your business plan for apple farming effectively.
Business Plan Writing Steps
Writing a comprehensive business plan for apple farming requires careful preparation and strategic thinking. Below are essential steps that will guide you through the process, ensuring that your plan is thorough and effective.
Brainstorm Step Name #1: Conduct A Market Analysis
Conducting a thorough market analysis is a crucial initial step when writing a business plan for apple farming . This process enables you to understand the landscape in which you will operate and helps define your apple farming business strategy . A robust market analysis incorporates various elements, including understanding target demographics, identifying market trends, and assessing competitive forces.
To kick off your market analysis, consider the following key components:
- Market Size and Potential: Research the total market size for apples, focusing on organic apples, which are in high demand. For instance, the organic apple market has seen growth rates of over 15% annually, reflecting increasing consumer preference for healthier options.
- Target Market Segmentation: Identify your ideal customer. Are you targeting health-conscious consumers, restaurants, or grocery stores? Pinpointing your apple farming target market will refine your business direction.
- Trends in Consumption: Keep an eye on trends such as the rise in organic produce consumption. A report from the Organic Trade Association indicates that almost 7% of all fruits sold in the U.S. are organic, highlighting a shift in consumer behavior.
- Competitive Landscape: Conduct a thorough competitive analysis in agriculture . Analyze your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, market share, pricing strategies, and customer bases. This will help you identify opportunities where you can differentiate your apple farm.
- Pricing Strategies: Research current pricing models in the apple industry. Understanding average market prices for both conventional and organic apples will aid in establishing competitive pricing strategies.
To illustrate the competitive landscape for apple farming, consider the following benchmarks based on recent market reports:
In addition to these elements, leverage market research reports, surveys, and industry databases to deepen your understanding of the market. Establishing a connection between consumers and the source of their food can significantly enhance your marketing strategy.
Tips for Conducting Market Analysis
- Utilize online tools like Google Trends to gauge consumer interest in organic apples over time.
- Attend local agricultural fairs and farmer's markets to engage with potential customers and gather insights.
- Consider collaborating with local universities or agricultural extension services for data and research support.
Understanding these aspects will not only enhance your apple farming business plan but will also prepare you to make informed decisions as you move forward with developing your orchard. Remember, the insights gained from your market analysis can set the foundation for a successful apple farming venture.
Brainstorm Step Name #2: Define Your Unique Selling Proposition
Defining your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is a critical step in developing an effective business plan for apple farming . Your USP sets your apple farming venture apart from competitors and plays a vital role in attracting customers. For Apple Orchard Innovations, the focus should be on sustainability and technology integration, which can resonate deeply with the growing consumer demand for organic and environmentally responsible products.
Here are some key elements to consider when defining your USP:
- Sustainability Practices: Emphasize your commitment to organic farming methods, which align with current market trends. According to the Organic Trade Association, organic food sales in the U.S. alone reached $62 billion in 2021.
- Technological Integration: Highlight how modern farming techniques enhance productivity and product quality. Consumers are increasingly interested in how their food is grown, making transparency a selling point.
- Quality and Taste: Focus on producing premium organic apples that offer superior taste and quality compared to conventional apples. Engaging with taste tests and customer feedback can help establish this aspect of your USP.
Moreover, consider market dynamics that will bolster your USP:
Tips for Crafting Your USP
- Conduct a thorough market analysis for apple farming to identify what competitors offer and pin down your unique attributes.
- Engage directly with potential customers through surveys and social media to understand their preferences and values.
- Keep your messaging consistent across all marketing channels to build brand trust and recognition.
By clearly articulating your apple farming business strategy through a well-defined USP, you can effectively communicate your value to consumers. This clarity will not only influence your apple farming business plan steps but also help in securing partnerships, attracting investments, and ultimately driving sales.
For a comprehensive guide and template to writing a business plan for apple farming, consider exploring this resource .
Brainstorm Step Name #3: Gather Financial Data And Projections
Gathering financial data and projections is a crucial step in the process of writing a business plan for apple farming . This aspect not only helps in understanding the viability of your venture but also in securing funding and ensuring sustainable growth. Accurate financial projections will allow you to demonstrate the potential profitability of your apple farming business strategy and how it aligns with current market trends.
To develop realistic financial forecasts, consider the following components:
- Startup Costs: Estimate expenses such as land acquisition, equipment, seeds, irrigation systems, and labor costs. For example, the average startup cost for an acre of apple orchard can range from $30,000 to $50,000 .
- Operational Costs: Include annual costs such as maintenance, pest control, harvest, and marketing. In many regions, ongoing costs can be between $5,000 and $10,000 per acre annually.
- Revenue Projections: Assess potential income based on the expected yield per acre. An established apple orchard can yield between 15,000 to 20,000 pounds of apples per acre. With market prices ranging from $0.50 to $2.00 per pound, annual revenue could potentially reach $30,000 to $40,000 .
To further refine your financial projections, it’s essential to conduct thorough market research for apple farming. Understanding the demand in your specific area can significantly affect your pricing strategy and projected revenue.
Additionally, consider the funding options for apple farming . Grants and loans can significantly aid startups, with many agricultural programs offering financial assistance. Collaborating with local agricultural offices can provide valuable insights into available funding.
Tips for Financial Data Gathering
- Utilize agricultural financial planning tools to streamline forecasting.
- Connect with local apple growers for industry insights and benchmarks.
- Regularly update financial projections based on changes in market prices and operational costs.
By meticulously gathering financial data and projections, you are not merely filling numbers into your apple farming business plan steps ; you're creating a comprehensive and persuasive case for your venture, ultimately guiding your decision-making and informing potential stakeholders.
Brainstorm Step Name #4: Create A Detailed Production Plan
Creating a detailed production plan is a crucial step in writing a business plan for apple farming. This plan outlines the operational aspects of your apple orchard, ensuring that you have a clear roadmap from planting to harvesting and beyond. A well-crafted production plan helps you maximize productivity and efficiency while also addressing potential challenges. Here are the essential components to include:
- Site Selection: Evaluate soil quality, climate conditions, and water availability to determine the best location for your apple farm.
- Variety Selection: Choose the apple varieties that best suit your target market and local growing conditions. Popular choices include Fuji, Gala, and Granny Smith.
- Planting Schedule: Develop a timeline for planting, taking into account the optimal planting season and the maturity rates of your chosen varieties.
- Production Techniques: Assess sustainable practices such as organic farming, integrated pest management, and precision agriculture to enhance crop yield and quality.
- Labor Requirements: Estimate the labor force needed for planting, maintenance, and harvesting. This includes seasonal labor to manage fluctuations in demand.
- Equipment and Technology: Identify the necessary tools and technology for efficient apple farming, such as tractors, irrigation systems, and pest control solutions.
- Harvesting Plan: Establish methods for picking and transporting apples to minimize spoilage and maximize freshness.
- Post-Harvest Management: Develop a strategy for storage, packing, and distribution to ensure that your apples reach consumers in optimal condition.
To provide further clarity, here's a quick view of the recommended production benchmarks:
Tips for Developing a Robust Production Plan
- Regularly review and adjust your production plan based on market trends and yield data.
- Implement technology, like farm management software, to streamline operations and track production metrics.
- Incorporate feedback from experienced apple farmers and agricultural advisors.
By focusing on these elements within your apple farming business strategy, you can ensure a successful and sustainable operation. For more comprehensive guidance on crafting a business plan for apple farming, consider exploring resources that provide structured templates and expert insights, such as this detailed business plan template .
Brainstorm Step Name #5: Establish Partnerships And Collaborations
Establishing strong partnerships and collaborations is a critical step in developing a robust business plan for apple farming. These strategic alliances can enhance your apple farming business strategy by leveraging shared resources, expertise, and networks, which are essential for achieving success in a competitive market. Collaborating with local businesses, agricultural organizations, and research institutions can provide valuable support for your apple orchard's growth and sustainability.
Here are some key types of partnerships to consider:
- Local Farmers - Collaborating with neighboring farms can help in sharing knowledge of best practices and pooling resources to reduce costs.
- Research Institutions - Partnering with universities or agricultural research centers can provide access to innovative farming techniques, pest control methods, and sustainability practices.
- Food Distributors - Establishing relationships with food distributors ensures a reliable market for your produce, helping to streamline the sales process.
- Local Restaurants and Grocery Stores - Building partnerships with local businesses can promote your apples directly to consumers who prioritize local and organic options.
Moreover, the importance of collaboration can be reflected in the numbers. According to the USDA, farms that engage in collaborative practices see an average of 30% increase in their profitability compared to those that operate independently. This is particularly relevant in the current landscape where the demand for organic produce is rising. In fact, organic apple sales have seen a growth of 18% annually over the last five years.
Tips for Establishing Effective Partnerships
- Network regularly - Attend local agricultural fairs, workshops, and conferences to meet potential partners.
- Leverage social media - Use platforms like LinkedIn to connect with other professionals in the agricultural sector.
- Join local farming cooperatives - This can enhance your influence and presence in the market while allowing for knowledge sharing.
Additionally, funding options can be significantly enhanced through partnerships. For example, partnering with local schools for educational programs on sustainable apple farming can open doors to grants and sponsorships aimed at community-oriented projects. According to recent surveys, farms that create educational partnerships can increase their funding opportunities by nearly 25% .
Lastly, crafting a collaborative framework in your business plan for apple farming is essential. Including specific goals, expected outcomes, and responsibilities will ensure that all parties are aligned. This not only fosters healthy relationships but also strengthens the overall operational plans for apple farming.
Establishing a network of partnerships and collaborations can truly position your apple farming venture for success. As you proceed with writing a business plan for your apple farm, consider these strategic alignments invaluable in not only enriching your operational capabilities but also fostering a sustainable and profitable business ecosystem. For a comprehensive approach, explore this apple farming business plan that can guide you through the intricacies of agricultural business planning.
Brainstorm Step Name #6: Identify Funding Sources And Investment Opportunities
Identifying funding sources and investment opportunities is a crucial step in the process of creating a business plan for apple farming . The success of your apple orchard, like Apple Orchard Innovations , greatly depends on securing the necessary capital to implement sustainable practices and innovative technologies. Consider the following funding options:
- Self-Funding: Utilizing personal savings or funds can provide immediate capital with no debt obligations.
- Government Grants and Subsidies: Investigate federal and state programs aimed at supporting sustainable agriculture. For example, grants under the USDA’s Organic Certification Program might be available.
- Bank Loans: Traditional financing options such as agricultural loans can provide the necessary funds while allowing you to maintain equity ownership of the farm.
- Angel Investors and Venture Capital: Seek out investors interested in agricultural innovations and sustainable farming practices that align with your apple farming business strategy .
- Crowdfunding: Online platforms allow you to reach a broader audience who may invest in your vision and mission for sustainable apple farming.
To make informed decisions, it's important to analyze the requirements, benefits, and potential risks of each funding source. Below is a table showcasing some common funding avenues with potential amounts and terms:
In addition to funding sources, consider how to enhance your investment appeal:
Tips for Attracting Investment
- Develop a robust and transparent apple farming business plan that outlines your operational strategies and financial projections.
- Showcase sustainable practices that resonate with the growing trend of environmental responsibility.
- Network within the agriculture community and attend industry events to meet potential investors.
Understanding your financial needs and aligning them with appropriate funding sources can significantly boost your chances of successfully launching your apple farming venture. By leveraging various funding avenues, you can position Apple Orchard Innovations for growth while meeting the demands of today's health-conscious consumers.
Brainstorm Step Name #7: Outline Marketing Strategies And Channels
As you develop your business plan for apple farming , outlining your marketing strategies and channels is essential for creating a strong presence in the competitive agricultural market. For Apple Orchard Innovations , the focus on premium organic apples requires a tailored approach to effectively reach the target market and communicate the value of sustainable farming practices. Here’s a checklist of marketing strategies and channels:
- Digital Marketing: Utilize social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to showcase your apple farm's journey, from cultivation to harvest. Engaging content, such as videos and images, can connect consumers to the farming process.
- Email Marketing: Build an email list to share newsletters highlighting seasonal updates, new product launches, and promotions. This approach fosters a direct relationship with your clientele.
- Local Farmers' Markets: Participate in local farmers' markets to promote your brand and engage with the community. This face-to-face interaction can enhance brand loyalty.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Collaborate with local restaurants and grocery stores to feature your organic apples. A partnership can help increase visibility and credibility in your community.
- Online Sales Platforms: Establish a website with an online store to facilitate direct-to-consumer sales. Using e-commerce platforms can expand your reach beyond local customers.
- Content Marketing: Create a blog that addresses topics related to apple farming, sustainable practices, and healthy eating. Valuable content can attract potential customers and establish your expertise.
Consider these key statistics to reinforce your marketing approach:
Marketing Tips for Apple Farming
- Utilize seasonal promotions to attract customers, especially during harvest season when your apples are fresh and plentiful.
- Incorporate customer testimonials and reviews in your marketing materials to build trust and encourage new customers to purchase.
- Educate your audience about the benefits of organic apples and sustainable farming through engaging content and workshops.
In the realm of apple farming business strategy , it’s essential to align your marketing efforts with the overall vision and goals of Apple Orchard Innovations . Integrating these marketing strategies into your apple farming business plan will facilitate effective outreach and establish a strong brand identity that resonates with consumers. For more detailed guidance on crafting your apple farming plan, explore resources like the [Apple Farming Business Plan](/products/apple-farming-business-plan).
Brainstorm Step Name #8: Prepare An Operational Plan
Preparing an operational plan is a crucial element when writing a business plan for apple farming. This step ensures that all operational aspects of your apple farm are well defined, allowing for smoother execution and management. In crafting an effective operational plan, Apple Orchard Innovations can outline the key processes that will drive the success of their sustainable farming approach.
An operational plan should detail the day-to-day functions necessary to run the apple farming business efficiently. Here are the critical components to consider:
- Production Schedule: Establish a timeline for planting, maintaining, and harvesting apples. For instance, the typical apple growing cycle may include:
- Spring: Planting and initial care
- Summer: Pest control and irrigation
- Fall: Harvesting
- Winter: Pruning and preparing for the next cycle
- Resource Management: Identify the resources required, including labor, equipment, seeds, and technology. This also includes budgeting for these resources, ensuring you have adequate funding, as operational costs for apple farming can reach up to $10,000 per acre depending on the scale and style of farming.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Determine the logistics of getting products from the orchard to the consumer. This involves planning for transportation, storage facilities, and distribution channels.
- Quality Control Measures: Implement processes to maintain the quality of the apples harvested. This could involve regular soil testing, monitoring pest populations, and ensuring compliance with organic farming standards.
- Workforce Planning: Define the number of employees needed, their roles, and hiring timelines. Depending on the farm size, it may require anywhere from 5 to 20+ seasonal workers during peak periods.
- Technology Utilization: Identify the technological tools needed to enhance productivity. This includes precision agriculture tools, irrigation management systems, and data analytics for crop performance monitoring.
It's essential to integrate these operational components into the overall business plan for apple farming. This operational plan can then serve as a reference that aligns with the strategic goals laid out in the business plan.
Operational Plan Tips:
- Establish clear timelines and responsibilities for each operational task.
- Regularly review and adjust your operational plan based on harvest yields and market conditions.
- Engage your workforce in the planning process to leverage their expertise and insights.
For more detailed strategies and templates for your operational plan, check out the complete guide available at Apple Farming Business Plan .
Brainstorm Step Name #9: Set Measurable Goals And Objectives
Setting measurable goals and objectives is a crucial step in the writting a business plan for apple farming . It not only provides a direction for your apple farming business strategy but also establishes benchmarks that help track progress and success. Effective goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Your apple farm startup guide should include steps to evaluate your progress towards these goals. Here are key areas to focus on:
- Production Efficiency: Monitor the yield per acre and adjust production methods as necessary.
- Financial Performance: Regularly assess your revenue and expenses to ensure operating margins are on track.
- Market Penetration: Measure the number of customers acquired compared to the initial target.
Additionally, you should conduct regular reviews to assess whether your objectives align with changes in the market environment. Use the following strategies to refine your goals:
Goal Refinement Tips
- Regularly compare actual performance against your planned benchmarks.
- Be flexible and willing to adjust your goals based on market conditions or unforeseen challenges.
- Engage your team in the goal-setting process to foster commitment and accountability.
For an effective apple orchard business plan , clearly defined goals can be tied to specific financial projections for apple farming. For example, if your goal is to capture a specific share of the organic apple market, calculate the necessary production levels and sales strategies needed to achieve that target.
Setting measurable goals ensures that you can evaluate not just your production capabilities but also the effectiveness of your market research for apple farming and your overall apple farming business plan steps . Remember to document these goals in your plan, as they will serve as guiding principles for your farming operations moving forward. For support in creating a comprehensive business plan, consider utilizing templates available at Apple Farming Business Plan .
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
Apple Farming: Business Plan And Guide For Beginners
- Pinterest 8
Commercial apple farming is a very old business. Apple is a very common fruit and found throughout the world. It is very nutritious and very popular fruit. Apples are available in in all parts around the globe. Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus.
Apple tree originated in Central Asia, where it’s wild ancestor (Malus sieversii) is still found today. And apples actually have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apple is a very important fruit in many countries. And it has religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek and European Christian tradition.[ 1 ]
Apple trees are generally large in size if grown from seed. But today, commercial apple producers used to propagate apple cultivars by grafting onto rootstocks (which control the size of the resulting tree). Today, there are numerous varieties/cultivars of apples available throughout the world. Each of these varieties has especial characteristics. Different varieties are bred for various tastes and uses including cooking, cider production or eating raw.
Apple is actually a deciduous tree, generally standing between 6 and 15 feet tall in commercial cultivation and up to 30 feet in the wild. When cultivated, the size, shape and branch density are determined by rootstock selection and trimming method. Leaves of the apple trees are alternately arranged dark green-colored simple ovals with serrated margins and slightly downy undersides.
Today, apple is among the most popular fruits. Total worldwide production of apples in the year of 2018 was 86 million tones, with China accounting for nearly half of the total. Secondary apple producing countries are United States and Poland.
Table of Contents
Nutrition and Uses of Apples
All parts of the fruit (including skin, but not the seeds) are suitable for human consumption. The core, from stem to bottom, containing the seeds, is usually not eaten and is discarded. These fruits can be consumed in many different ways: juice, raw in salads, baked in pies, cooked into sauces and spreads like apple butter, and other baked dishes. They are sometimes used as an ingredient in savory foods, such as sausage and stuffing. Apple is a very nutritious fruit. A raw apple is about 14% carbohydrates, 86% water and negligible content of fat and protein. According to healthline , one medium apple (around 182 grams) offers the following nutrients:
- Carbs: 25 grams
- Calories: 95
- Fiber: 4 grams
- Potassium: 6% of the RDI (Reference Daily Intake)
- Vitamin C: 14% of the RDI
- Vitamin K: 5% of the RDI
In a word, apples are a good source of fiber and vitamins. They also contain polyphenols, which may have numerous health benefits.

Health Benefits of Apples
Consuming apples daily has many health benefits. You are probably familiar with the common English-language proverb “An apple a day keeps the doctor away”. Here we are trying to describe about the top advantages of consuming apples.
- Apples are a very good source of fiber and vitamins. They also contain polyphenols, which may have numerous health benefits.
- Apples are good source of fiber, so they are filling. You will be hungry less. And thus apples may aid weight loss.
- Consuming apples regularly promote hearth health in several ways. Apples are high in soluble fiber, which helps lower cholesterol.
- Eating apples is linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. This is possibly due to their polyphenol antioxidant content.
- Apples contain pectin, a type of fiber that acts as a prebiotic. This means it feeds the good bacteria in your gut.
- Apples have several naturally occurring compounds that may help fight cancer. Observational studies have linked them to a lower risk of cancer and death from cancer.
- Apples contain antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds that may help to regulate immune responses and protect against asthma.
- Consuming apples is also beneficial for promoting bone health, because it contains antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Apples contain compounds that may help protect your stomach lining from injury due to NSAID painkillers.
- According to animal studies, apple juice may help prevent the decline of neurotransmitters that are involved in memory.
- In a word, apple is very nutritious and safe for human health. You can consume apples daily.
Advantages of Apple Farming Business
Commercial apple farming is a very old and popular business. It is a very common business in many countries. There are numerous benefits/advantages of commercial apple farming business. Here we are trying to describe about the top advantages of commercial apple farming business.
- Commercial apple farming is a very old and popular business. Many people are already doing this business.
- If you are a beginner, you can learn more about apple farming from existing farmers.
- Commercial apple production is very profitable, and you will be able to make good profits from this business.
- You don’t have to worry about the future of this business. Because it is an old and established business.
- Apple trees are very hardy and grow easily, and it’s very easy to take care of them. You can easily take care of them, even if you are a beginner.
- Marketing apples is very easy. Because this fruit already has an established market demand and price. So, you don’t have to worry about marketing your products.
- Commercial apple farming is a profitable business. So, it can be a great employment source for the people. Especially for the unemployed educated people.
- Capital requirement in commercial apple farming business is relatively less. But you will get profits for many years.
- Apples are very nutritious and have numerous health benefits. You can enjoy fresh apples if you start your own apple production business.

How to Start Apple Farming Business?
Apple trees are very strong and hardy and they generally require less caring, and caring the plants is very easy and simple. You can learn practically from an experienced farmer in your area before starting this business commercially. You can take good care of the plants even if you are a beginner. Here we are trying to describe more information about starting and operating commercial apple farming business from planting, caring to harvesting and marketing.
Step 1. Select Good Site
You have to select a very good location for starting your apple farming business. Apple plants grow well in loamy soil which is rich in organic matter. Good drainage system is a must, because apple plants can’t tolerate water logging. pH range of the soil should be between 5.5% and 6.5%. Although, you can use your existing land if the land meet all the demands listed above.
Step 2. Prepare Soil
Preparing the soil perfectly before planting is very important for growing apple plants. Do ploughing, cross ploughing of land and then level the land. And then prepare the land in such way that water stagnation should not occurred in field. Because, apple plants can’t tolerate water logging. You should add as much organic content as you can while preparing the soil. Adding organic content will help the plants to grow well and produce more.
Step 3. Consider Climate Requirements
Apple plants can be grown in right climatic conditions. These plants can be grown at altitudes 1500 to 2700 meter above sea level.[ 2 ] Temperature during the apple growing season should be around 21°C and 24°C . These trees require between 100 cm to 125 cm of annual rainfall (evenly spread throughout the year). Too much of rainfall and fog near the fruit maturity period will result in poor fruit quality with improper color development of fruit and fungal spots on the fruit surface. Apple cultivation is not suitable where the high velocity of winds are expected.

Step 4. Choose Right Apple Variety
Currently, there are numerous varieties/cultivars available to choose from. You can choose any variety which grows well in your area. Consult with some existing farmers for better recommendation. Common and popular cultivars are Alice, Ambrosia, Ananasrenette, Arkansas Black, Aroma, Belle de Boskoop, Bramley, Cox’s Orange Pippin, Cox Pomona, Cripps Pink, Discovery, Egremont Russet, Fuji, Gala, Bloster, Golden Delicous, Goldrenette, Granny Smith, Honeycrisp, James Grieve, Jonagold, Lobo, Mclntosh, Pacific Rose, Red Delicious, Shampion, Stark Delicious, SugarBee, Summerred, Tellissaare, Yellow Transparent etc.
Step 5. Propagation
Commercial propagation of apple plants is done by budding and tongue grafting methods. Purchase the planting material required for apple farming from the registered nurseries.
Step 6. Purchase Plants
Apple plants are easily available in the areas where the plants grow. You can easily purchase from any of your nearest nurseries. Today, many nurseries have online presence. So, you can order the plants online.
Step 7. Planting
Apple plants can be planted at anytime. But it is recommended to plant the plants during January and February months. Average number of plants in an area of one hectare may range from 200 to 1250. Although, stocking density depends on numerous factors. Stocking density can vary depending on the planting system. 4 different types of planting density are implemented. Such as low, moderate, high and ultra high density. Generally less than 300 plants per hectare in the less density type, 300-500 plants in moderate density, 500-1300 plants in high density, and more than 1300 plants per hectare in high density type.

Step 8. Caring
Apple plants are very strong and hardy. They generally grow well in less caring and other management. Although, taking additional caring will help the plants to grow well and produce more. Here we are trying to describe more about the caring process in commercial apple farming business.
Fertilizing: Providing the plants with adequate fertilizers is very important for good growth of the plants. Provide adequate organic fertilizers (such as farm yard manure) along with other chemical fertilizers. The ratio of K, P, and N which is applied in an orchard of optimal fertility is 70:35:70 grams per year age of the tree. Use appropriate application of fertilizer for deficiency of boron, zinc, manganese and calcium.
Watering: Irrigation requirement in commercial apple farming is around 115 cm per annum which should be scheduled in 14 to 20 watering/irrigation. Watering should be provided at an interval of 6 to 10 days during the summer season, and at an interval of 3-4 weeks during the winter season. And at least 8 irrigation are required during the critical period (April to August), after fruit set.
Weeding: Weeds consume nutrients from the soil, and the plants suffer. So, timely and regular weeding is very important.
Inter-cropping: Inter-cropping is a great way to earn some extras. It also helps to minimize weed problem. Green manuring crops like bean and sunflower can be cultivated in the early years of apple planting in order to increase soil texture and nutrients of the soil.
Mulching: Mulching helps to retain moisture into the soil. It will also help to reduce the growth of weeds. You can use organic materials as mulch.
Training and Pruning: For getting good growth of the plants and good production, timely training and pruning is very important. The apple plants are trained as per growth habit and vigor of the rootstocks. The standard apple plants are trained on a modified central leader system to receive proper light. This improves fruit color and also minimizes the effect of heavy snowfall and hail. Spindle bush system is best suitable for high-density apple planting under mid hill conditions.
Step 9. Control Pests and Diseases
As we have mentioned above ‘apple trees are very strong and hardy’. And they are less susceptible to pests, diseases or other problems. The main pests in apple farming are eriosoma lanigerum, quadraspidiotus perniciosus, thrips rhopalantennalis, pseudoulacaspis sp. etc. And the main diseases found in apple farming are venturia, inaequilis, phytophthora cactorus, agrobacterium tumefaciens, sclerotium rolfsii, cankers, die-back diseases, etc. You can apply carbendazim, copper oxychloride, mancozeb and other fungicides for controlling the diseases.
Step 10. Harvesting and yield
Depending on the variety, the apple trees start bearing fruits from the 8th year. Apple productivity goes on increasing from the 8th year to 17th year, and afterward production remains constant up to 30 years. Lifespan of the apple trees can be extended up to even 40 years depending upon the climatic conditions. Generally the fruits are harvested before they are fully ripe.
There are many tasks/activities to follow after harvesting apples. Post-harvesting tasks are pre-cooling, grading according to their size and weight, storage, packing and transporting. Do all these activities very carefully. It’s not possible to tell the exact amount. Because exact number depends on numerous factors. On average, you can expect around 10-12 tonnes per hectare.

Step 11. Marketing
Marketing apples is very easy and simple. Apples have very good demand and value throughout the world. You will be able to easily sell your products in the local market.
These are the common steps and ways for starting and operating a successful apple farming business. Hope this guide has helped you! Good luck!
Recommended for You

Grape Farming: Business Plan And Guide For Beginners

Almond Farming: Business Plan And Guide For Beginners

Olive Farming: Business Plan And Guide For Beginners

Coconut Farming: Is It Profitable? Best Business Plan!

Orange Farming: Business Plan And Guide For Beginners

Dragon Fruit Farming: Business Plan For Beginners
4 thoughts on “apple farming: business plan and guide for beginners”.
Thankyou sir , nice article on apple 🍎 farming.
I am interested in commercial apple farming business. I have more then 10 acres land. Is it possible to start commercial apple farming in Nadia, West Bengal, India?
No, your location is probably not suitable for commercial apple farming business. Please consider another fruit production business. Good luck!
Hi Sujit Malakar I have 5000 tons aplle in cold storage. I want sell my apples and india have big potantial for this but ı am not able to find a buyer in India can you help me? İf you can help me please contact with me ı can send you our products photos. İt could be profitable for both of us E-mail:[email protected]
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
A successful apple orchard business requires a combination of agricultural skills, business acumen, and an understanding of market dynamics. Steps on How to Write an Apple Orchard Business Plan. Executive Summary; Daniel Conwell® Apple Orchard, Inc. is a thriving agricultural enterprise located in Traverse City, Michigan.
Orchard Size. Apple production requires a lot of labor, and will take a lot of your time. You'll probably also need additional seasonal help for harvesting and packing the fruit. Although every farm system is unique, 10 acres could be considered a minimum size for a commercial apple-growing business. A 10-acre operation is large enough to use ...
When you start to harvest, you might produce 20,000 bushels a year, bringing in $800,000 in revenue. That would mean $160,000 in profit, assuming that 20% margin. If you expand your orchard, you might produce 30,000 bushels per year, bringing in $1,200,000 in revenue. That would give you a nice annual profit of $240,000.
Embarking on a new business venture can be an exhilarating yet daunting journey. Before crafting your business plan for an Apple Orchard, it's crucial to lay the groundwork.This comprehensive 9-step checklist will guide you through the essential preparatory measures, ensuring your venture is poised for success from the outset.. Steps Prior To Business Plan Writing
Sale of 50 Gallons of Fresh Apple Cider at $5 per Gallon: Total Revenue = $250, Profit = $125. Pick-Your-Own Entry Fee for 50 Visitors at $10 each: Total Revenue = $500, Profit = $450 (after considering operational costs). ... Business Plan Template for a Fruit Orchard. Executive Summary: Overview of your fruit orchard's mission, vision, and ...
For the Orchard Origins business plan, let's assume a target of 5 acres of land to accommodate 500-750 apple trees. Consider the optimal tree spacing for your chosen apple varieties, which can range from 12 to 18 feet between rows and 8 to 15 feet between trees within the row.
For an effective apple orchard business plan, clearly defined goals can be tied to specific financial projections for apple farming. For example, if your goal is to capture a specific share of the organic apple market, calculate the necessary production levels and sales strategies needed to achieve that target.
New Apple Grower - Overview . Mike Basedow. CCE ENYCHP. Dec 2019 . Modified from A. Wallis (2016) and K. Iungerman. (2009) ... economic profile will differ for direct retail and/orpick your own orchards. A strong business plan is the best way to plan for a successful orchard business. Business plan guidance can be found in the beginning
Step 1. Select Good Site. You have to select a very good location for starting your apple farming business. Apple plants grow well in loamy soil which is rich in organic matter. Good drainage system is a must, because apple plants can't tolerate water logging. pH range of the soil should be between 5.5% and 6.5%.
Step 2: Choose Your Apple Tree Variety. The core of starting an apple orchard comes down to the varieties you are growing. There are so many types of apples to choose from! Luckily, apple trees do best in a mixed orchard, so it is beneficial to select multiple varieties.