Captain's Log
Business News, Issues, Insights, Controversies


Business Case vs Business Plan: Do You Know the Difference?

Captain’s Log, Entry 7286.4 — Business Case, Business Plan. Do the Terms Mean the Same Thing? It’s a question you may have to answer many times for your colleagues. In brief, the case is organized around an action, while the plan is organized around the business.
Many people ask: What’s the difference between a Business Case , on the one hand, and a Business Plan on the Other? Surprisingly few people in business are prepared to answer such questions in clear terms.
People often use the terms interchangeably or ask for one of them when they mean the other. Why?
Business Case, Business Plan. Do the Terms Mean the Same Thing?
Firstly, they no doubt confuse the two because both tools support decision-making and planning. Secondly, they confuse the two probably because both tools project future business results. The conclusion, briefly, is that these tools complement each other, but they differ. They address different questions. And they serve different purposes.
Before you set out to build a business case or build a business plan, or before you ask someone to bring you one or the other, be sure that everyone understands clearly the special focus of each.
Business Case, Business Plan: About the Action Or About the Business?
The business case and the business plan both look into the future and complement each other. How do they differ? In a nutshell, a business case concerns an action , while the business plan focus is the business.
Firstly, use the business case instead to answer “What happens if…?” questions like these:
- What are the financial outcomes if we choose the IBM proposal? And what can we expect if we choose the HP Proposal?
- What will we need as a capital budget next year if we decide to buy the service vehicles instead of leasing them?
- And, does the investment in new phone technology justify the cost? And, is there a positive ROI?
Secondly, use the business plan to answer questions about the future of the business such as these:
- What will we see in sales and margins next year? And, what can we expect in revenue growth next year?
- What should we set as targets for strategic business goals? And, what are our business performance and financial position when we reach those goals?
- How many years will it take before this startup company starts earning profits?
Business Case vs Business Plan
When deciding which tool you need, or when explaining the difference to someone else, start with the major differences that follow from focusing either on an action or focusing on the business:
| A or single decision and its alternatives. | An or the enterprise. The plan may cover a single product or product line or an organization. | |
| and major non-financial impacts that follow from the action. Also predicts financial metrics, such as ROI, IRR, NPV and Payback Period. | of the business. Predicts the main income statement categories, such as revenues and profits. May also include Pro-forma financial statements for future years. | |
| Business for the . Also, refers to major components of proposed action. | Business for the Also, focuses on for reaching goals | |
| A and a for the case and for one or more action scenarios. | The for the This shows where and how the business makes money. This model is similar to an income statement, but with trends and competitor actions. | |
| such as NPV, IRR, ROI, payback period, and TCO. These refer to future cash flows. Also include important . | in terms of revenues, margins, and profits. Also measures in terms of important balance sheet categories | |
| The scope of the case may include benefits and instead of the parent organization. | May focus on May also focus on the to work the within budget. |
Business case vs Business Plan: Take Action!
The article Business Plan presents an overview of business plan contents and usage. The article Business Case introduces case building and business case analysis.
Visit the Master Analyst Shop online. Download the premier business case ebooks and software today!
Learn and practice the premier case building methods at a Business Case Seminar . Learn case building from our books, the Business Case Guide and the best selling authority, Business Case Essentials .
By Marty Schmidt . Copyright © 2004-2023. Solution Matrix Ltd, Publisher.
Author: Marty Schmidt
Marty Schmidt is Founder and President of Solution Matrix Limited, a Boston-based firm specializing in Business Case Analysis. Dr. Schmidt leads the firm's Management Consulting, Publishing, and Professional Training activities. He holds the M.B.A degree from Babson College and a Ph.D. from Purdue University. View all posts by Marty Schmidt
Transform teamwork with Confluence. See why Confluence is the content collaboration hub for all teams. Get it free
- The Workstream
- Project management
- Business case
How to write a successful business case
Browse topics.
In business, having a great idea is only the first step toward bringing it to life. While a unique and innovative concept is essential, you will also need resources and support to guarantee success.
To secure the necessary resources and support, you must present a compelling argument that demonstrates the value and feasibility of your proposed project or initiative. A well-crafted business case can make all the difference.
In this article, you’ll learn what a business case is, its key components, and how it differs from a business plan. You’ll also discover the benefits of having a solid business case and get a blueprint for creating one that effectively conveys the value of your initiative.
What is a business case?
A business case is a document that justifies undertaking a project or initiative. Its main purpose is to assess the potential benefits, costs, and risks, providing evidence to decision-makers on why the investment is worthwhile.
Key elements of a business case
A well-structured business case typically includes the following key elements:
- Executive summary : This is a concise overview of the business case, highlighting the business problem, proposed solution, and expected benefits.
- Problem statement : This clearly describes the business issue or opportunity the project aims to address.
- Analysis of options : This involves evaluating potential solutions, including their pros, cons, and estimated costs.
- Recommended solution : Based on the analysis, this is the proposed course of action, along with a justification for its selection.
- Implementation plan : This involves making a high-level roadmap outlining the project timeline , milestones, necessary resources, and key deliverables.
- Financial analysis : This includes a cost-benefit analysis that breaks down the project's expected costs, benefits, and return on investment (ROI).
- Risk assessment : This helps identify potential risks associated with the project and strategies to mitigate them, including sensitivity analysis.
- Stakeholder analysis : This is an overview of the individuals or groups that the project impacts and their level of influence and interest.
- Conclusion : This summarizes the key points and offers a compelling call to action for decision-makers to approve the project.
Who typically writes a business case?
The business case is usually written by the individual or group proposing the project. This could be a project manager , entrepreneur, or other stakeholder advocating for a particular course of action. Some companies may have a designated role or team responsible for developing business cases.
The project sponsor usually prepares the business case, but all relevant team members should contribute. This includes subject matter experts from finance, HR, IT, and other pertinent functions who can offer specialized insights and information.
What’s the difference between a business case and a business plan?
A business case and a business plan serve different purposes:
- A business case justifies a specific project by outlining its benefits, costs, and risks. It focuses on a single initiative to secure approval and funding.
- A business plan provides a comprehensive overview of an entire business, detailing its business strategy, market analysis, financial projections, and operational plans. It serves as a long-term roadmap for the company.
In summary, a business case is a targeted, short-to-medium-term analysis of a particular project. In contrast, a business plan is a broader, long-term strategic document encompassing the whole business.
What are the benefits of having a business case?
A well-crafted business case provides numerous benefits for companies undertaking projects or initiatives.
Defined problem and solution
A business case clearly defines the problem or opportunity and outlines the proposed solution. It provides a roadmap for the project, ensuring all stakeholders understand the goals and business objectives.
Informed decisions based on analysis
A business case enables informed decision-making by presenting a thorough analysis of costs and benefits. It allows leaders to weigh the project’s merits against other priorities and make evidence-based choices.
Efficient use of resources
A business case helps optimize resource allocation by justifying the investment necessary for the project. It helps direct people and funds toward initiatives with the most significant strategic value and ROI.
Identification and mitigation of risks
A business case identifies potential pitfalls through a comprehensive risk assessment and outlines mitigation strategies. This proactive approach increases the likelihood of project success and minimizes the impact of challenges that may arise.
Alignment of expectations
A business case aligns stakeholder expectations by documenting the expected outcomes, timelines, and responsibilities. It also serves as a communication tool and a point of reference throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring everyone remains focused on the agreed-upon objectives.
Step-by-step guide to creating a business case
Developing a compelling business case involves a systematic approach to gathering information, analyzing options, and presenting a clear recommendation.
Define the problem
Start by identifying the issue or opportunity that the project aims to address. Clearly articulate the problem statement and its impact on the company. Gather relevant data and evidence, such as customer feedback, market trends, or internal metrics to support the problem statement.
Brainstorm potential solutions
Engage key stakeholders to generate a range of possible solutions. Consider both internal capabilities and external resources. Evaluate each option based on its feasibility, cost, and alignment with organizational goals. A brainstorming template can help keep the conversations productive.
Analyze your financials
Conduct a thorough financial analysis of the proposed solutions. Estimate the costs associated with each option, including upfront investments and ongoing expenses. Project the expected benefits and ROI over a defined time frame.
Assess risk
Identify potential risks of each solution, such as technical challenges, market uncertainties, and resource constraints. Develop mitigation strategies to address these risks and reduce their impact on the project's success. A risk assessment matrix template simplifies the process.
Engage stakeholders
Collaborate with key stakeholders throughout the process to gather input, build consensus, and secure buy-in. Regularly communicate progress and seek feedback to ensure alignment and support for the recommended solution.
Draft the business case
Compile the gathered information into a comprehensive document. Include an executive summary, problem statement, analysis of options, recommended solution, implementation plan, financial analysis, and risk assessment. Use clear, concise language and visuals to convey the key points.
Review and refine
Share the draft business case with relevant stakeholders for review and feedback. Incorporate their input and refine the document to ensure clarity, accuracy, and persuasiveness. Prepare to present the business case to decision-makers and address any questions or concerns.
Implement and monitor
Develop a detailed implementation plan post-approval such as with a project plan template . Assign responsibilities, allocate resources, and establish timelines. Regularly monitor progress against milestones and key performance indicators. Communicate updates to stakeholders and make adjustments as necessary to ensure successful project delivery.
Write a winning business case with Confluence
Whether presenting a proof of concept or seeking approval for a large-scale initiative, a well-crafted business case is essential. It demonstrates the project’s alignment with the company’s strategic plan and justifies the investment of time, resources, and budget.
Confluence simplifies this process with built-in best practices and templates. It allows key company-wide and project-related knowledge to be centralized in one place, making it instantly accessible and ready to move your business forward.
Create a business case that gets attention and approval with Confluence:
- Collaborate in real-time : Invite your peers to collaborate with you through real-time editing and inline comments. Project collaboration is vital to developing a comprehensive business case that you can share with the broader organization.
- Templates and structure : Organize your content logically and professionally with business case templates and project templates . These templates help cover all essential elements, from project scope to financial analysis.
- Visual appeal : Use charts, graphs, and other visuals to make your data compelling and easy to understand. Compelling visuals can help convey the value and feasibility of your proposed project.
- Centralized information : Keep all your documents, data, and feedback in one place so everyone is on the same page. Centralized information facilitates efficient project planning and project execution .
- Easy sharing : Share your business case with stakeholders effortlessly and get real-time feedback to make necessary adjustments. Seamless sharing and collaboration streamline the approval process.
Confluence eases the headache of scattered documents, unreliable information, and disconnected team members by bringing all your work into a single, connected workspace. Content-integrated pages feed into secure workspaces that become your company’s source of truth, whether you’re working at startup velocity or enterprise scale. With Confluence, you can develop a business case that effectively communicates your project’s strategic value. From defining the project scope to outlining the implementation plan, Confluence provides the tools for successful project collaboration. Start building your winning business case today and turn your ideas into reality. Make a free business case with Confluence today.
You may also like
Project poster template.
A collaborative one-pager that keeps your project team and stakeholders aligned.
Project Plan Template
Define, scope, and plan milestones for your next project.
Enable faster content collaboration for every team with Confluence
Copyright © 2024 Atlassian

Business Plan vs Business Case: What is the Difference

Businesses use a variety of documents to plan and track their progress. Two common types of business documents are business plans and business cases. Both document the current state of the business, outline future goals and detail how those goals will be met. However, there is a key difference between these two types of documents: a business case focuses on strategy while a business plan focuses on investment and viability.
A business plan is a high-level overview of the entire company. It includes the company's mission statement, an analysis of the competitive landscape, market research, target audience definitions, objectives and strategies for achieving them as well as important financial projections and SWOT analysis.
A business plan is often focused on gaining investment or deciding if a business will be viable going forward
What is a Business Case?
On the other hand, a business case is primarily used as an internal document to justify an action or strategy within an existing business.
A business case will often include a cost-benefit analysis which weighs the pros and cons of taking a particular course of action. This type of analysis is helpful in decision-making because it forces businesses to consider all potential outcomes before committing to anything.
Project vs Overall Business Strategy
Often, the best way of deciding whether a business plan or a business case is needed is by considering the aims.
If you or your business are looking at a specific project or strategy, a business case may be more suited to your needs. For example
- A new product launch
- An expansion into a new market
- The introduction of a new process or technology
On the other hand, if you are starting up a business or want to take a more holistic view of your company's direction, then a business plan may be what you need.
Scope & Aims of a Business Case
A business case cannot be considered a business plan for a particular project or strategy. A business plan is a high-level document that looks at the entire business and not a specific project or goal.
A business case is a more specific document that looks at a particular project or strategy. It includes a cost-benefit analysis which weighs the pros and cons of taking a particular course of action. This type of analysis is helpful in decision-making because it forces businesses to consider all potential outcomes before committing to anything.
The Key Differences: Business Plan vs Business Case
| Used for overall business strategy and planning | Used for projects |
| Used for start-ups and businesses looking to grow | Used to make key decision within an existing business |
| More comprehensive and focus on financial viability | Looks at the risks of the project |
| Used to convince investors | Used to convince managers and boards |
Looking for a Business Plan For Your Business or Startup?
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions

- Strategy Templates
Consulting Templates
- Market Analysis Templates
- Business Case

- Consulting Proposal
- Due Diligence Report
All Templates
How to write a solid business case (with examples and template).

Table of contents
What is a business case, business case vs. business plan, how to structure your business case, how to write a business case.
- Business Case PowerPoint template
ROI calculator template
- Key elements of a strong Business Case
Frequently asked questions
Nearly every new project requires approval—whether it's getting the green light from your team or securing support from executive stakeholders. While an informal email might suffice for smaller initiatives, significant business investments often require a well-crafted business case. This guide, written by former consultants from McKinsey and Bain, will help you write a compelling business case. It provides the steps and best practices to secure the necessary support and resources for a successful project.
A business case is a written document (often a PowerPoint presentation) that articulates the value of a specific business project or investment. It presents the rationale for the project, including the benefits, costs, risks, and impact. The main objective is to persuade internal stakeholders to endorse the project.
A business case answers the questions:
- Why should we do this?
- What is the best solution?
- What will happen if we proceed with this investment decision?
Business cases can serve many purposes, but here are a few common reasons for developing one:
- Implementation of a new IT system
- Launching a new product line
- Construction of a new manufacturing plant or data center
- Opening new retail locations or expanding into international markets
- Implementation of new compliance and risk management systems
- Acquiring a competitor or a complementary business
- Investing in building a new capability
- Obtaining additional resources for an ongoing initiative
- Deciding whether to outsource a function
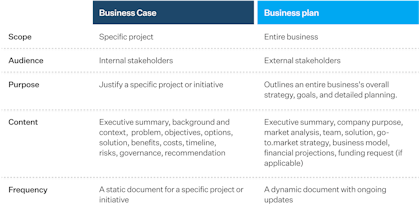
Simply put, a business case justifies a specific project or initiative, while a business plan outlines an entire business's overall strategy, goals, and detailed planning.
Investors use a business plan to make informed decisions about investing. It details the financial, strategic, and operational aspects of a business, helping investors assess the potential return on investment. In contrast, a business case is narrowly focused on a particular project or initiative. It helps stakeholders evaluate the potential impact of that specific project on the business. Both documents require thorough research, careful writing, and effective presentation. Here's an overview of their differences:
Before writing your business case
The fate of your project or initiative will usually lie with a small group of decision makers. The best way to increase your chances of getting a green light is to engage with stakeholders, gather their insights, and build support before writing the business case. Use their input to construct a rough draft and present this draft back to key stakeholders for feedback and approval. Only once you have understood their priorities and concerns should you proceed with writing the final business case.
To get buy-in from your stakeholders, you must tell your "story" so that it is easy to understand the need, the solution you're proposing, and the benefits to the company. Generally, decision-makers will care most about ROI and how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals – so keep those issues front and center.
In our experience, the business case structure below is the most logical and effective, but you should generally use whatever format or template your company uses. If no templates exist, use the structure below and find a solid template (you'll find a link to a template later in this post).
Whatever structure or template you apply, remember that your story needs to be clear above all else.
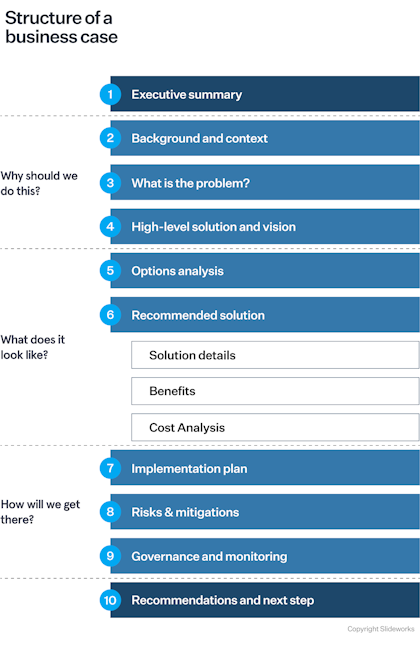
Let's go through each of the 10 sections one-by-one:
1. Executive Summary
A one-page summary providing a concise overview of the business case.
Highlight the key points, including the problem or opportunity, proposed solution, and expected benefits.
We recommend structuring your summary using the Situation-Complication-Solution framework (See How to Write an Effective Executive Summary ) . The executive summary should be the final thing you write.
2. Background and context
Start with the why. Outline the situation and the business problem or opportunity your business case addresses. Clearly describe the problem's impact on the organization.
This section may include an overview of the macro environment and dynamics, key trends driving change, and potential threats or opportunities. Share data that conveys urgency . For example: Is customer satisfaction dropping because of a lack of product features? Is an outdated IT system causing delays in the sales process? Are you seeing growing competition from digital-first players in the market? Are you seeing an opportunity as a result of changing customer needs?
3. What is the problem?
This is a key part of your business case. Your business case is built from your analysis of the problem. If your stakeholders don't understand and agree with your articulation of the problem, they'll take issue with everything else in your business case.
Describe the underlying issues and their solutions using data. You might include customer data, input from end users, or other information from those most affected by the problem.
4. High-level solution and vision
Start with a high-level description of the solution. Clarify the specific, measurable objectives that the project aims to achieve. Ensure these objectives align with the organization's strategic goals.
5. Option analysis
You have now answered the question: Why should we do this project? - and you have outlined a compelling solution.
In this section, you identify and evaluate different options for addressing the problem. Include a "do nothing" option as a baseline for comparison. Assess the pros and cons of each option, considering factors like cost, feasibility, risk, and potential benefits.
See a more in-depth article on how to think about and present risks in our blog post " Mastering Risk Mitigation Slides: A Best Practice Guide with Examples ".
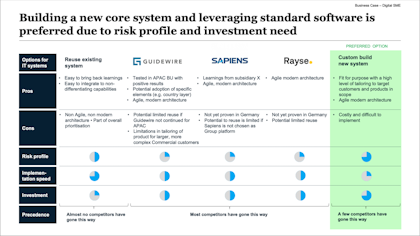
Slide summarizing various options for a new IT system. Example from Slideworks Business Case Template Slide
6. Recommended Solution
Solution Details Propose the preferred solution based on the options analysis. Describe the solution in detail, including scope, deliverables, and key components. Justify why this solution is the best choice.
Benefits Describe the benefits (e.g., cost savings, increased revenue, improved efficiency, competitive advantage). Include both tangible and intangible benefits, but focus on benefits you can quantify. Your stakeholders will want to know the financial impact.
Be very clear about where your numbers come from. Did you get them from colleagues in Marketing, Finance, HR, or Engineering? Stakeholders care about the sources for these assumptions and are more likely to trust your numbers if they come from (or are validated by) people they trust.
Cost Analysis In this section, you provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with the proposed solution. Include initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and any potential financial risks.
Compare the costs against the expected benefits to demonstrate return on investment (ROI).
7. Implementation plan
Outline a high-level plan for implementing the proposed solution . Include key milestones, timelines, and dependencies. Describe the resources required, including personnel, technology, and funding.
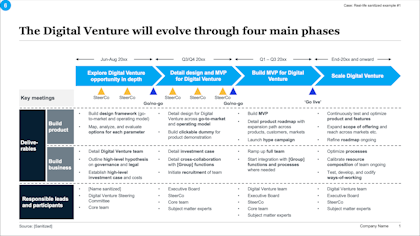
Roadmap example - New digital venture. Slideworks Business Case Template
8. Risks and mitigations
In this section, you highlight potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Try to focus on the most important risks (you don't need to account for every potential scenario). These typically include those affecting cost, benefits, and schedule, but they can also include risks to the team, technology, scope, and performance.
Be realistic when you write this section. Transparency will gain the confidence of stakeholders and will demonstrate your foresight and capability.
Consider ranking your identified risk areas according to "likelihood of risk" and "impact of risk" (as shown in the example below). Then, propose mitigation strategies to manage and minimize risks.

Example of Risks Slide - Slideworks Business Case Template

Risks and mitigation slide - Slideworks Business Case Template
9. Governance and monitoring
Establishing a clear governance structure ensures that there is a defined hierarchy of authority, responsibilities, and accountability. A definition of the following groups and roles are often included:
- Steering Committee : A group of senior executives or stakeholders who provide overall strategic direction, make high-level decisions, and ensure that the project aligns with organizational goals.
- Project Sponsor : An individual or group with the authority to provide resources, make critical decisions, and support the project at the highest level. The sponsor is often a senior executive.
- Project Manager : The person responsible for day-to-day management of the project, ensuring that the project stays on track, within budget, and meets its objectives. The project manager reports to the steering committee and project sponsor.
- Project Team : A group of individuals with various skills and expertise necessary to carry out project tasks. The team may include internal staff and external consultants.
You might also define what monitoring and reporting mechanisms that will be used to track the project's progress, identify issues early, and ensure accountability. These mechanisms often include specific Project Management Tools, ongoing status reports, and meetings.
10. Recommendations and next steps
In this last section, you summarize the key points of the business case and make a final recommendation to the decision-makers . Remember to Include your ROI number(s) again and repeat how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals.
Consider ending your business case with a final slide outlining the immediate actions required to move forward with the recommended solution.
Learn about how to fit in a business case in your commercial due diligence report in our article here .
Business Case PowerPoint template
An effective business case requires both the right content and structure. A strong template and a few best practice examples can ensure the right structure and speed up the process of designing individual slides.
The Slideworks Business Case Template for PowerPoint follows the methodology presented in this post and includes 300 PowerPoint slides, 3 Excel models, and three full-length, real-life case examples created by ex-McKinsey & BCG consultants.
Often, companies have a preferred method of calculating a project's ROI. If this is not the case, you should use the one most appropriate to your project—break-even analysis, payback period, NPV, or IRR.
Key elements of a strong Business Case
Involve subject-matter experts To develop a comprehensive business case, draw on insights from experts who understand the problem's intricacies and potential solutions. Involve colleagues from relevant departments such as R&D, sales, marketing, and finance to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Involve key stakeholders Get input from all relevant team members, including HR, finance, sales, and IT. This collaborative approach ensures the business case is built on verified expert knowledge. Encouraging teamwork and buy-in from internal stakeholders helps build a strong foundation of support.
Understand audience objectives Align your business case with the company’s strategic objectives and future plans. Clearly demonstrate how the project supports long-term company success. Consider the competition for resources and justify the investment by showing its relevance and importance.
Set a clear vision Communicate the purpose, goals, methods, and people involved in the initiative clearly. Detail what the project aims to solve or achieve and its impact on the organization. This clarity helps stakeholders understand the overall vision and direction of the project.
Be on point Be concise and provide only the necessary information needed for informed decision-making. Base your details on facts collected from team members and experts, avoiding assumptions. This precision ensures your business case is credible and actionable.
Check out our Go-To-Market Strategy post to take the next step on bringing your business idea to life.
What is the difference between a project business case and a project charter?
A project charter and a business case are distinct but complementary documents. The business case is created first and serves to justify the project's initiation by detailing its benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. It is used by decision-makers to approve or reject the project.
Once the project is approved, a project charter is often developed to formally authorize the project, outlining its objectives, scope, key stakeholders, and the project manager's authority. A summary of the business case is often included in the project charter.
How long should a business case be?
A comprehensive business case doesn't have a specific page count but should be detailed enough to clearly communicate the project's benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. For small projects, it may be a few pages; for larger or complex projects, it typically ranges from 10-20 word pages (30-50 slides), excluding appendices. Sources: Harvard Business Press - Developing a Business Case
Download our most popular templates
High-end PowerPoint templates and toolkits created by ex-McKinsey, BCG, and Bain consultants

Create a full business case incl. strategy, roadmap, financials and more.

- Market Analysis
Create a full market analysis report to effectively turn your market research into strategic insights

- Market Entry Analysis
Create a best-practice, well-structured market study for evaluating and comparing multiple markets.
Related articles

Picking apart a McKinsey consulting proposal
In this blog post, we’ll break down a McKinsey consulting proposal, look at what works and why, and discuss how to write a winning consulting proposal.
Oct 12, 2024

20 PowerPoint shortcuts every consultant must know
We surveyed a group of top-tier consultants and identified their top PowerPoint shortcuts. This post explains how to use them efficiently.
Sep 23, 2024

How to Write Key Takeaway Slides (with Examples and Free Template)
This guide, written by an ex-McKinsey consultant, teaches you how to create best-practice key takeaway slides based on a proven framework.
Sep 2, 2024

- Consulting Toolkit
- Business Strategy
- Consulting Maps Bundle
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Digital Transformation
- Product Strategy
- Go-To-Market Strategy
- Operational Excellence I
- Operational Excellence II
- Operational Excellence III
- Full Access Bundle
- Consulting PowerPoint Templates
- How it works
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 Slideworks. All rights reserved
Denmark : Farvergade 10 4. 1463 Copenhagen K
US : 101 Avenue of the Americas, 9th Floor 10013, New York
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
How to write a business case: the formula for getting project approval from stakeholders.
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
April 29, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
Do you feel you’ve found a solution to one of your company’s most pressing problems? Do you want to go straight to your seniors and tell them about your idea, basking in the glory of your eureka moment? 💡
Before you do that, take a deep breath and consider if your solution requires a significant financial commitment or a shift into critical business functions . If it does, you should learn how to write a business case to properly present your idea to the higher-ups.
Never done that before? No worries. In this article, we’ll explore:
- The concept of a business case
- The difference between a business case and a business plan
- The process of building a compelling business case
- Some real-life examples to understand how business cases help win project approval
Importance of a business case in project management
What is the difference between a business case and a business plan, 1. executive summary, 2. project definition, 3. financial appraisal, 4. project goals and success criteria , 5. project scope and schedule, 6. risks and mitigation strategies, step 1: problem identification, step 2: stakeholder identification, step 3: drafting background information and project definition, step 4: cost-benefit analysis and financial appraisal, step 5: evaluation of alternatives, step 6: describing the project scope and implementation approach, step 7: drafting the executive summary, step 8: putting it all together, lean startup example, venture capital funding example, outsourcing example, supply chain example, 1. drafting it alone, 2. not taking stakeholder feedback, 3. not reviewing or proofreading, create a compelling business case with clickup.
What Is a Business Case?
A business case explains how the rewards of investing in a business idea or initiative outweigh the risks and costs .
It’s one of the many project management documents (like a project charter or a project plan ) you may have to create when seeking the green light to proceed with a project. A well-crafted business case can be crucial for obtaining approval from your client, management, or other stakeholders in the early stages of your project’s lifecycle . 🟢
The key role of a business case is to justify an investment . It plays other important roles that make project management more efficient . Some of them include:
- Providing clarity: Drafting a business case requires careful planning and research, which brings clarity of thought and improves your understanding of the initiative or project you’re going to propose
- Resource optimization: A business case helps ensure that the company’s resources are being used productively and contributing to its long-term strategic objectives
- Removing doubt: By comparing different solutions, the document eliminates any doubt that an alternative way to fix a business problem is better than what you’re proposing
Preparing a business case can take a lot of time and effort, so it only makes sense when a project or an initiative requires a significant financial commitment. For all other approvals, you can use the project charter. Some scenarios in which a business case can make sense include:
- A new project
- New product line
- Introduction of a new customer persona to your marketing strategy
- Major changes to the supply chain, like introducing new suppliers or distributors
While a business case may seem like a synonym for a business plan , based on its definition, content, and name, there are major differences between them. The most notable ones are:
- Use case: A business plan is made for an entirely new business, while a business case is created when asking for a substantial financial commitment within an existing business
- Purpose: A business plan aims to hammer out the complete business strategy, while a business case tries to explain the advantages of a specific initiative
- A company’s mission and vision
- Financial projections
- SWOT Analysis
- Market analysis
- Go-to-market strategy
- Team profile
A business case, on the other hand, includes only financial projections, risks, and costs of a project
- Level of detail: Given the scope of information they need to cover, business plans tend to be much more detailed than business cases
Key Elements of a Business Case
While the exact structure of a business case will vary based on a specific situation, here are some of the essential components:
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the critical details covered in your business case.
Given that managers and executives are usually strapped for time, the executive summary will often be the only part of the document they actually read. That’s why it’s crucial to get this part of the document right and leave a powerful first impression.
The project definition sets the context for your business case by explaining the problem you aim to solve. It highlights an unfulfilled business requirement, outlines why it’s not being met, and finally presents your solution for addressing the mentioned shortcomings.
This is the crux of the matter—the financial appraisal part outlines the ROI your proposed initiative or project will likely generate for the business. It also covers the expected cost of executing your project or implementing your solution.
This part of the business case defines all the objectives and key results (OKRs) you want to achieve through the proposed project or solution. It also explains how those goals align with the company’s short-term and long-term goals. Lastly, it establishes success criteria for your project in the form of KPIs and key metrics .
The project scope sets limits and boundaries for your project by allocating resources and budgets and developing a schedule for completion.
A business case has to list all the risks associated with implementing the proposed solution and the mitigation strategies for dealing with them. It also weighs in on alternative approaches and their respective risks to explain why your initiative should be the preferred option.
How to Write a Business Case in 8 Steps
Writing a business case is an elaborate task that requires extensive research and numerous analyses, from SWOT and cost-benefit analysis to stakeholder analysis. It’s no walk in the park, but it becomes much easier with an exceptional project management platform like ClickUp .
ClickUp equips project managers and business professionals with all the tools they need to craft a business case that will win the hearts and minds of their superiors—from ready-made templates to AI-powered document management features. Let’s find out how to write a business case in eight steps with the help of ClickUp.
Many business ventures fail because they create solutions to non-existing problems. To prevent this scenario, make sure you consider the following:
- Objective(s) your company wants to achieve. Examples include achieving a revenue target , meeting an unaddressed customer need, or achieving a competitive advantage
- Problem(s) holding your company from achieving its desired objectives. Examples include a lack of operational efficiency , incorrect customer targeting, and supply chain issues
- The solution you want to propose to solve the problem and meet the objectives
- Evidence and case studies to prove that your proposed solution can indeed solve the problem
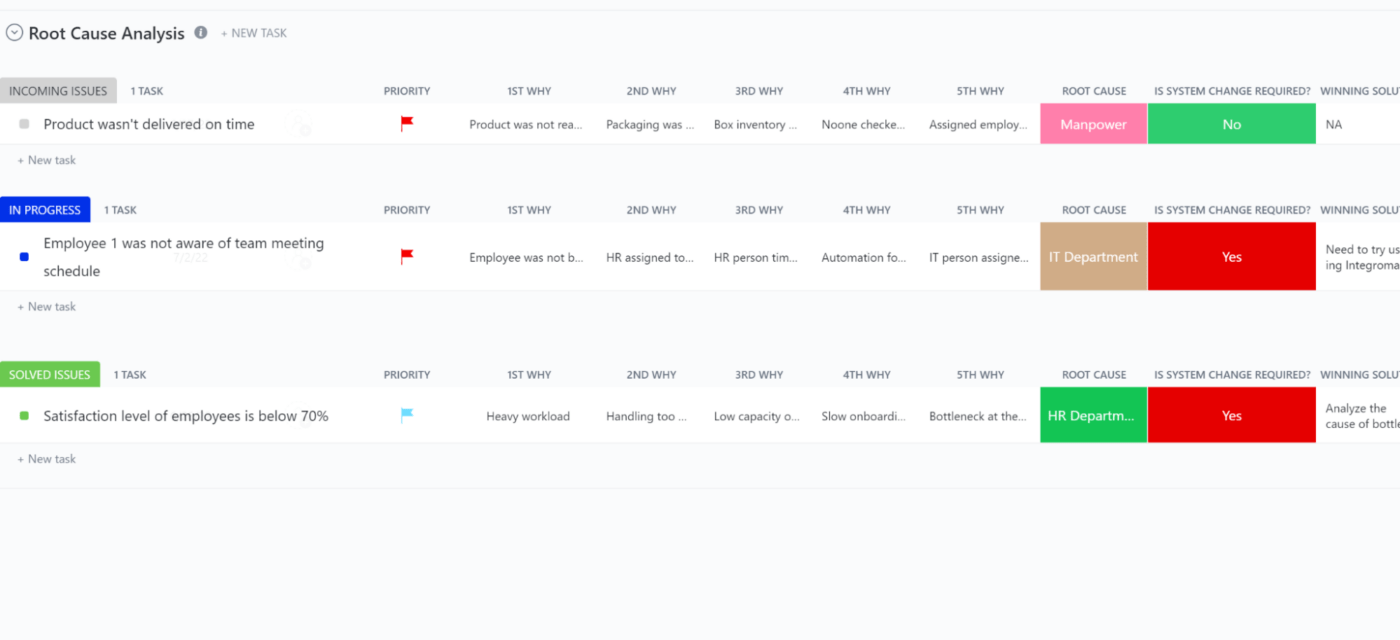
A structured way to identify your business problems is to use the ClickUp Root Cause Analysis Template . Classify everything going wrong with your business into multiple “Why” columns and then add their root causes in the relevant color-coded blocks. Once you analyze the root causes, you can tailor your solution to target and fix them.
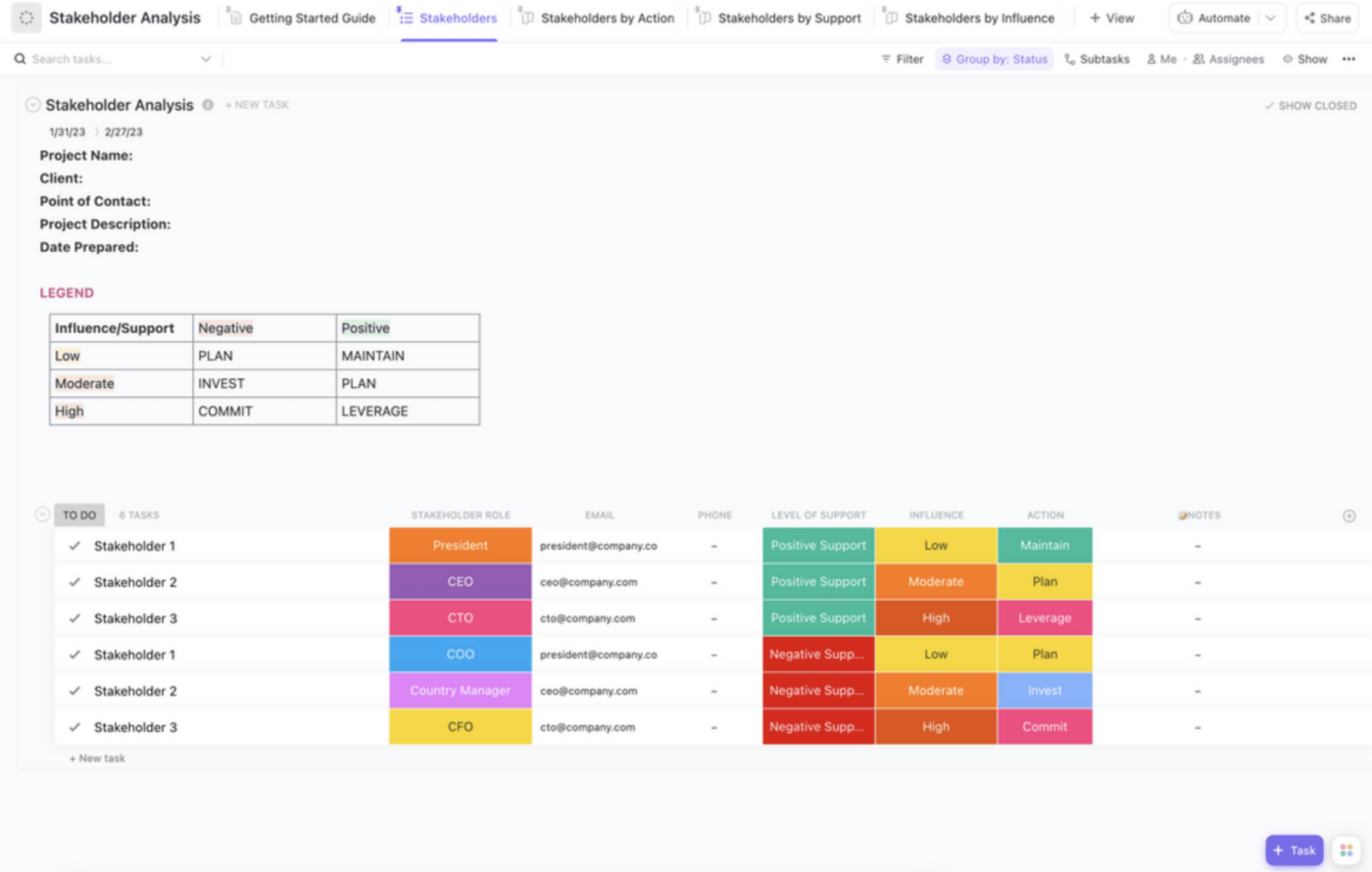
After pinpointing the problem, the next step is identifying the stakeholders to whom you’ll pitch your business case. A stakeholder is anyone who has a say in approving your business case . Depending on the scope and complexity of your business case, one or all of the following stakeholders may play a role in its approval:
- The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the company
- The head of the finance department
- The head of business operations
- The head of the marketing and sales department
- The representative of a client
Discuss your initiative with the stakeholders to see whether they’re interested in it or not. It can also help you understand their perspective on the problem you’re aiming to solve. After all, you don’t want to put your efforts into a full business case only for the stakeholders to reject it. 🙅♂️
The easiest way to identify key stakeholders is to leverage the ClickUp Stakeholder Analysis Template . This framework can help you gauge the influence and support level of all stakeholders who will play a role in approving your business case. This information can also come in handy when you want to collect feedback from a stakeholder.
Once you’ve identified your problem and the involved stakeholders, it’s time to start drafting your business case.
The first part is the project definition section, which sets the background for presenting your case before stakeholders . It covers the problem your business case proposes to solve and explains why solving the problem is important. The section should cover the following:
- The problem you identified and its impact on business functions
- How your project or solution can fix it
- The goals your project or initiative wants to achieve
- How project goals align with the company’s near-term objectives
- The success criteria for your project or initiative
- How its success will move the company towards its long-term strategic goals
The best tool for drafting this part of the document is ClickUp Docs —ClickUp’s built-in text editor and documentation management platform.
With ClickUp Docs’ collaborative editing possibilities, you and your stakeholders can work on the business case document in real time, ensuring its speedy and accurate completion. Stakeholders can also comment on areas for improvement . Finally, you can add a cover image to make your business case look more appealing or use slash commands to quickly add compelling blocks of formatted text.
After setting the background, the next step is the financial appraisal part. This section will be examined carefully during your pitch and serves to capture the stakeholders’ interest in your business case. For maximum accuracy, consult with a colleague from the finance department while drafting this part of the document.
Some of the information you may want to cover here includes:
- Projections about financial gains
- Costs to be incurred by the project
- Cash flow forecast
- Cost-benefit analysis and return on investment (ROI)
- Sensitivity analysis to explain the margin of error in your numbers
Besides the financial aspects, this section also deals with risk analysis . Information on all potential risk factors identified through SWOT analysis, Monte Carlo analysis, and other risk identification strategies are outlined along with their respective mitigation strategies . It’ll be best to discuss the project risks with stakeholders identified in the first step—they can often share hidden insights and perspectives.
ClickUp provides a number of tools to help you conduct each of these analyses. For instance, you can use the ClickUp Cost Benefit Analysis Template to complete your cost-benefit analysis.
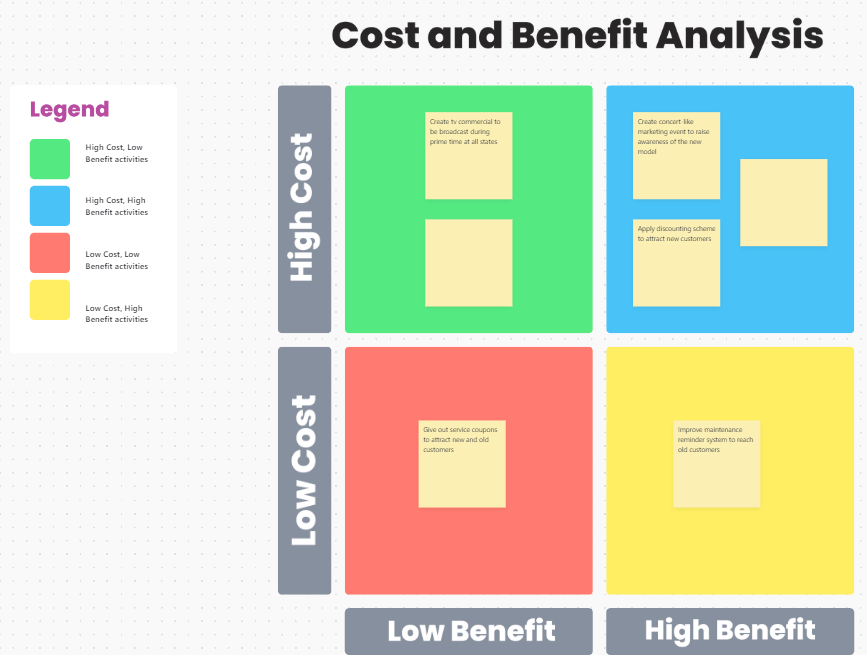
Similarly, the ClickUp SWOT Analysis Template can save you from jotting down rows of data to identify your initiative’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It is a visually rich template that lets you easily identify high-impact activities and functions.

In this section, you should evaluate the alternatives to your proposed solution in the business case. Highlight the pros and cons of each option so the stakeholders can have a complete overview of every possible solution. Make sure to include your proposed solution in the comparison as well to explain why it’s better than all the alternatives.
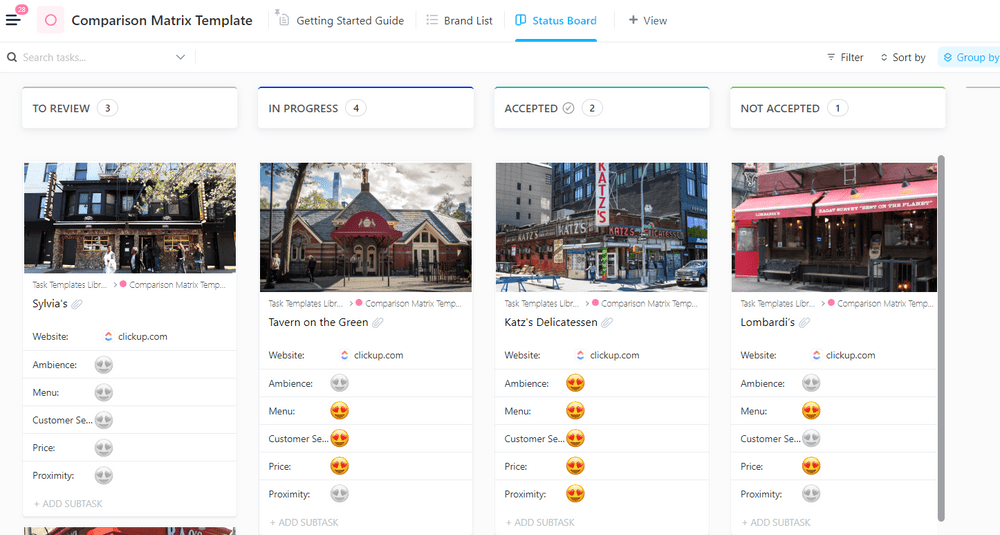
If you need help examining and comparing the alternatives, fall back on the ClickUp Comparison Matrix Template . Use it to record all the information about each possible alternative in different fields and then compare them on a Kanban board. Its visual format makes decision making easier, while its fully customizable fields allow you to record as many comparison parameters as you wish.
After you detail all the financial aspects of your project and compare it to alternatives, define a project scope in your business case. This section sets boundaries for the pending work and limitations on resources needed to complete it. Crucial information covered in it includes:
- Budget and resource allocation: Financial and other resources, like team members, workspace, equipment, etc., that should be allocated to the project
- Deadlines: Time required to complete each part of the project
- Dependencies and relationships : Details of current business functions that may be affected by the project
- Deliverables: What you plan to deliver by the end of your project
- Exclusions: What’s not a part of your project
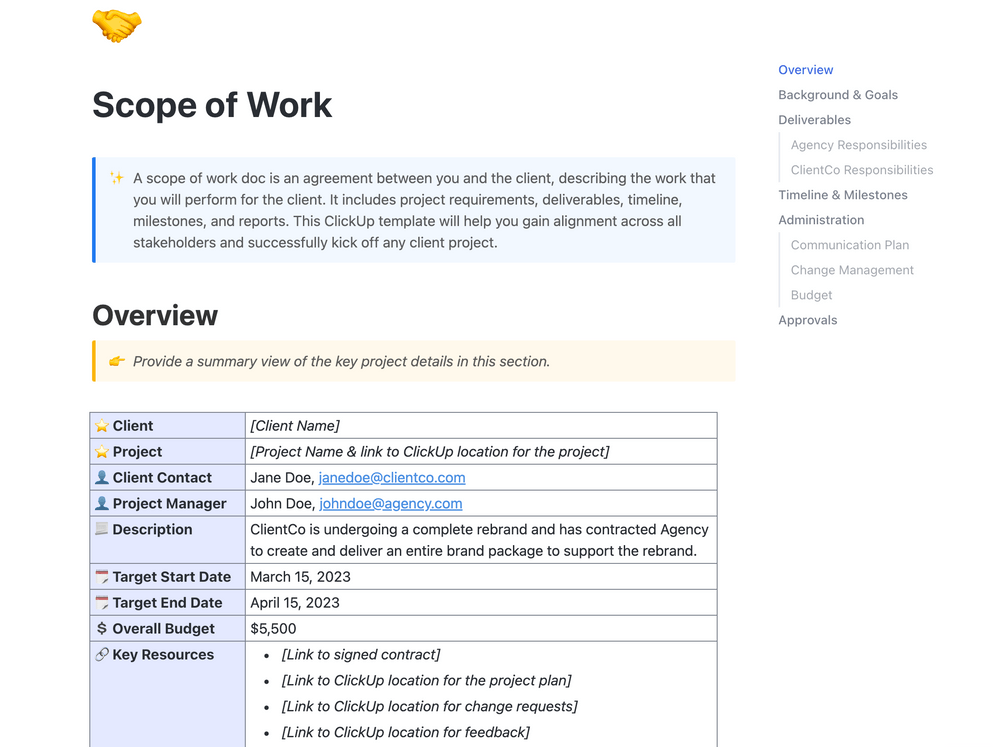
Once you define the project scope, outline the exact steps for implementing it. The easiest way to do this is to use the ClickUp Scope of Work Template . It allows you to record every aspect of the project scope in a well-organized manner to share with your stakeholders and get their opinions.
Once all major sections of your business case have been completed, you need to draft an executive summary to digest the crucial details from each section. This summary should be concise, ideally no longer than two pages. It will appear as the first item in your business case, providing stakeholders with a quick overview of your proposed project.
If you need help drafting your executive summary, team up with ClickUp Brain , a neural network and AI writing assistant built into ClickUp Docs. In mere seconds, it can generate a pitch-perfect summary of any business case document prepared until now.
Once you have your executive summary draft, use the ClickUp Executive Summary Template to format and organize it in a structured and presentable manner.

Now, it’s time to put together and structure all the sections drafted to this point to finalize your business case. That’s where the ClickUp Business Case Analysis Template can be a lifesaver.
The template includes dedicated sections to record each part of the business case. All sections are arranged in a structured manner to ensure that when you pitch your case, it makes a lasting impact on your stakeholders.

Real-Life Examples of Business Cases
Now that you know how to write a business case, let’s check out some real-life examples of how business cases allow companies to approve major projects and make strategic decisions:
A lean startup operating in the healthcare space is facing workforce issues, which are preventing it from launching its product on time. The head of the product development team wants to hire three more engineers to speed up the product development process .
However, since it’s a lean startup with budget constraints , the team head needs approval from the startup founders before making the decision. So, the product team compiles a business case for hiring additional employees , and here are the main elements of their proposal:
- A brief overview of how insufficient staffing is delaying product development and pushing the product launch beyond the planned deadline
- Elaboration of how three new engineers can bring product development back on track
- Cost-benefit analysis of the move
- Exploration of the involved risks
- Presentation of alternatives and their associated risks
- Scope of the change, like the nature of work the new engineers will perform
A venture capital-funded fintech startup decides to launch a new product line of credit cards . It will allow the startup to onboard a slew of new customers but will also require significant financial investment for marketing and lending purposes. So the company prepares a business case for this new product line in an effort to obtain funding for it. Here’s what they detail in their business case:
- The need for this new product line and how it complements the company’s other offerings
- The market opportunity with revenue projections and cost-benefit analysis
- Risks involved in the project, like competition, mass default, and regulatory scrutiny
- Alternatives available, like launching prepaid debit cards, which probably wouldn’t be as useful for customer acquisition
- Scope of the project, like team members working on it, the budget allocated, launch schedule, and timeline
A SaaS software vendor based out of Silicon Valley wants to reduce customer service spending without compromising service quality . The product manager of one of their leading products comes up with the idea of outsourcing customer service . So, they decide to prepare a business case before proposing the solution to the management. The business case outlines:
- The problem, which is a significant share of revenue going into customer service operations and how outsourcing can help bring it down
- Risks associated with outsourced customer service and mitigation strategies for them, like having an escalation mechanism for unresolved support tickets
- Alternatives and their risks, like using AI chatbots to automate customer service , which can be frustrating for customers who need human guidance
- Cost-benefit analysis of making the change
- Scope of change, like how many of the customer support employees will be laid off
A construction company in Virginia is facing raw material supply issues . The cement supplier they work with repeatedly fails to meet the demand, so the project supervisor decides to add some redundancy by onboarding a new vendor.
This change can greatly influence the project, so the supervisor prepares a business case to propose the initiative to the management. The case addresses the following:
- How the new cement supplier can keep the project from being delayed
- The supplier’s reliability, as demonstrated by the years of industry presence, major companies for which they have supplied cement, etc.
- Alternative suppliers, their capacity, and reliability information
- Cost-benefit analysis of making the change, since the rates of this supplier are slightly higher than those of the existing vendor
- Scope of change, including how much of the supplies will be delivered by the new supplier, for how long, and at what price

Potential Business Case Challenges and How to Overcome Them
There are a number of mistakes project managers make when drafting a business case, which can jeopardize the approval of the entire project or initiative. Now that we’ve covered the complete process of writing a compelling business case, let’s look at the most common pitfalls and explore ways to avoid them.
The details of a business case require extensive research and knowledge of different business functions. No project manager can do it all alone without making mistakes or errors of judgment, so look for help from different departments in your company, whether it’s finance, marketing, or operations. 💁
Another crucial mistake when building a business case is presenting the document to stakeholders out of the blue. When you don’t involve relevant stakeholders at any stage in your business case development process, you increase the risk of it being rejected. That happens because:
- You don’t know their expectations
- They didn’t have any role in your business case, which keeps them detached from your work
To avoid this scenario, involve stakeholders at different stages of your business case drafting process and get your progress reviewed regularly.
The last thing you want when pitching your business case is a typo or a misrepresentation of facts. That can leave a bad impression on the stakeholders listening to your pitch. They may not take you seriously and ultimately reject your project proposal .
To ensure a bulletproof document, you should always review and proofread your entire business case before submitting it . Pay special attention to numbers and facts and double-check that they’re correct. Then, go ahead with your pitch.
A solid business case is the first step to getting project approval from your stakeholders. However, building it requires careful planning and the right tools to streamline the entire process. Fortunately, ClickUp equips you with everything you need at each step of building your business case—from ready-made templates and documentation tools to AI-powered writing assistance.
Sign up for ClickUp today and write a business case that will earn support and trust for your project or initiative.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, business case template, how to write a business case, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case, watch our business case training video.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project outweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
When Should You Write a Business Case?
Around 70 percent of businesses that survive longer than five years follow a strategic business plan. And every project an organization undertakes should demonstrate real business value via a business case. A business case is created during the initiation phase of a project. At this point, the project is being conceptualized and evaluated on what the potential return on investment could be. The business case document helps determine the project’s needs and allows decision-makers to determine if the project aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
For example, a business case may be used when there’s a new project proposal, when entering into a new market, when upgrading software solutions or when there’s a major capital expenditure. Once the business case has been approved, the project will move to the planning phase.
Why Is It Important to Write a Business Case Document?
A business case document benefits projects for several reasons.
- Justifies why a project is needed, outlining costs, benefits and risks
- Engages stakeholders and gets their buy-in and support
- Allows decision-makers to assess feasibility and make choices based on data
- Provides estimates for costs, resources and timelines to improve resource allocation
- Helps hold teams accountable for delivering on commitments
Overall, it helps guide the project initiation and execution to result in thoughtful and strategic decisions.
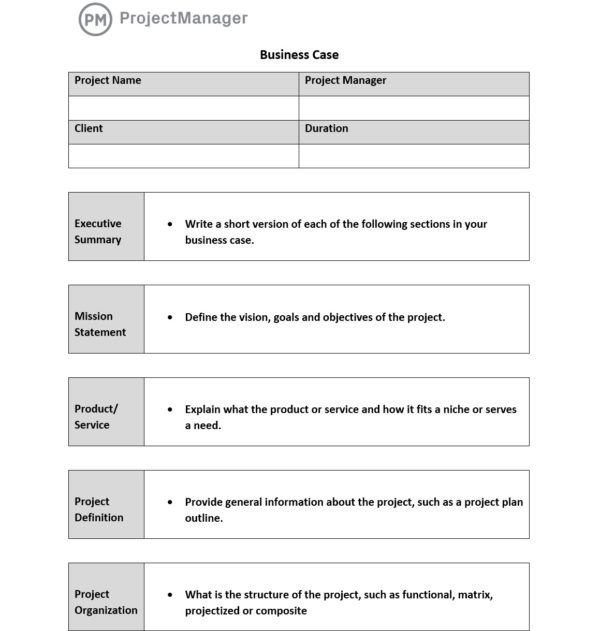
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project to help them understand the project’s purpose, benefits and implications. Some components of an executive summary include the project overview, business need, proposed solution to the need, cost estimate, return on investment, risks, timeline and a call to action.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline. It offers a comprehensive overview of the project including its objectives and scope. Here, include details such as the objectives, stakeholders, scope, expected outcomes and constraints.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives. Think of it as establishing the project’s boundaries to help stakeholders better understand what to expect. A well-defined scope can also improve resource allocation and project planning, two key factors of the project’s long-term success.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
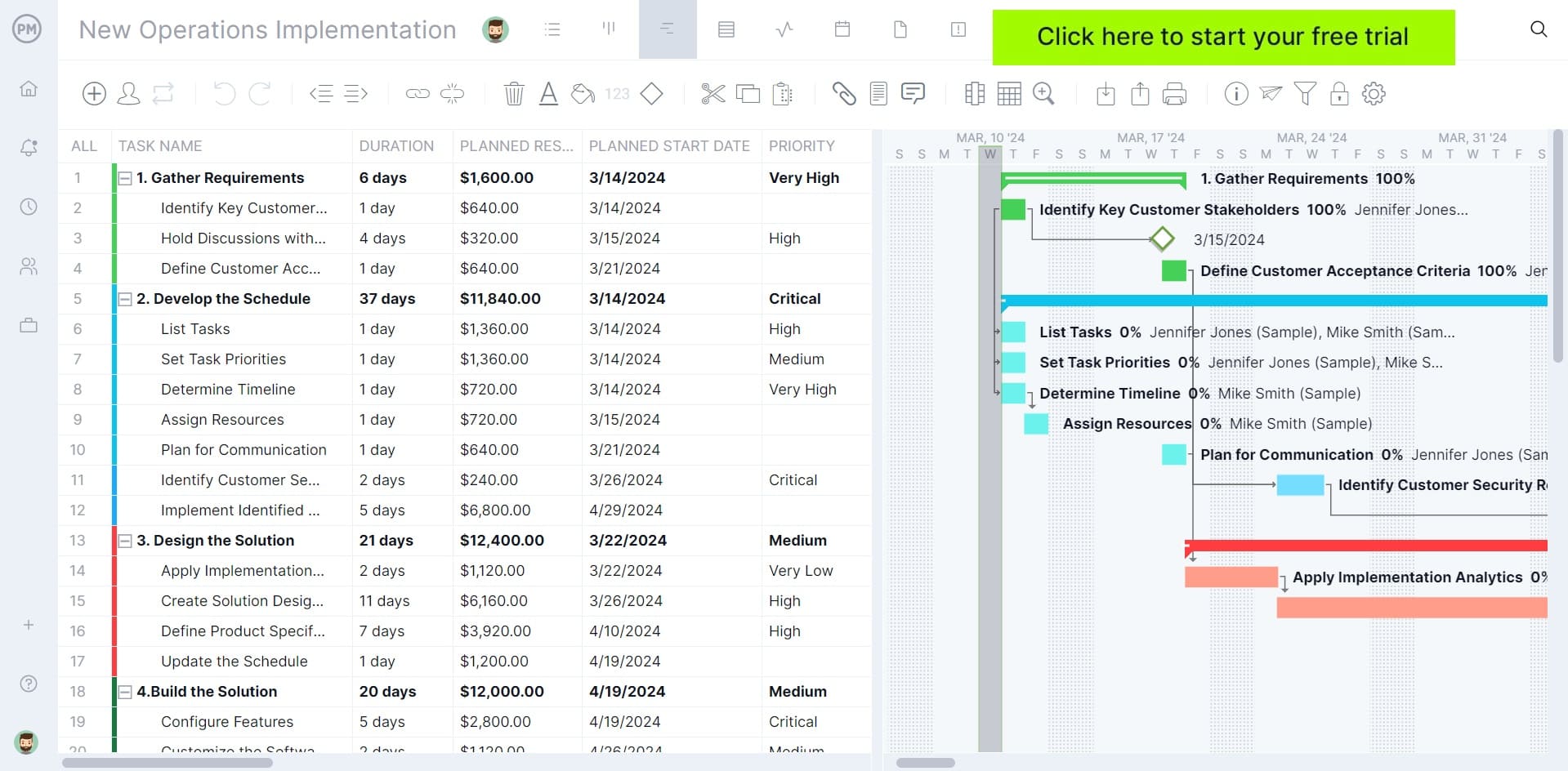
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted. It outlines the financial resources such as personnel costs, software or hardware costs, consulting fees, training costs and contingency funds. It also provides the return on investment information and shows how the benefits will outweigh the costs.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle. The communication plan can help foster an atmosphere of transparency and engagement among stakeholders. The plan outlines how, when and what will be communicated so that everyone is informed and on the same page.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats. The market assessment can also help outline the overall market condition and how that could impact the project. For example, what are the current market needs and trends? Are there any barriers to entry that could impact the project such as strong competition or high capital requirements? Note all of this information in this section of the business case.
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy. For example, how does each competitor position itself in the market? What pricing strategy do they implement and where is there room for differentiation? Then, use this information to help guide future decisions.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external. This is a structured approach to help stakeholders make more informed decisions and outlines how to better leverage internal and external resources. The SWOT analysis helps ensure that the project aligns with organizational goals and market conditions.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities. From there, you can assess the likelihood and impact of each and rank them based on this information. The risk assessment makes it easier to focus on the most pressing risks and includes a mitigation strategy to reduce the impact in case the risk comes to fruition.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
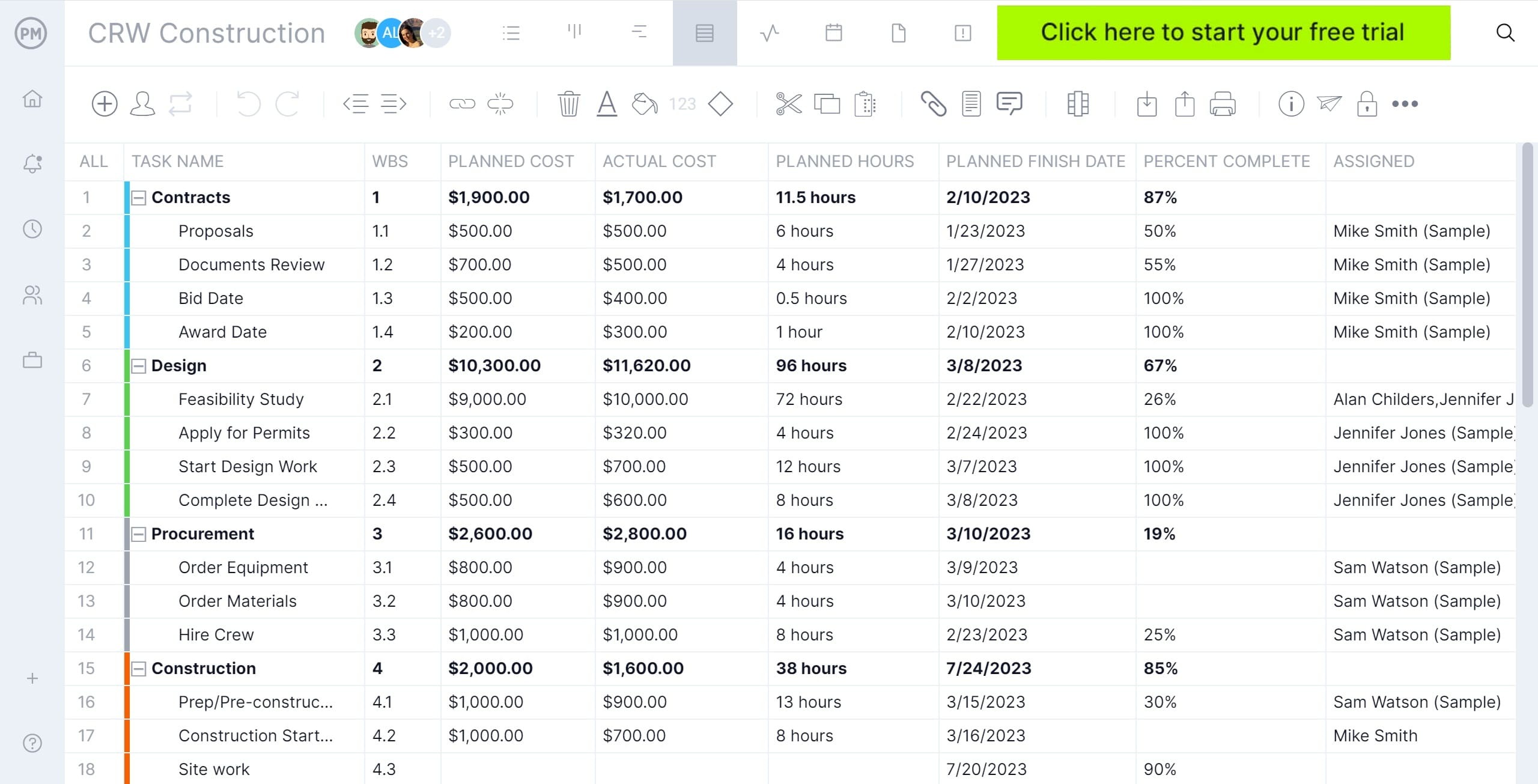
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- home Business Case Insights
- home Customer Experience Insights
- home Innovation Insights
- home Strategy Insights
- home My Business Case Hub®
- home AI Business Case Tools
- home 6 Essential Templates
- home Business Case Course
- home Business Case Coaching
- home Business Case Presentations
- home Business Case Reviews & Feedback
- home Business Case Microcredential
- home Professional Development
- home AI Business Case Creation Workshop
- home Business Case Corporate Program
- home Business Case Masterclass
- home Business Cases Webinar Replay (May 2024)
- home My AI Strategy Toolkit
- home My Business Cases
- home My Financial Analysis
- home My Risk Analysis
- home My Project Plans
- home My Slide Decks
- home My Opportunities
- home My Strategic Plans
- home My Proposals
- home CLIENT STORIES
- home Overview
- home Advisory Boards
- home Strategic Business Planning
- home Business Cases
- home Customer Research
- home Innovation Strategy
- home Innovation Sprint
- home Performance Improvement
- home Business Intelligence
- home Program Evaluation
- home About Chase
- home Code of Ethics
- home Privacy Policy
- home CONTACT
The Business Case Dictionary
A business case is different to the strategic business plan, let's explore this in more detail..
Copyright © Chase Consulting Group 2024 - All Rights Reserved

Difference between business model, business plan, business case

The business model
The business plan, the business case, the chronological order.

The IAPM certification
The certification can be taken via a reputable online examination procedure. The costs are based on the gross domestic product of your country of origin.
From the IAPM Blog
Become a network official.
Do you want to get involved in project management in your environment and contribute to the further development of project management? Then become active as an IAPM Network Official or as a Network Official of the IAPM Network University.


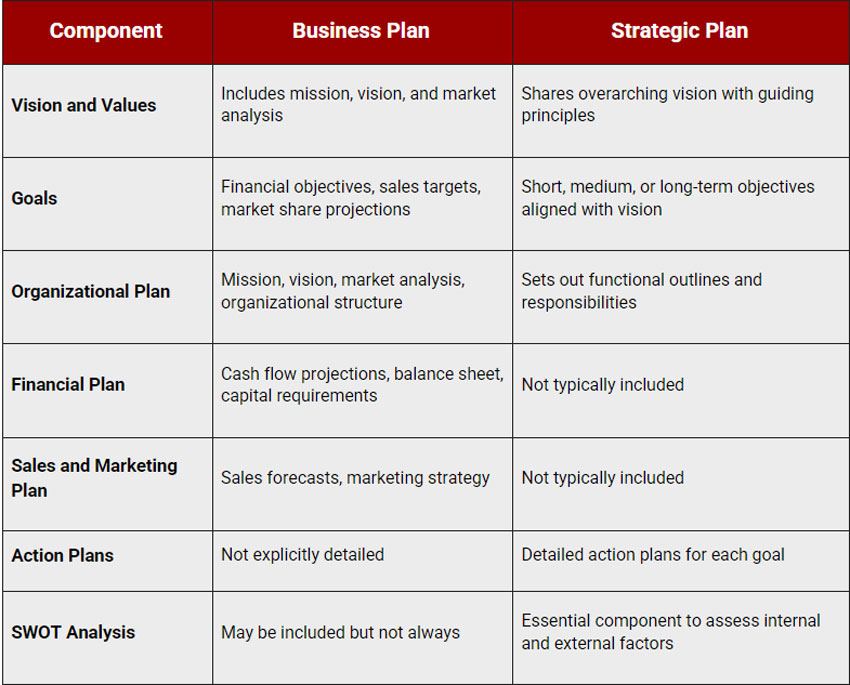














































IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business plan is based on a series of hypothesis, action plans, and a long-term calendar. Contrastingly, a business case is concrete - mainly because it's aimed at creating a short-term gain for the business with a well defined return on investment. To sum-up: a business plan is a strategic document, whereas a business plan is a tactical one.
A Business Case: A Business Plan: Is organized around: A single action or single decision and its alternatives.: An organization or the enterprise. The plan may cover a single product or product line or an organization. Predicts: Cash flow results and major non-financial impacts that follow from the action. Also predicts financial metrics, such as ROI, IRR, NPV and Payback Period.
A business case justifies a specific project by outlining its benefits, costs, and risks. It focuses on a single initiative to secure approval and funding. A business plan provides a comprehensive overview of an entire business, detailing its business strategy, market analysis, financial projections, and operational plans.
John Spacey, updated on March 04, 2017. A business plan is a proposal for a new business or major change to an existing business. A business case is a proposal for a strategy or project. A business plan is typically targeted to investors. It may include a pitch, financial plan, business model, cost estimates, market analysis, competitive ...
However, there is a key difference between these two types of documents: a business case focuses on strategy while a business plan focuses on investment and viability. A business plan is a high-level overview of the entire company. It includes the company's mission statement, an analysis of the competitive landscape, market research, target ...
A business case is a written document (often a PowerPoint presentation) that articulates the value of a specific business project or investment. It presents the rationale for the project, including the benefits, costs, risks, and impact. The main objective is to persuade internal stakeholders to endorse the project.
"What's the difference between a business case and a business plan?" Few people can produce a ready answer to that question. After all, both business plans and business cases make predictions about future outcomes, but there is a big difference between the two. Business plans. are based on the business model or business line of an ...
Step 6: Describing the project scope and implementation approach. After you detail all the financial aspects of your project and compare it to alternatives, define a project scope in your business case. This section sets boundaries for the pending work and limitations on resources needed to complete it.
Business case template. Free download How to Write A Business Case. Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn't address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.
A Business Case is Different to the Strategic Business Plan. A strategic business plan and a business case are different yet related documents. The strategic business plan lays out the overall strategy, outlining goals and objectives for the organization. In contrast, the business case justifies spending resources on one unique opportunity.
The business model forms the foundation and encompasses the core idea of a business, while the business plan serves as a detailed roadmap for the implementation of the vision. The business case, on the other hand, analyses specific projects or investments within the company to ensure that they are in line with the overall objectives.
Share. A business case is a business-related concept that is both practical and profitable; while a business plan gives the details and elucidates the financial steps necessary to create or grow a successful business. Its purpose is to examine the business dynamics of a proposed project as part of the evaluation and selection process.
Business case vs business plan - what's the difference?Business case vs business plan - what's the difference? Here's the difference between your business ca...
Introducing The Business Plan. A business plan is exactly what the name suggests— a plan to start and run a business or a new entity of an existing business; usually either an expansion in a newer region or a diversification into a new market. Business plans are mainly created for internal reference purposes or external funding purposes, with ...
The simplest way to think about your business model canvas is to map it out visually. A business model canvas covers nine key areas: Value proposition: A company's unique offering in the market and why it will be successful. Key activities: The actions that a company takes to achieve its value proposition.
The key difference between a business model and a business plan. It is easy to confuse a business model with a business plan. Yet those tools have specific functions, in some cases similar, in most other cases completely different. ... In some cases, though, a business plan might also work for that purpose, especially a one-page business plan.
The business model is the mechanism through which the company generates its profits, while the business plan is a document presenting the company's strategy and expected financial performance for the years to come. As you can see, the business model is at the center of the business plan.
The biggest difference between a strategic plan vs. a business plan is its purpose. Existing companies use the strategic plan to grow their business, while entrepreneurs use business plans to start a company. There is also a different timeframe for each plan. Generally, a strategic plan is conducted over several years while a business plan ...
First, let's look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review: A business plan covers the "who" and "what" of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains "how" the business will get there, providing a long-term view. In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
Running a successful startup requires careful planning and strategic decision making. As an aspiring entrepreneur looking to bring your innovative ideas to