
25 Thesis Statement Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
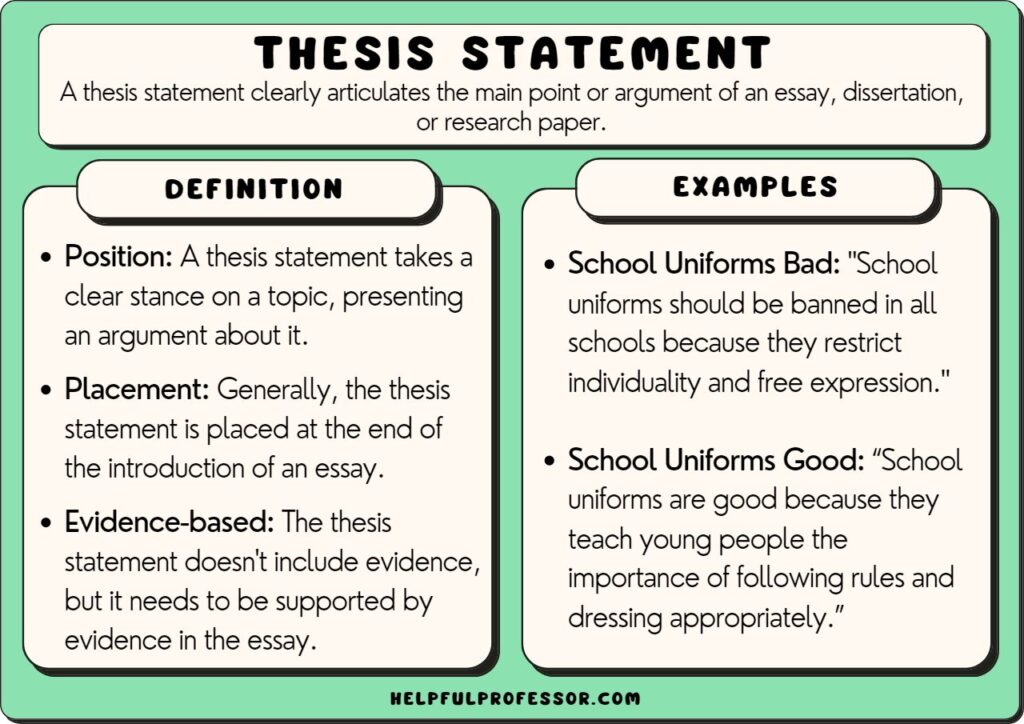
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
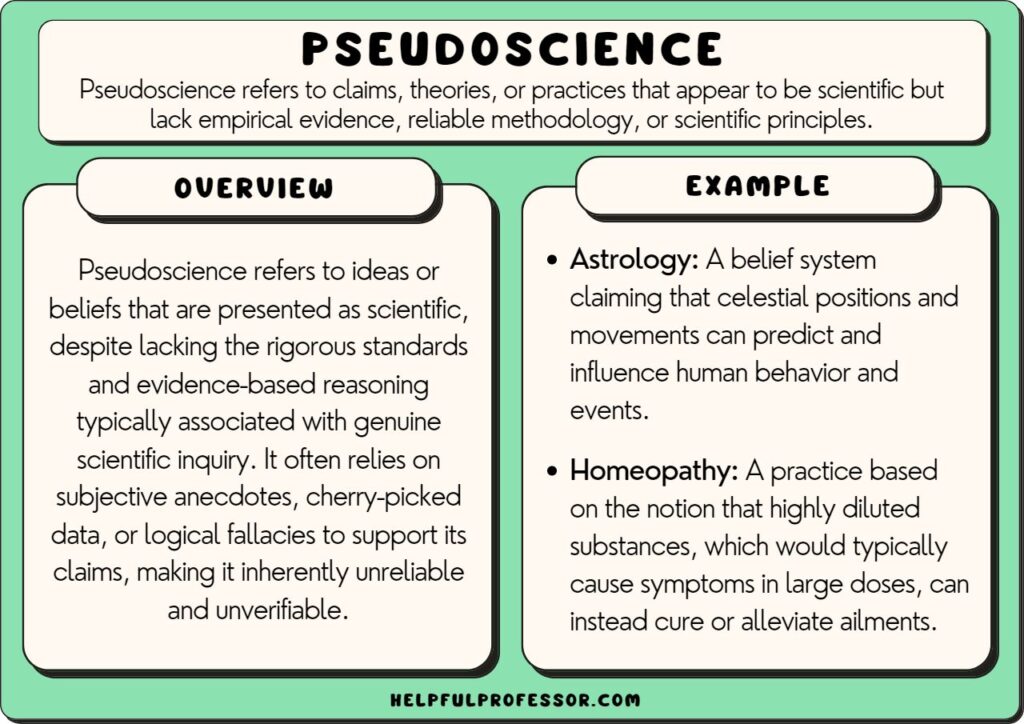
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
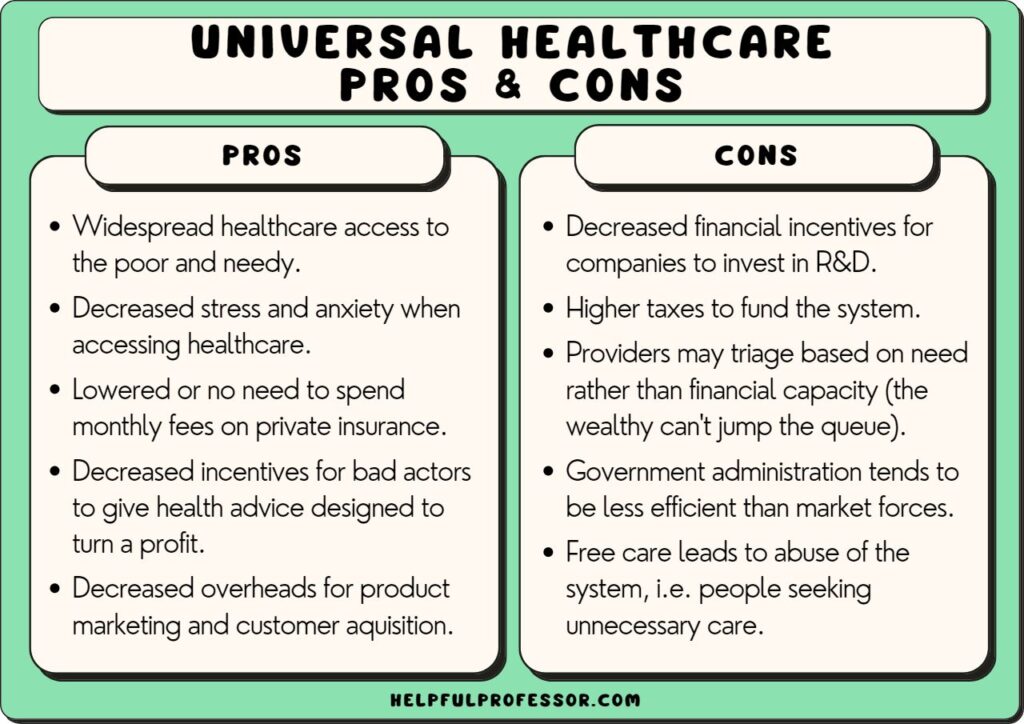
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
275 Education Argumentative Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 28 September 2024
- Icon Page 3306 words
- Icon Clock 15 min read
Education, a cornerstone of societal development, is a fertile field for writing papers. In this case, education argumentative essay topics can range widely, from debates over traditional vs. digital classrooms, the effectiveness of standardized testing, and the necessity of college education in the 21st century to the balance between academics and character development. Arguments can consider whether current school curriculums cater adequately to the needs of all students or primarily reinforce societal inequalities. Examining education policies at the local, national, or international levels can provide further insights. In turn, exploring the role of educational institutions in preparing students for the future workforce, including discussions on vocational training and entrepreneurial education, is another promising direction for developing argumentative essay topics in education.
What Is an Education Argumentative Essay Topic and Its Purpose
According to its definition, an education argumentative essay topic is a specific issue, idea, policy, or practice within an educational system that provoke debate and critical thinking. For example, the main purpose for selecting an education argumentative essay topic is to persuade readers to adopt a specific viewpoint or to challenge an existing perspective regarding educational matters (Mertler, 2024). In writing, common ideas cover a wide range of subjects, including an effectiveness of standardized testing, an impact of technology in classrooms, educational equity, and a necessity of certain curriculum changes. Further on, by exploring these themes, students engage in thorough research, presenting evidence to support their arguments while addressing counterarguments to strengthen their positions (Crossley & Tian, 2022). Basically, an ultimate goal is to encourage readers to critically evaluate their beliefs and implications of educational policies on students, educators, and society as a whole. Moreover, through effective argumentative essay topics, authors not only contribute to a discourse surrounding education but also promote informed decision-making and advocacy for positive change within educational institutions (Li et al., 2020). Thus, education argumentative essay topics serve as a vital platform for dialogue, aiming to influence both public opinion and educational reform.

How to Choose
Choosing a compelling education argumentative essay topic requires a careful consideration and evaluation of several key factors to ensure relevance and engagement. Firstly, students should select ideas that resonates with current educational debates or challenges, such as an effectiveness of online versus traditional learning environments or an impact of socio-economic factors on educational access (Koons, 2021). Essentially, conducting preliminary research can help them to identify areas where there is a lack of consensus or significant ongoing discussion, providing a fertile ground for argumentation. Further on, a selected education argumentative essay topic should align with personal interests and expertise, as this aspect will enhance a student’s ability to articulate informed arguments and engage readers effectively (Kleemola et al., 2022). In principle, they should consider an availability of credible sources and data to support their positions, while using robust evidence is critical for persuasive writing. Moreover, a well-defined and focused subject will facilitate a clear thesis statement, guiding an essay’s structure and its arguments (Goodson, 2024). As such, evaluating potential counterarguments can enrich an entire discussion and strengthen an overall argument, making it more persuasive. In turn, some steps for picking a good education argumentative essay topic include:
- Identify Current Issues: Explore contemporary debates and challenges within an educational landscape to ensure a central idea is relevant and timely.
- Reflect on Personal Interests: Choose a subject that aligns with your passions and expertise to enhance engagement and an overall quality of your arguments.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Investigate existing literature and studies to determine an entire availability of credible sources and data that can support your position.
- Narrow a Focus: Select a specific aspect of a broader issue to create a more manageable and focused argument that allows for in-depth analysis.
- Consider Counterarguments: Anticipate opposing viewpoints to strengthen your central argument and demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of education argumentative essay topic, enhancing the essay’s persuasiveness.
Best Education Argumentative Essay Topics
- Balancing School Curriculum: Is Art Education as Important as Science?
- Roles of Technology in Enhancing Educational Outcomes
- The Ethics of Using Animals for School Biology Experiments
- Parental Influence on a Child’s Academic Success
- University Tuition Fees: Necessary Expense or Excessive Burden?
- Should Physical Education Be Mandatory in Schools?
- Importance of Teaching Life Skills alongside Traditional Subjects
- Grading System: Helping Students Learn or Adding Undue Pressure?
- Incorporating Meditation in Schools for Improved Mental Health
- Homeschooling vs. Traditional Schooling: Which Prepares Students Better?
- Examining the Role of Sex Education in Preventing Teenage Pregnancy
- Importance of Introducing Multicultural Education in Schools
- Mandatory Community Service as Part of the Curriculum: Pros and Cons
- Cyberbullying: Should Schools Take Responsibility?
- Unraveling the Effects of School Uniforms on Student Behavior
- Gender-Separated Classes: Beneficial or Discriminatory?
- Are College Degrees Worth the Financial Investment?
- The Role of Teachers’ Salaries in Ensuring Quality Education
- Digital Textbooks vs. Traditional Books: Which Is More Effective?
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Homework in Enhancing Learning
- The Pros and Cons of Year-Round Schooling
- Roles of Parent-Teacher Communication in Enhancing Students’ Performance
- Effectiveness of Distance Learning: Is It Comparable to Traditional Learning?
- Should Controversial Topics Be Discussed in School?
Easy Education Essay Topics
- Exploring the Impact of School Lunch Programs on Student Health
- Is Cursive Writing Necessary in Today’s Digital Age?
- Teaching Consent in Schools: A Necessity or Overstepping Bounds?
- Gifted Programs: Are They Unfair to Other Students?
- Bilingual Education: Key to Global Competency or Detrimental to Native Culture?
- Implementing Zero Tolerance Policies in Schools: Beneficial or Harmful?
- Should Teachers Be Allowed to Carry Firearms for Classroom Protection?
- Influence of School Infrastructure on Student Learning Outcomes
- Incorporating Climate Change Education in School Curriculums
- Should Students Be Grouped by Ability in Classrooms?
- Effectiveness of Anti-Bullying Campaigns in Schools
- The Right to Privacy: Should Schools Monitor Student’s Online Activities?
- Evaluating the Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development
- The Need for Financial Literacy Education in Schools
- Freedom of Speech: Should Students Be Allowed to Express Controversial Opinions in School?
- Potential Benefits of Single-Sex Schools
- Relevance of History Education in Modern Times
- The Influence of Religious Beliefs on Education
- Foreign Language Requirements: Necessity or Unnecessary Burden?
- Are Teachers’ Unions Beneficial or Detrimental to Education Quality?
- Impacts of Parental Educational Background on Children’s Academic Achievement
- Does Grade Inflation Devalue a College Degree?
- Does Early Childhood Education Have Long-Term Benefits?
- Are College Admissions Processes Fair?
Interesting Education Essay Topics
- The Consequences of Educational Budget Cuts
- Exploring the Role of Sports in Academic Achievement
- Effects of Teacher Burnout on Student Learning
- Is Educational Equality Achievable in a Capitalist Society?
- Are Private Schools Necessarily Better than Public Schools?
- Role of Social Media in Education: Distraction or Useful Tool?
- Is Traditional Discipline Effective in Modern Schools?
- Examining the Effectiveness of Montessori Education
- Are Standardized Curriculum Frameworks Limiting Teachers’ Creativity?
- Is There a Place for Character Education in Today’s Schools?
- Importance of Critical Thinking Skills in the Curriculum
- Do Student Evaluations of Teachers Improve Teaching Quality?
- Music Education’s Influence on Academic Performance
- Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Academic Achievement
- Should Children Be Taught Entrepreneurship in Schools?
- Educational Benefits of Field Trips in Curriculum
- Does School Counseling Effectively Address Students’ Mental Health Needs?
- The Role of Games in Enhancing Math Education
- Is the Current Emphasis on STEM Education Justified?
- The Influence of Family Structure on Children’s Educational Outcomes
- Does Multitasking with Technology Hinder Learning?
- Should Political Education Be Mandatory in Schools?
- Effects of Classroom Diversity on Student Learning and Empathy
Academic Level Difference
Academic level differences significantly influence a whole nature and complexity of education argumentative essay topics, shaping an entire depth of analysis required at each stage of educational development. At a high school level, common ideas revolve around foundational issues, such as an effectiveness of various teaching methods, a relevance of standardized testing, or an impact of technology on learning (Koons, 2021). Basically, they tend to be more straightforward, allowing students to build critical thinking skills while exploring familiar concepts. In contrast, undergraduate-level education argumentative essay subjects may cover more nuanced discussions, such as potential implications of educational policy changes, roles of socioeconomic factors in educational attainment, or ethics of educational practices (Mertler, 2024). As such, these themes demand a greater degree of research, analytical thinking, and an ability to engage with scholarly sources. At a graduate level, key subjects require a sophisticated understanding of theoretical frameworks and methodologies, addressing complex issues, like systemic inequalities in education or an efficacy of educational reforms (Goodson, 2024). In principle, this progression illustrates how academic level differences not only influence a whole selection of education argumentative essay topics but also dictate an entire depth of inquiry and argumentation, ultimately shaping crucial skills and perspectives students develop throughout their educational journeys.
Education Essay Topics for High School
- Does Standardized Testing Accurately Reflect a Student’s Knowledge?
- Should Schools Invest More in Arts Education?
- Is a Year-Round School Calendar Beneficial for Learning?
- Are School Uniforms Necessary for a Conducive Learning Environment?
- Does Homework Actually Benefit Students?
- Should Advanced Courses Be Made Available to All High School Students?
- Can Online Learning Replace Traditional Classroom Teaching?
- How Is Essential Sex Education in High School Curriculum?
- The Impact of School Infrastructure on Quality of Education
- Are School Sports Essential for Student Development?
- Does Bilingual Education Enhance Cognitive Skills?
- Does Parental Involvement Improve Academic Performance?
- Is There a Need to Reinvent School Discipline Policies?
- How Does the Use of Technology in Schools Affect Learning?
- The Role of Schools in Promoting Healthy Eating Habits
- Are School Field Trips Essential for Practical Learning?
- Should Schools Introduce Personal Finance Classes?
- Physical Education Classes: Necessity or Luxury?
- Effect of Bullying on Academic Performance
- The Influence of Peer Pressure on Students’ Performance
- Should We Teach Entrepreneurship in High Schools?
- Does a Longer School Day Improve Learning Outcomes?
- Roles of Moral Education in Character Building
Education Essay Topics for College Students
- Incorporating Technology in Classrooms: Necessity or Distraction?
- Standardized Testing: An Effective Evaluation Tool or a Hindrance to Creativity?
- University Degrees: Essential for Success or Overrated?
- Pros and Cons of Single-Sex Education: A Deep Dive
- Private vs. Public Schools: Who Provides a Better Education?
- Traditional Education vs. Online Learning: Comparing Effectiveness
- Impact of Extracurricular Activities on Academic Performance
- Bilingual Education: Potential Benefits and Challenges
- Vocational Training: Does It Deserve More Emphasis in the Curriculum?
- Effects of Class Size on Student Learning Outcomes
- Homeschooling vs. Traditional Schooling: Weighing the Outcomes
- Mandatory Physical Education: A Boon or Bane?
- College Athletes: Should They Be Paid?
- Education in Rural vs. Urban Settings: Exploring Disparities
- Funding: How Does It Impact the Quality of Education?
- Role of Sex Education in Schools: Analyzing the Importance
- Uniforms in Schools: Do They Promote Equality?
- Plagiarism Policies: Are They Too Strict or Not Enough?
- Art Education: Is It Being Neglected in Schools?
- Teaching Soft Skills: Should It Be Mandatory in Schools?
- Tuition Fees: Do They Restrict Access to Higher Education?
- Inclusion of Students With Disabilities: Analyzing Best Practices
Education Argumentative Essay Topics for University
- Cyberbullying: Should Schools Have a Greater Responsibility?
- STEM vs. Liberal Arts: Which Provides a Better Future?
- Impacts of Mental Health Services in Schools
- Grade Inflation: Does It Devalue a Degree?
- Diversity in Schools: Does It Enhance Learning?
- Gap Year: Does It Help or Hinder Students?
- Recess: Is It Necessary for Students’ Well-Being?
- Early Childhood Education: Does It Contribute to Later Success?
- Parental Involvement: How Does It Influence Student Performance?
- Value of Internships in Higher Education
- Curriculum: Is It Outdated in Today’s Fast-Paced World?
- Digital Textbooks vs. Paper Textbooks: Evaluating the Differences
- Learning a Second Language: Should It Be Mandatory?
- Censorship in School Libraries: Freedom or Protection?
- Life Skills Education: Is It Missing From Our Curriculum?
- Teachers’ Pay: Does It Reflect Their Value in Society?
- College Rankings: Do They Truly Reflect Educational Quality?
- Corporal Punishment: Does It Have a Place in Modern Education?
- Student Loans: Are They Creating a Debt Crisis?
- Learning Styles: Myth or Real Educational Framework?
- Grading System: Is It the Best Measure of Students’ Abilities?
Education Argumentative Essay Topics for Master’s and Ph.D.
- Assessing the Impact of Remote Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance
- Should Standardized Testing Be Abolished in Favor of More Holistic Assessment Methods?
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Bilingual Education Programs in Improving Academic Outcomes
- How Do Teacher Training Programs Impact Classroom Management and Student Success?
- Implications of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Learning and Its Ethical Considerations
- Exploring the Correlation Between Early Childhood Education and Long-Term Academic Achievement
- The Importance of Inclusive Education Practices for Students With Disabilities
- Are Online Degree Programs a Viable Alternative to Traditional Education Pathways?
- The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Enhancing Academic Performance and Social Skills
- Should Higher Education Institutions Prioritize Vocational Training Over Traditional Degree Programs?
- Evaluating the Role of Arts Education in Developing Creativity and Innovation in Students
- Should the Curriculum Include Comprehensive Financial Literacy Education for Students?
- The Necessity of Cultural Competence Training for Educators in Diverse Classroom Settings
- Should Schools Implement Year-Round Education to Improve Academic Performance?
- Evaluating the Need for Comprehensive Sex Education in High Schools
- Are Charter Schools More Effective Than Traditional Public Schools in Improving Student Achievement?
- The Importance of Sustainability Education in Preparing Students for Future Challenges
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Classroom Management Strategies on Student Behavior
- Should College Athletes Be Compensated for Their Participation in Sports Programs?
- The Influence of Cultural Diversity on Curriculum Development in Multicultural Education
Academic Topics Essay
- Fostering Creativity: Should Schools Prioritize the Arts?
- Student Debt: Consequences and Possible Solutions
- Bullying Policies in Schools: Are They Effective?
- Teaching Ethics and Values: Whose Responsibility?
- Distance Learning: The New Normal Post-Pandemic?
- School Censorship: Are There Limits to Freedom of Speech?
- College Admissions: Is the Process Fair?
- Standardizing Multilingual Education: A Possibility?
- Learning Disabilities: How Can Schools Provide Better Support?
- Does Class Size Impact the Quality of Education?
- Integrating Technology: Are There Potential Risks?
- Affirmative Action in College Admissions: Fair or Biased?
- The Role of Private Tuition: Supplemental Help or Unfair Advantage?
- Military-Style Discipline in Schools: Effective or Harmful?
- Should Schools Implement Mental Health Curriculums?
- Early Education: Does It Pave the Way for Success?
- Grading System: Is it an Accurate Measure of Student Ability?
- Career Counseling in Schools: Should It be Mandatory?
- Addressing Racial Bias in Educational Materials
- The Debate Over Prayer in Schools: Freedom of Religion or Church-State Separation?
- The Impact of Zero-Tolerance Policies on the School Environment
- Education Funding: The Pros and Cons of School Vouchers
- University Rankings: Helpful Guide or Harmful Pressure?
- Personal Finance Education: Should It Be Included in the Curriculum?
Argumentative Essay Topics on Education
- Impacts of Standardized Testing on Students’ Creativity
- Digital Learning Platforms vs. Traditional Classroom Teaching
- Effectiveness of the Montessori Education System
- Mandatory Foreign Language Education: A Necessity or Luxury?
- Single-Sex Schools’ Role in Modern Society
- Teachers’ Salaries: A Reflection of Their Value in Society?
- Technological Devices in Classrooms: A Boon or Bane?
- Inclusion of Life Skills in the Curriculum
- Ethical Education: Its Significance and Implementation
- Educating Children About Climate Change and Sustainability
- Homeschooling vs. Traditional Schooling: Which Yields Better Results?
- School Uniforms: Do They Encourage Uniformity Over Individuality?
- The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Holistic Education
- Importance of Critical Thinking in the Curriculum
- Corporate Sponsorship in Schools: Ethical Considerations
- Increasing Parental Involvement in Children’s Education
- Vocational Training in High School: Is It Necessary?
- The Merits and Demerits of Charter Schools
- Prioritizing Health Education in the School Curriculum
- Diversifying History Lessons: The Impact on Cultural Understanding
- Gifted and Talented Programs: Unfair Advantage or Necessary Support?
- Implementing Mindfulness Training in Schools
- Mandatory Physical Education: Is It Vital for Health?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Year-Round Schooling
- The Potential of Virtual Reality in Education
Education Persuasive Essay Topics
- Enhancing Creativity: The Importance of Art Education in Schools
- Mandatory Coding Lessons: Preparing Students for the Digital Future
- Bilingual Education: Encouraging Multilingualism From an Early Age
- Parental Involvement: Crucial for Academic Success or an Invasion of Privacy?
- Cyberbullying Awareness: Should It Be Part of the School Curriculum?
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education: Boon or Bane?
- Sex Education: Essential for Reducing Teen Pregnancy and STD Rates
- Standardized Tests: Accurate Measure of a Student’s Capabilities or Outdated Practice?
- Religious Studies: The Necessity of Teaching World Religions in Public Schools
- Homework Overload: Assessing the True Impact on Students’ Mental Health
- School Uniforms: Encouraging Discipline or Suppressing Individuality?
- Inclusion in Classrooms: The Benefits of Educating Special Needs Students Alongside Their Peers
- Teacher Salaries: The Need for Higher Pay to Attract Quality Educators
- Educational Video Games: Revolutionizing Learning or Distraction From Studying?
- Student Athletes: Balancing Academics and Sports Participation
- Year-Round Schooling: Improving Learning Retention or Overloading Students?
- Early Education: The Benefits of Pre-School Programs
- Social Media: Its Role in Modern Education
- Field Trips: Enhancing Learning Outside the Classroom
- Classroom Size: The Impact on Learning and Engagement
- Vocational Training: Essential for Preparing Students for the Workforce
- Distance Learning: Exploring its Advantages and Disadvantages
Education Research Paper Topics
- Extracurricular Activities: The Importance in Students’ Holistic Development
- Multiple Intelligence Theory: Implementing Diverse Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Decor: Its Influence on Student Engagement and Learning
- Mindfulness Practices: Promoting Emotional Health in Schools
- Sustainability Education: Fostering Environmentally-Conscious Citizens
- Cultural Diversity: Promoting Inclusion and Acceptance in Schools
- Physical Education: Addressing Childhood Obesity through School Programs
- Gifted and Talented Programs: Benefits and Drawbacks
- Homeschooling: Advantages Over Traditional Schooling
- Alternative Assessment Methods: Moving Beyond Exams and Grades
- Bullying Prevention: The Role of Schools and Teachers
- College Admissions: The Controversy Around Legacy Preferences
- Ethics Education: Instilling Moral Values in Students
- Student Loans: The Crisis and Its Impact on Higher Education
- Nutrition Education: Promoting Healthy Eating Habits in Schools
- Digital Literacy: Essential Skills for the 21st Century
- Grade Inflation: The Deterioration of Academic Standards in Higher Education
- Climate Change Education: Teaching the Next Generation About Global Warming
- Character Education: Building Integrity and Responsibility in Students
- Music Education: Its Influence on Cognitive Development
- Literacy Programs: Overcoming Reading and Writing Challenges
- Mentorship Programs: Enhancing Student Success and Confidence
- Financial Literacy: Preparing Students for Real-World Money Management
Strong Education Argumentative Essay Topics
- Is Censorship Justified in School Libraries?
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of Single-Sex Schools
- Is College Preparation in High School Adequate?
- Are Teachers’ Salaries Commensurate With Their Job Responsibilities?
- Cyberbullying: Should Schools Intervene?
- The Importance of Cultural Diversity in Education
- Should Mental Health Education Be Mandatory in Schools?
- Do School Rankings Reflect the Quality of Education?
- The Relevance of Cursive Writing in Today’s Digital World
- Should Religious Studies Be Part of the School Curriculum?
- Are Students Overburdened with Excessive Schoolwork?
- The Implications of Zero Tolerance Policies in Schools
- School Safety: Responsibility of Schools or Parents?
- Does Grade Inflation Diminish the Value of Education?
- Are Life Skills Education Necessary in Schools?
- The Debate on Home Schooling vs. Traditional Schooling
- Is it Necessary to Teach World Religions in High Schools?
- Does a School’s Location Affect the Quality of Education?
- The Argument for Teaching Emotional Intelligence in Schools
- Should Attendance Be Mandatory in High School?
- Could Meditation and Mindfulness Improve Students’ Concentration?
- The Role of Music Education in Student Development
- Do Students Learn More From Books or Computers?
- The Need for Environmental Sustainability Education in Schools
Crossley, S., & Tian, Y. (2022). Argumentation features and essay quality: Exploring relationships and incidence counts. Journal of Writing Research , 14 (1), 1–34. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2022.14.01.01
Goodson, P. (2024). Becoming an academic writer: 50 exercises for paced, productive, and powerful writing . Sage.
Kleemola, K., Hyytinen, H., & Toom, A. (2022). The challenge of position-taking in novice higher education students’ argumentative writing. Frontiers in Education , 7 , 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.885987
Koons, M. (2021). Writing an argumentative essay: The complete introductory guide to writing an argumentative essay for beginner students . Write Illusion LLC.
Li, Y., Wang, K., Xiao, Y., & Froyd, J. E. (2020). Research and trends in STEM Education: A systematic review of journal publications. International Journal of STEM Education , 7 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00207-6
Mertler, C. A. (2024). Introduction to educational research . SAGE Publications.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

797 Sports Argumentative Essay Topics & Persuasive Speech Ideas
- Icon Calendar 28 May 2023
- Icon Page 8338 words

570 Technology Argumentative Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 27 May 2023
- Icon Page 6242 words

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.

Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis

Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement
Argumentative essay thesis statement generator.

Crafting a compelling argumentative essay requires a strong thesis statement that encapsulates the essence of your stance on a contentious issue. An argumentative essay thesis statement serves as the core of your paper, guiding your readers through your persuasive arguments. This guide delves into a collection of impactful argumentative essay thesis statement examples, providing you with insights on how to craft one effectively and offering valuable tips to enhance the persuasiveness and coherence of your essay.
What is an Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement? – Definition
An argumentative essay thesis statement is a concise declaration that presents the main point of your essay and outlines the position you intend to defend. It serves as a roadmap for your readers, indicating the central argument you’ll be addressing and the stance you’ll be advocating throughout the essay. The Good thesis statement in an argumentative essay is typically debatable and invites discussion.
What is an Example of a Thesis Statement for Argumentative Essay?
Example: “The government should implement stricter regulations on the use of plastic materials to mitigate the environmental crisis, reduce pollution, and safeguard the future of our planet.”
In this thesis statement for an argumentative essay, the claim asserts the necessity for stricter plastic regulations, and the preview of main points indicates the environmental benefits. This thesis sets the stage for an essay that presents evidence and persuasive arguments supporting the need for increased plastic regulation.
100 Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement Examples

Size: 294 KB
Explore a diverse array of argumentative essay thesis statement examples, each encapsulating a unique perspective on critical issues. From climate change policies to gun control measures, these statements illustrate the art of persuasive writing. Delve into the complexities of societal impact, ethical considerations, and policy implications while refining your skills in crafting compelling arguments that drive meaningful discussions and encourage critical thinking. In addition, you should review our final thesis statement .
1. Social Media and Mental Health The pervasive influence of social media on mental health demands urgent attention to its negative impact on self-esteem, anxiety, and emotional well-being.
2. Universal Healthcare Coverage Universal healthcare coverage is essential for promoting equitable access to medical services, improving health outcomes, and ensuring the well-being of all citizens.
3. Climate Change and Human Responsibility The urgency of addressing climate change requires acknowledging human responsibility, embracing sustainable practices, and implementing policies that combat global environmental threats.
4. Online Privacy and Data Security Stricter online privacy regulations are necessary to safeguard personal data, protect user confidentiality, and counter the increasing threats of cyberattacks and identity theft.
5. Education Reform and Student Success Education reform must prioritize student success by revamping curriculum, promoting individualized learning, and investing in educators to enhance overall educational quality.
6. Gun Control and Public Safety Implementing comprehensive gun control measures is vital to curbing gun violence, preventing mass shootings, and ensuring the safety of communities nationwide.
7. Gender Pay Gap and Workplace Equality Eliminating the gender pay gap requires enforcing equal pay policies, addressing occupational biases, and challenging societal norms that perpetuate wage disparities.
8. Capital Punishment and Human Rights Abolishing capital punishment is crucial for upholding human rights, fostering justice systems that prioritize rehabilitation, and acknowledging the inherent fallibility of legal systems.
9. Legalization of Marijuana for Medicinal Use The legalization of marijuana for medicinal use is a necessary step in providing effective pain management options, promoting research, and improving the quality of life for patients.
10. Technology and Interpersonal Relationships The integration of technology in interpersonal relationships necessitates a balance between virtual communication and face-to-face interaction to preserve genuine human connections.
11. Artificial Intelligence and Job Displacement The rise of artificial intelligence demands proactive measures to address job displacement, prioritize retraining programs, and ensure a balanced coexistence of human and AI roles in the workforce.
12. Obesity Epidemic and Public Health Combatting the obesity epidemic requires comprehensive public health interventions, including promoting healthy lifestyles, regulating marketing of unhealthy foods, and ensuring access to nutritious options.
13. Animal Rights and Ethical Treatment Recognizing the moral significance of animals necessitates ethical treatment, advocating for animal rights, and adopting regulations that prevent cruelty and exploitation.
14. Renewable Energy Transition and Sustainable Future Embracing a transition to renewable energy sources is pivotal for achieving a sustainable future, reducing carbon emissions, and mitigating the impact of climate change.
15. Vaccination and Community Immunity Mandatory vaccination policies are essential for maintaining community immunity, preventing disease outbreaks, and protecting vulnerable populations from preventable illnesses.
16. Digital Divide and Access to Education Closing the digital divide requires equitable access to technology, bridging educational disparities, and ensuring all students can benefit from online learning opportunities.
17. Cultural Appropriation and Respectful Engagement Addressing cultural appropriation demands respectful engagement, understanding the significance of cultural symbols, and acknowledging the importance of mutual respect.
18. Parental Leave and Work-Life Balance Enforcing paid parental leave policies is vital for promoting work-life balance, gender equality, and supporting parents in their caregiving responsibilities.
19. Social Inequality and Wealth Redistribution Tackling social inequality necessitates wealth redistribution, progressive taxation policies, and investing in social programs to narrow the wealth gap.
20. Mental Health Support in Schools Providing comprehensive mental health support in schools is crucial for early intervention, destigmatizing mental health issues, and fostering students’ emotional well-being.
21. Online Learning and Traditional Education Exploring the benefits and drawbacks of online learning versus traditional education reveals the need for adaptable approaches that combine the strengths of both modalities.
22. Body Positivity and Media Representation Promoting body positivity requires challenging unrealistic media representations, advocating for diverse beauty standards, and encouraging self-acceptance regardless of body type.
23. Human Cloning and Ethical Concerns The ethical considerations surrounding human cloning necessitate thorough examination of scientific advancements, potential medical benefits, and potential societal implications.
24. Cyberbullying and Digital Responsibility Mitigating cyberbullying requires fostering digital responsibility, educating youth about online ethics, and establishing clear consequences for harmful online behaviors.
25. Nuclear Energy and Environmental Impact Assessing the viability of nuclear energy demands understanding its environmental impact, evaluating safety measures, and considering it as a potential solution to energy demands.
26. Freedom of Speech and Hate Speech Regulation Balancing freedom of speech with the regulation of hate speech involves crafting policies that protect individuals’ rights while preventing the spread of harmful rhetoric.
27. Privacy Rights and Surveillance Technology Striking a balance between privacy rights and the use of surveillance technology requires robust legal frameworks that protect individual freedoms while ensuring public safety.
28. Animal Testing and Scientific Advancement Examining the ethics of animal testing compels us to explore alternative research methods, prioritize animal welfare, and weigh scientific progress against ethical considerations.
29. Cultural Diversity and Education Recognizing the value of cultural diversity in education necessitates inclusive curricula, multicultural awareness, and fostering understanding among diverse student populations.
30. Space Exploration and Budget Allocation Analyzing the allocation of funds for space exploration prompts discussion about the importance of scientific discovery, balanced budget priorities, and societal benefits.
31. Artificial Sweeteners and Health Risks Investigating the health risks associated with artificial sweeteners requires evaluating potential benefits, understanding metabolic effects, and providing accurate consumer information.
32. Renewable Energy Incentives and Economic Growth Analyzing the impact of renewable energy incentives on economic growth entails assessing job creation, sustainable development, and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
33. Social Media and Political Activism Exploring the role of social media in political activism demands examining its influence on mobilization, awareness campaigns, and the democratization of information.
34. Euthanasia and End-of-Life Choices Delving into the ethical complexities of euthanasia necessitates considering individual autonomy, medical ethics, and the impact on patients and their families.
35. Food Waste and Environmental Sustainability Addressing the issue of food waste requires understanding its environmental consequences, promoting sustainable consumption, and implementing waste reduction strategies.
36. Genetic Engineering and Ethical Boundaries The exploration of genetic engineering’s ethical boundaries involves weighing the potential benefits against concerns about bioethics, consent, and unintended consequences.
37. Online Censorship and Freedom of Expression Navigating online censorship involves preserving freedom of expression while curbing hate speech, misinformation, and ensuring a safe digital environment.
38. Youth Engagement in Politics Encouraging youth engagement in politics requires dismantling barriers to participation, promoting civic education, and empowering young voices in policy decisions.
39. Artificial Intelligence and Human Workforce Examining AI’s impact on the human workforce prompts discussions about retraining programs, job displacement, and ethical considerations in automation.
40. Body Cameras and Police Accountability The debate around police accountability involves analyzing the effectiveness of body cameras in improving transparency, reducing misconduct, and rebuilding community trust.
41. Privacy Rights in the Digital Age Navigating privacy rights in the digital age requires addressing data collection, surveillance, and striking a balance between personal freedom and national security.
42. School Uniforms and Student Expression The debate over school uniforms centers on balancing students’ self-expression with creating a sense of community, reducing peer pressure, and minimizing distractions.
43. Access to Birth Control and Reproductive Rights The conversation about access to birth control delves into reproductive autonomy, healthcare equity, and ensuring comprehensive family planning options for all.
44. Space Exploration and Environmental Preservation Evaluating space exploration’s impact on environmental preservation necessitates considering resource allocation, scientific advancements, and the Earth’s fragile ecosystem.
45. Online Learning and Academic Integrity Examining academic integrity in online learning environments involves implementing strategies to prevent cheating, uphold educational standards, and verify student authenticity.
46. Cybersecurity and National Defense The intersection of cybersecurity and national defense requires prioritizing cyber threats, enhancing digital defenses, and safeguarding critical infrastructure from cyberattacks.
47. Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) and Food Security Assessing the role of GMOs in food security involves weighing potential benefits against environmental concerns, health implications, and ethical considerations.
48. Police Reform and Community Policing Promoting police reform through community policing necessitates enhancing community engagement, fostering mutual trust, and addressing systemic issues in law enforcement.
49. Internet Access as a Basic Right Advocating for internet access as a basic right involves bridging the digital divide, ensuring equal opportunities for education and information, and empowering marginalized communities.
50. Medical Ethics and Human Cloning Exploring medical ethics in human cloning debates involves considering the potential for medical breakthroughs, individual rights, and the potential for unethical exploitation.
51. Renewable Energy Transition and Job Creation Evaluating the renewable energy transition’s impact on job creation necessitates understanding its potential to boost employment while addressing environmental concerns.
52. Social Media and Political Polarization Analyzing the role of social media in political polarization involves exploring echo chambers, filter bubbles, and their influence on public discourse and civic engagement.
53. Mental Health Support in Schools Advocating for mental health support in schools requires addressing stigma, promoting early intervention, and creating safe spaces that foster emotional well-being.
54. Artificial Intelligence and Ethical Dilemmas Navigating the ethical dilemmas posed by AI involves grappling with issues of bias, accountability, and the implications of delegating decision-making to machines.
55. Internet Privacy and Data Ownership The conversation about internet privacy delves into users’ rights over their personal data, requiring transparent data practices, consent, and protection against misuse.
56. Social Justice Movements and Intersectionality Understanding social justice movements demands acknowledging intersectionality, recognizing the interconnectedness of social issues, and advocating for inclusive solutions.
57. Cultural Preservation and Tourism Balancing cultural preservation with tourism development involves respecting indigenous knowledge, engaging local communities, and fostering sustainable cultural exchange.
58. Gun Control and Second Amendment Rights The debate over gun control must respect Second Amendment rights while addressing public safety concerns, background checks, and reducing gun-related violence.
59. Genetic Editing and Human Enhancement Exploring genetic editing’s potential for human enhancement requires ethical considerations, weighing medical benefits against concerns of inequality and unintended consequences.
60. Universal Basic Income and Economic Equality Discussing universal basic income involves evaluating its potential to address poverty, stimulate economic growth, and create a safety net in an evolving job landscape.
61. Climate Change and Global Cooperation Addressing climate change demands global cooperation, involving policy alignment, international agreements, and joint efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
62. Immigration Reform and Human Rights The discussion on immigration reform necessitates respecting human rights, creating pathways to citizenship, and striking a balance between national security and compassion.
63. Internet Addiction and Mental Health Understanding internet addiction’s impact on mental health requires recognizing its prevalence, providing digital well-being education, and developing strategies for healthy online habits.
64. Education Funding and Equal Opportunity Investing in education funding is crucial for ensuring equal opportunity, bridging educational gaps, and breaking the cycle of generational poverty.
65. Genetic Privacy and DNA Data Sharing Examining genetic privacy involves safeguarding DNA data from misuse, securing consent for sharing, and balancing scientific advancements with individual rights.
66. Cultural Appropriation and Creative Expression The discourse on cultural appropriation requires distinguishing between appreciation and appropriation, encouraging cross-cultural understanding, and respecting cultural ownership.
67. Cybersecurity and Personal Privacy Balancing cybersecurity with personal privacy necessitates robust digital defenses, encryption standards, and ensuring individuals’ autonomy over their online information.
68. Youth Activism and Social Change Exploring the impact of youth activism involves recognizing young voices in shaping societal norms, challenging systemic inequalities, and advocating for positive change.
69. Internet Censorship and Free Speech Navigating internet censorship involves preserving free speech while curbing harmful content, disinformation, and fostering responsible digital citizenship.
70. Education Technology and Pedagogical Innovation The integration of ed-tech in education requires thoughtful pedagogical design, addressing digital literacy gaps, and leveraging technology to enhance learning outcomes.
71. Animal Rights and Scientific Research Balancing animal rights with scientific research involves ensuring ethical treatment, seeking alternative methods, and adhering to standards that prioritize animal welfare.
72. Income Inequality and Wealth Redistribution Addressing income inequality demands progressive taxation, redistributive policies, and promoting economic mobility to create a more just and equitable society.
73. Health Care Reform and Affordable Access Discussing health care reform involves ensuring affordable access, lowering prescription drug costs, and creating comprehensive health care coverage for all citizens.
74. Gender Equality in Sports Promoting gender equality in sports entails equal pay, opportunities, and dismantling gender stereotypes that perpetuate inequalities in athletic participation and representation.
75. Nuclear Disarmament and Global Security Advocating for nuclear disarmament requires diplomatic efforts, arms control agreements, and collaboration among nations to ensure global peace and security.
76. Cyberbullying Prevention and Digital Literacy Preventing cyberbullying involves educating students about digital ethics, empathy, and fostering a safe online environment that promotes positive interactions.
77. Mental Health Care Accessibility Improving mental health care accessibility necessitates dismantling stigma, increasing funding, and expanding resources to ensure individuals can access quality care.
78. Human Rights and Refugee Protection Addressing human rights in refugee protection involves creating safe havens, advocating for fair treatment, and finding sustainable solutions to the global refugee crisis.
79. GMO Labeling and Consumer Awareness Discussing GMO labeling requires transparent information for consumers, empowering them to make informed choices, and promoting transparency in the food industry.
80. Cultural Diversity and Workplace Inclusion Promoting cultural diversity in the workplace involves embracing inclusivity, valuing diverse perspectives, and fostering a welcoming environment that supports all employees.
81. Technology Addiction and Digital Detox The conversation about technology addiction necessitates recognizing its effects, advocating for balanced tech use, and promoting mindfulness in the digital age.
82. Criminal Justice Reform and Rehabilitation Advancing criminal justice reform involves shifting focus from punishment to rehabilitation, addressing systemic biases, and fostering reintegration into society.
83. Indigenous Rights and Land Conservation Supporting indigenous rights requires respecting land ownership, preserving cultural heritage, and partnering with indigenous communities for sustainable land conservation.
84. Voting Rights and Democracy Protecting voting rights involves combating voter suppression, ensuring equal access, and upholding the democratic principle of every citizen’s right to vote.
85. Mental Health Education in Schools Promoting mental health education in schools involves training educators, reducing stigma, and equipping students with tools to navigate their emotional well-being.
86. Alternative Energy Sources and Energy Independence Transitioning to alternative energy sources promotes energy independence, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigates the impact of climate change.
87. Privacy Rights in the Workplace Balancing privacy rights in the workplace involves protecting employee data, regulating surveillance, and ensuring a respectful work environment that values personal privacy.
88. Affirmative Action and Diversity in Education Discussing affirmative action entails promoting diversity in education, addressing historical inequalities, and creating inclusive learning environments that reflect society’s richness.
89. Social Media and Democracy Analyzing social media’s impact on democracy requires recognizing its potential for disinformation, promoting digital literacy, and safeguarding informed political participation.
90. Parental Rights and Children’s Autonomy Navigating parental rights and children’s autonomy involves striking a balance between guiding children’s decisions and respecting their individual agency.
91. Climate Change and Economic Growth Addressing climate change without hindering economic growth involves transitioning to sustainable practices, investing in green technologies, and creating new economic opportunities.
92. Immigration Policies and Family Reunification Promoting humane immigration policies involves prioritizing family reunification, treating migrants with dignity, and fostering cultural diversity and understanding.
93. Mental Health Parity in Insurance Advocating for mental health parity in insurance requires ensuring equal coverage for mental health treatments, reducing disparities, and acknowledging mental health’s importance.
94. Online Hate Speech and Social Media Responsibility Combating online hate speech involves holding social media platforms accountable for moderation, promoting respectful discourse, and preventing the spread of harmful content.
95. Human Trafficking and Criminal Justice Addressing human trafficking involves strengthening laws, supporting survivors, and collaborating across borders to dismantle criminal networks and protect vulnerable individuals.
96. Green Technology Innovation and Sustainability Encouraging green technology innovation requires investment in research, incentivizing eco-friendly practices, and transitioning to sustainable solutions for a greener future.
97. Internet Accessibility in Rural Areas Promoting internet accessibility in rural areas involves bridging the digital divide, providing equitable opportunities for education and economic growth, and overcoming infrastructure challenges.
98. Arts Education in Schools Advocating for arts education in schools involves recognizing its role in fostering creativity, critical thinking, and well-rounded development for students.
99. Food Security and Agricultural Practices Addressing food security requires promoting sustainable agriculture, reducing food waste, and ensuring equitable access to nutritious food for all.
100. Democracy and Civic Engagement Sustaining a healthy democracy relies on fostering civic engagement, promoting informed citizen participation, and strengthening the foundation of transparent and accountable governance.
What are the 3 Parts of an Argument Thesis Statement?
An argument thesis statement comprises three essential parts that collectively establish the foundation for your persuasive essay:
- Claim or Assertion: This is the central argument you’re making in your essay. It should be clear, specific, and debatable to engage your readers and encourage them to consider your viewpoint.
- Reasons or Supporting Points: These are the key points that bolster your claim. Each reason should be backed by evidence, logic, or examples to provide substantial support for your argument.
- Counterargument or Rebuttal: Anticipate potential objections to your claim and address them briefly. Acknowledging counterarguments adds credibility to your essay and demonstrates your thoughtful consideration of opposing viewpoints.
How do you Write a Thesis Statement for an Argumentative Essay? – Step by Step Guide
- Choose a Controversial Topic: Select a topic that sparks debate and has multiple viewpoints to provide a solid foundation for your argument.
- Identify Your Position: Determine where you stand on the topic and craft a clear claim that encapsulates your stance.
- Brainstorm Supporting Points: List three to four main reasons that support your claim. These reasons will become the core of your argument.
- Address Counterarguments: Consider potential counterarguments and identify how you’ll address them in your thesis statement or later in your essay.
- Craft a Draft: Combine your claim, reasons, and potential counterargument into a concise sentence that serves as your thesis statement.
- Ensure Clarity and Precision: Make sure your thesis statement is straightforward, avoiding vague or convoluted language.
- Maintain a Strong Tone: Frame your thesis statement assertively to convey confidence in your argument.
- Avoid Broad Statements: Keep your thesis statement focused on your specific argument, avoiding generalizations.
- Review and Refine: Revisit your draft, ensuring it accurately represents your viewpoint and effectively encapsulates your argument.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement for Argumentative Essay
- Be Clear and Concise: Your thesis statement should convey your argument succinctly, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Take a Definite Position: Make a clear and unequivocal assertion in your thesis statement to guide your essay’s direction.
- Use Strong Language: Choose impactful words that emphasize the strength and significance of your argument.
- Provide Evidence: While not required in the thesis statement itself, ensure that you have evidence to back up your supporting points.
- Consider Your Audience: Tailor your thesis statement to resonate with your intended readers, considering their background and beliefs.
- Avoid First Person: Keep your thesis statement in the third person to maintain an objective and professional tone.
- Review and Revise: As you draft your essay, revisit your thesis statement to ensure it aligns with the arguments presented in your essay.
- Stay Focused: Your thesis statement should encompass the main theme of your argument, avoiding tangential points.
- Seek Feedback: Share your thesis statement with peers or mentors to gain insights and refine its effectiveness.
By carefully crafting your argument thesis statement, you set the tone for your entire essay, outlining your position, key arguments, and addressing potential counterarguments. Through concise and persuasive language, your thesis statement becomes the cornerstone of your argumentative essay. You may also be interested in our strong thesis statement .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement on the necessity of college education.
Create an Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement arguing for the legalization of marijuana.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
Select a year to see courses
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
OC Test Preparation
- Selective School Test Preparation
- Maths Acceleration
- English Advanced
- Maths Standard
- Maths Advanced
- Maths Extension 1
- English Standard
- Maths Extension 2
Get HSC exam ready in just a week
- UCAT Exam Preparation
Select a year to see available courses
- English Units 1/2
- Maths Methods Units 1/2
- Biology Units 1/2
- Chemistry Units 1/2
- Physics Units 1/2
- English Units 3/4
- Maths Methods Units 3/4
- Biology Unit 3/4
- Chemistry Unit 3/4
- Physics Unit 3/4
- UCAT Preparation Course
- Matrix Learning Methods
- Matrix Term Courses
- Matrix Holiday Courses
- Matrix+ Online Courses
- Campus overview
- Castle Hill
- Strathfield
- Sydney City
- Year 3 NAPLAN Guide
- OC Test Guide
- Selective Schools Guide
- NSW Primary School Rankings
- NSW High School Rankings
- NSW High Schools Guide
- ATAR & Scaling Guide
- HSC Study Planning Kit
- Student Success Secrets
- Reading List
- Year 6 English
- Year 7 & 8 English
- Year 9 English
- Year 10 English
- Year 11 English Standard
- Year 11 English Advanced
- Year 12 English Standard
- Year 12 English Advanced
- HSC English Skills
- How To Write An Essay
- How to Analyse Poetry
- English Techniques Toolkit
- Year 7 Maths
- Year 8 Maths
- Year 9 Maths
- Year 10 Maths
- Year 11 Maths Advanced
- Year 11 Maths Extension 1
- Year 12 Maths Standard 2
- Year 12 Maths Advanced
- Year 12 Maths Extension 1
- Year 12 Maths Extension 2
Science guides to help you get ahead
- Year 11 Biology
- Year 11 Chemistry
- Year 11 Physics
- Year 12 Biology
- Year 12 Chemistry
- Year 12 Physics
- Physics Practical Skills
- Periodic Table
- VIC School Rankings
- VCE English Study Guide
- Set Location
- 1300 008 008
- 1300 634 117
Change your location
To ensure we are showing you the most relevant content, please select your location below.
How To Write A Thesis Statement | Essay Writing Part 1 [2022 UPDATE]

Guide Chapters
- 1. Thesis statement
- 2. Introduction structure
- 3. Topic sentence
- 4. Body paragraph structure
- 5. Conclusion
This post, How to Write a Thesis Statement, is the first post in our 5 part Essay Writing Series. In this series, we will break essay writing into a series of parts and solve some commonly asked questions to give you the tools to write consistent essays.
Some common questions about essay structure are:
What is a thesis statement?
- What does a thesis statement do?
- Is the thesis statement important?
- How do I write a good thesis statement?
In this post, we’ll give you an overview of essay structure and explain why a thesis statement is important for your essay. We’ll then give you a step-by-step guide for writing a Band 6 thesis.
Table of Contents
- Essay Structure
- What is a thesis statement
- 1. Underline key words in the question
- 2. Note down relevant topics/themes
- 3. Decide on the argument you want to present in your thesis statement
- 4. Turn that argument into a thesis statement
Common mistakes that students make in their thesis statements
What should you do instead, essential essay structure: how to write a thesis statement | essay writing part 1.
Learning how to write a good essay is something developed through practice and logic, not innate skill or talent. Anybody can write a good essay with practice and instruction.
In this series of posts, we will show you some of the skills that Matrix students use as they learn to write Band 6 responses. First, we will learn about the structure of an essay, and then we will look at why the thesis is the solid foundation on which we build our argument.
What is Essay Structure?
Essay structure is the logical sequencing of information we use when composing a written argument. When you break it down, essay writing is actually a fairly straightforward process.
- Introduce your main argument ( thesis )
- Explain the key 2 or 3 ideas ( themes ) that will support your main argument
- Explain how these ideas fit together logically
- Introduce a specific idea
- Present evidence that supports your idea
- Connect this idea to your main argument
- Repeat these ‘2. Body Paragraph’ steps for the other ideas that support your main argument
- Restate your argument
- Make a concluding statement
When you break essay writing down into a process, it becomes straightforward and systematic.
We can take the process of essay writing and look at it in a diagram:
In this post, we will look at the first step of this process. The thesis statement.
Let’s have a look at what it does.
Last chance to finesse your thesis statement writing!
Develop essay writing confidence before the HSC exams with our Year 12 English Matrix Course! Learn more .
Start HSC English confidently
Expert teachers, detailed feedback, one-to-one help! Learn from home with Matrix+ Online English courses.
The thesis is the foundation of your essay. It structures your argument. Having a good thesis is essential to getting a Band 6 result, regardless of what module or level of English you are doing.
Your thesis needs to be concise, but also answer the question. It must introduce an idea that you can readily repeat throughout your essay so that your reader is constantly aware of what you are arguing.
Now we know what a thesis is and how it functions within an essay, let’s look at a step-by-step process for writing one!
How to write a thesis statement – A step-by-step guide
We’ll now look at the process for writing a thesis statement. To do so, we will use a HSC question as an example and develop it throughout this series.
Step 1: Underline key words in the question
You need to properly address the question to score a Band 6. Underlining key words in the question will take less than a minute and give your essay clear direction.
Let’s look at how we would annotate the 2021 HSC question for the Common Module:
Analyse how your prescribed text represents the ways individuals respond to the challenges they face.
Step 2: Note down relevant topics/themes
Now that you know the key points that the question wants you to discuss, you can jot down relevant topics/themes from your prescribed you’d want to discuss in your essay.
Step 3: Decide on the argument you want to present in your thesis statement
Your argument is essentially your super passionate response to the question. It’s subjective and opinionated, which is why you need a whole essay to try to convince your marker that you are right.
You don’t have to use fancy wording to get your point across. Write it how you would say it in a conversation; this step is for you to know what you are going to spend the next 40 minutes writing furiously about.
Be strategic about it. Pick a stance that:
- You can back up with evidence — if you can’t remember any quotes from the text that support your argument, you probably want to quietly come up with a different argument that you can confidently discuss.
- Aligns the module statement — a lot of really smart people spent a long time coming up with the module statements, so you’ll probably have a hard time arguing that individuals don’t have experiences or responses to challenges. If you want to flex your creative side, do that in your nuanced analysis of the textual evidence, instead of blatantly rejecting everything your teachers spent an entire year teaching you.
You don’t necessarily have to personally believe that your argument is true. You can play devil’s advocate or be overly pessimistic if you think that’s the easiest route to take.
Here’s an example of an argument that you can make in response to the 2021 HSC Common Module question:
“Even though everyone responds to challenges in different ways, at the end of the day, we all selfishly prioritise our own needs and safety before anyone else.”
It’s a very drastic and upsetting thing to believe, but you can see how we could effectively use evidence from Nineteen Eighty-Four to prove it.
Step 4: Turn that argument into a thesis statement
Now that you know exactly what your overarching argument is going to be, you can write a thesis statement from that. To turn your argument into a thesis statement, you need to:
- Specify details relevant to the themes in your prescribed text
- Be as concise as possible
- Avoid using first or second-person language
Don’t write the 94851 th essay that your marker has to read with these mistakes.
Mistake 1: Repeating the question
The most common error when composing thesis statements is repeating the question.
As senior students, you are expected to analyse the question and construct a personal and logical response to it. Repeating the question back at the marker as a thesis statement does not demonstrate an understanding of the question, module, or text. Instead, such a response demonstrates that you have a limited understanding of both.
Let’s look at the 2021 HSC question for Module A:
How do the extracts provided contribute to a broader textual conversation between the pair of prescribed texts that you have studied in Module A?
You can find the extracts the question refers to here .
We’ve written examples for the prescribed texts The Tempest and Hag-Seed .
Mistake 2: Using uncertain terms
Don’t be vague or use low modality words and expressions in your thesis.
Students have it drilled into them that “they know nothing” or “don’t have the experience” to say things with certainty. This is said to stop students making broad sweeping statements about human existence or genres of writing, but it must not apply to your understanding of the text.
Let’s have a look at the 2020 HSC Module A question to see what we mean:
In textual conversations, the later text is often seen as a shadow, lacking the originality and power of the earlier.
To what extent is this statement true of the two prescribed texts you have studied in Module A?
A common thesis mistake was to state something along the lines of:
“Margaret Edson’s play ‘W;t’ (1995) may appear to merely echo the concepts John Donne explores in his poems. However, her play could be also seen as nuanced commentary of Donne’s poetry that creates a highly engaging textual conversation about the death, separation and salvation of one’s physical and mental being.”
This statement uses the verb “could” which lacks certainty. You want to avoid verbs like “may,” “might,” or “could” , or replace them with verbs like “will,” “does,” and “shall” that have high-modality or high certainty.
People are more inclined to give credibility to assertive and confident voices. This is why the following thesis statement sounds so authoritative:
“It would be grossly unfair to say that Margaret Edson’s later play ‘W;t’ (1995) merely echoes the concepts that John Donne explores in his poems. In fact, Edson’s nuanced commentary of Donne’s poetry creates a highly engaging textual conversation about the death, separation and salvation of one’s physical and mental being.”
Mistake 3: Trying to fit it all in one sentence when it really doesn’t fit
The term thesis statement can be misleading. We hear “statement” and we often think “sentence.” The two words are not synonymous, though. It is far better to use an extra sentence to add detail to your sentence rather than stubbornly pack it into one. You need to explain the logic of your argument in a thesis, not just outline an argument.
Compare these two thesis statements:
“The storytelling of narratives that have been denied or repressed leads individuals to reconsider their knowledge of things.”
“The storytelling of narratives that have been denied or repressed profoundly impacts an individual’s perspective of society. The process of uncovering these stories compels individuals to reassess the political regime they live in and adjust their understanding of truth in their world.”
The second thesis is obviously better, but why?
The first thesis statement is competent, but it does not help the marker into your understanding of the module or the question. By splitting the statement over two sentences in the second example, we detail the logic of our argument. The second statement explains how the process of storytelling works, rather than merely noting that it occurs.

Mistake 4: Not answering the question asked
Too often students will write the thesis they have prepared and not the one that responds to the question they have been given. This is common amongst students who prefer to write “generic” essays and “mould” them to suit a question.
Let’s consider the 2021 HSC question for Module B:
‘Literature forces us to ask questions and look for answers. Even if those answers do not exist.’
To what extent is this true?
In your response, make close reference to your prescribed text.
One of the key things to note is that this question asks you ‘ To what extent is this [statement] true’. You can answer that in a range of ways:
1. The statement is completely true
2. the statement is completely false, 3. the statement is partly true.
In an exam, you usually won’t have enough time to write out all the different stances you could make to address the question. However, at the very least, you should dedicate a minute to annotating parts of the question that you agree and disagree with, and think about how you can use the evidence you remember to support your thesis.
You have already got off to a good start by going through these steps to writing a thesis statement. From here, it’s all about practice and making sure you don’t let down your fabulous thesis statement with the rest of your essay.
Tip 1: Practice
Essay writing is a skill that develops the same way as juggling a soccer ball or playing the panpipes. You will not become adept unless you invest many hours writing and rewriting responses to a variety of questions.
If you want to learn how to produce that killer thesis go to the NESA website and work your way through their practice questions until you’re an expert.
Tip 2: Learn how to write a thematic framework
Now you’ve got a thesis, you need to use it to structure an essay. The next step is to choose the themes that you will discuss and introduce them to your reader.
How to Structure Your Essay Introduction | Essay Writing Part 2
© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2023. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
Related courses
Year 3 english.
Year 3 English tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their reading and writing skills.
Learning methods available
Year 3 Maths
Year 3 Maths tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their maths skills and confidence.
Year 4 English
Year 4 English tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their reading and writing skills.
Year 4 Maths
Year 4 Maths tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their maths skills and confidence.
Sydney's best OC prep tutoring by experienced teachers and tried, tested resources. Learn online or on-campus. Try free now.
Year 5 Maths
Year 5 Maths tutoring at Matrix will help your child improve their maths skills and confidence.
More essential guides

How to Study Effectively During Isolation or at Home

The English Literary Techniques Toolkit for The HSC

The Visual Techniques Toolkit

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Education is the cornerstone of societal progress, and an argumentative essay thesis statement can explore its multifaceted impact. A thesis statement could be: "Mandatory financial literacy education in schools should be implemented to empower students with essential life skills, promoting responsible financial decision-making.
A thesis statement in an argumentative essay needs to present a point of view.The biggest mistake you can make is to provide a thesis statement that doesn't demonstrate what your argument will be. So, your thesis statement should set a clear argument, perspective, or position in relation to a debate. Check out the examples below.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Education, a cornerstone of societal development, is a fertile field for writing papers. In this case, education argumentative essay topics can range widely, from debates over traditional vs. digital classrooms, the effectiveness of standardized testing, and the necessity of college education in the 21st century to the balance between academics and character development.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
The thesis needs to be narrow. Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
100 Thesis Statement Examples for College Essay. Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 236 KB. Download. Crafting an impactful thesis statement for a college essay requires both precision and depth. Serving as the foundation for your argument, a well-constructed thesis captures the essence of your essay topic and directs the narrative.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement. The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it. ... The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. ...
Thesis Statements. A thesis is the main claim you are making in an argument, similar to the hypothesis in a scientific experiment. It is what you are trying to prove or persuade your audience to believe or do. It's helpful to develop a working thesis to guide your composition process. "Working" is the operative word here; your ideas are ...
Now on to those 30 persuasive thesis statement examples I promised! 1. Is a college education necessary? A college education is not the right choice for everyone, as many students graduate with a large amount of student debt and limited job opportunities. 2.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Updated on April 13, 2023 Academic Writing. A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write!
A thesis statement is a one- to two-sentence statement that presents the main idea and makes an assertion about your issue. You may have a longer thesis for much longer essays, but one to two sentences is a good general guideline. And, remember, in an argumentative essay, the assertion you present in your thesis is going to be particularly ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
100 Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement Examples. Details. File Format. PDF. Size: 294 KB. Download. Explore a diverse array of argumentative essay thesis statement examples, each encapsulating a unique perspective on critical issues. From climate change policies to gun control measures, these statements illustrate the art of persuasive writing.
These argumentative thesis statement examples are meant to serve as possible inspiration-don't use them verbatim. That would be plagiarism, and besides, it would rob the world of your unique thoughts about the issues at hand. Look at each example and note what they have in common-each states a clear position on a given issue and then ...
Remember that the thesis statement is a kind of "mapping tool" that helps you organize your ideas, and it helps your reader follow your argument. After the topic sentence, include any evidence in this body paragraph, such as a quotation, statistic, or data point, that supports this first point. Explain what the evidence means. Show the reader ...
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader. 2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
1. Underline key words in the question. 2. Note down relevant topics/themes. 3. Decide on the argument you want to present in your thesis statement. 4. Turn that argument into a thesis statement. Common mistakes that students make in their thesis statements.