About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed

About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
- Faculty Recruiting
- See All Jobs
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets and Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Webinars
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Subscribe to Corporate Governance Emails
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
Xiaomi’s Globalization Strategy and Challenges
Xiaomi, the Chinese smartphone company founded in 2010, had quickly become an industry leader in the Chinese market. By 2016 it had started to expand internationally, and this case lays out the company’s globalization strategies and challenges moving forward. Hugo Barra, a top Android executive, had left Google a few years earlier to lead Xiaomi’s international growth. Xiaomi’s founder and CEO, Lei Jun, said the company’s ultimate goal was “making good but cheap things,” a low pricing strategy that had succeeded in China. The company sold over 70 million mobile phones in 2015—while aggressively building out a robust ecosystem. However, Xiaomi had expected to sell 80 to 100 million units that year; it was facing a declining domestic market and increased competition. Therefore, international expansion had become an important part of the company’s overall strategy.
But expanding to other countries would be a challenging road. For one, it would take considerable time and effort to tailor the company’s Android-based MIUI operating system for diversified markets—and obtain market-access qualifications. Xiaomi’s patent portfolio was thin compared to those of large competitors, and it ran the risk of lawsuits from companies that held patent rights in the countries it wanted to enter. Other challenges included building out sales channels, output capacity, and cross-culture management development. Xiaomi’s international plan included ten countries in Asia, Europe, and Latin America. The next year or two would be critical for Xiaomi—and it needed to make the right strategic decisions to succeed in its globalization efforts.
Learning Objective

- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Annual Alumni Dinner
- Class of 2024 Candidates
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Dean’s Remarks
- Keynote Address
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Marketing
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2024 Awardees
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- Career Change
- Career Advancement
- Career Support and Resources
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Program Contacts
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- RKMA Market Research Handbook Series
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships

- International Marketing
Xiaomi’s Global Strategy: From Local Hero to International Giant
- April 22, 2024
Table of contents
Xiaomi’s global strategy on the rise, xiaomi’s global rise: a recipe for success, a. product strategy: innovation meets affordability, b. building a strong brand: online and offline, c. distribution channels: a global network, d. localization: understanding the nuances of global markets, the role of translation services in xiaomi’s global success, challenges on the horizon, charting a course for continued growth, key learnings from xiaomi’s global strategy, actionable insights: lessons learned from xiaomi’s global success, faqs: xiaomi’s global strategy and localization.
Xiaomi, a prominent Chinese tech company, has become a major force in the global smartphone market in a remarkably short timeframe. Founded in 2010, Xiaomi has captured the attention of consumers worldwide with its innovative products and competitive pricing strategy. In 2022, nearly half (49.2%) of the company’s revenue came from international markets , highlighting the success of Xiaomi’s global strategy ( Xiaomi , 2023). This article delves into the key elements of this strategy, exploring how Xiaomi has achieved international recognition and continues to expand its reach.
We will analyze Xiaomi’s rise to prominence, examining the factors that have propelled the company forward. We will then dissect Xiaomi’s global strategy, exploring its product development, marketing tactics, distribution channels, and approach to localization. Furthermore, we will investigate the potential challenges Xiaomi might face in the future and explore possible directions for its continued growth. By understanding Xiaomi’s global strategy, we can gain valuable insights into the ever-changing landscape of the technology industry .
Xiaomi’s meteoric rise to the top of the smartphone market can be attributed to several key factors that align perfectly with its global strategy. First and foremost, the company has prioritized offering consumers high-quality products at competitive prices . This value proposition has resonated strongly, particularly in emerging markets where price sensitivity is high. Xiaomi’s smartphones boast impressive features and specifications, often rivaling those of more expensive brands.
Secondly, Xiaomi has capitalized on the power of the internet by establishing a robust online sales strategy . This approach has allowed them to bypass traditional retail markups, further reducing costs for consumers. Additionally, Xiaomi has fostered a strong online community, fostering brand loyalty and engagement.
Beyond price and online savvy, Xiaomi has invested heavily in building a powerful brand image . Effective marketing campaigns have helped Xiaomi establish itself as a company that understands the needs of its customers and delivers innovative products.
Finally, Xiaomi’s vision extends beyond smartphones. The company has embarked on an ambitious strategy to create an ecosystem of interconnected devices , similar to Apple’s successful model. This includes smart home appliances, wearables, and other consumer electronics. This diversification allows Xiaomi to tap into new markets and provide a more comprehensive user experience.
By combining these elements, Xiaomi has carved a unique niche in the global technology landscape . Its focus on affordability, online presence, strong branding, and ecosystem development has fueled its impressive growth and positioned it as a major player in the global smartphone market.
Deconstructing Xiaomi’s Global Strategy: A Winning Formula
Xiaomi’s global strategy is a carefully crafted blueprint for success, built upon several key pillars. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand how Xiaomi has achieved such a strong international presence .
At the heart of Xiaomi’s global strategy lies a product strategy focused on innovation and user experience, delivered at competitive prices . The company prioritizes offering feature-rich smartphones that rival high-end models, all without breaking the bank. This approach has been particularly effective in emerging markets where price is a major consideration for consumers.
Furthermore, Xiaomi doesn’t limit itself to just smartphones. Their product portfolio is expanding to encompass a wider range of consumer electronics, creating an interconnected ecosystem similar to Apple’s. This includes smart home appliances, wearables, and other devices. By offering a comprehensive suite of products that work seamlessly together, Xiaomi caters to a wider audience and strengthens its brand loyalty .
A cornerstone of Xiaomi’s global strategy is its commitment to building a powerful brand image. The company leverages both online and offline marketing channels to reach consumers effectively. They have invested heavily in creating a strong online presence, fostering a vibrant online community that fosters brand loyalty and engagement. Social media plays a crucial role in their marketing strategy, allowing Xiaomi to connect with customers in target markets and understand their specific needs.
However, Xiaomi doesn’t neglect traditional marketing channels. They have expanded their presence in physical retail stores , making their products more accessible to a wider range of consumers. This blended approach ensures maximum reach and brand recognition across different demographics.
Xiaomi’s global strategy prioritizes establishing a robust distribution network to reach customers worldwide. They have established a dominant online sales presence, allowing them to bypass traditional retail markups and offer competitive pricing to consumers . However, Xiaomi recognizes the importance of physical retail stores as well. They have been actively expanding their presence in brick-and-mortar stores , offering customers a chance to interact with their products firsthand.
Building strong partnerships with local distributors is another key aspect of Xiaomi’s distribution strategy. By partnering with companies familiar with the local market landscape, Xiaomi can ensure efficient product delivery and provide excellent customer service in each region they operate in .
A crucial element of Xiaomi’s global strategy is its focus on localization . The company understands that a one-size-fits-all approach won’t work in a global marketplace. They take the time to adapt their products and marketing messages to suit the preferences and cultural nuances of each target market. This might involve modifying product features, offering localized language support, and tailoring marketing campaigns to resonate with local audiences. By demonstrating a commitment to understanding regional differences, Xiaomi builds trust and strengthens its brand image on a global scale.
Taking a closer look at these key ingredients of Xiaomi’s global strategy, we can unlock the secrets behind their remarkable success. Their commitment to innovation, affordability, building a strong brand, utilizing diverse distribution channels, and adapting to different markets has rocketed them to the top of the global tech world.
While Xiaomi’s global strategy excels in product development, marketing, and distribution, a key ingredient often goes unnoticed: translation services . For a company aiming to dominate international markets, clear and culturally-sensitive communication is paramount. Partnering with a professional translation agency plays a crucial role in Xiaomi’s success on a global scale.
Here’s how translation services contribute to the effectiveness of Xiaomi’s global strategy :
- Accurate and Culturally-Sensitive Marketing Materials: Reaching a global audience requires messaging that resonates with local cultures. A professional translation company can ensure Xiaomi’s marketing materials, from website content to social media posts, are accurately translated and adapted to the specific cultural context of each target market. This includes translating humor appropriately, avoiding offensive language, and using culturally relevant imagery. By ensuring clear and culturally-sensitive communication, Xiaomi avoids misunderstandings and builds trust with potential customers.
- Reaching a Wider Global Audience with Localized Messaging: Language barriers can be a significant hurdle in reaching new customers. Professional translation services allow Xiaomi to overcome this obstacle. By translating marketing materials and product information into the local languages of their target markets, Xiaomi significantly expands its reach. This allows them to connect with a wider audience and generate interest in their products across the globe.
- Building Trust and Brand Reputation in New Markets: Effective communication is essential for building trust with consumers. When Xiaomi presents itself in a language and cultural context that resonates with local audiences, it demonstrates a genuine understanding of their needs and preferences. This, in turn, fosters brand loyalty and a positive reputation in new markets. Professional translation services ensure Xiaomi’s brand message is conveyed accurately and respectfully, laying the foundation for long-term success in each region they operate in.
We often hear about Xiaomi’s impressive phones and aggressive pricing, but there’s another key player in their global success story: translation services. Accurate translations that are clear and sensitive to different cultures are crucial for reaching new audiences. By making sure their message resonates in each market, translation services empower Xiaomi to build trust, expand their reach, and solidify their position as a tech giant on the world stage .
Future of Xiaomi’s Global Strategy
As Xiaomi continues its global expansion, its global strategy must adapt to new challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. While Xiaomi has achieved remarkable success, there are potential roadblocks to consider .
- Increased Competition: The smartphone market is fiercely competitive, with established brands like Apple and Samsung constantly innovating. Xiaomi will need to maintain its focus on delivering high-quality products at competitive prices while also investing in cutting-edge features to differentiate itself from the competition.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical tensions, such as the US-China trade war , can disrupt supply chains and impact market access. Xiaomi will need to develop strategies to mitigate these risks and ensure smooth operations across different regions.
- Maintaining Brand Reputation and Quality Control: As Xiaomi expands its product portfolio beyond smartphones, maintaining a consistent brand image and ensuring quality control across a wider range of devices will be crucial. This requires a robust quality control system and clear communication to customers about product features and specifications.
Despite these challenges, Xiaomi’s global strategy presents exciting possibilities for future growth . Here are some potential directions Xiaomi might explore:
- Continued Innovation Across Product Categories: Xiaomi’s commitment to innovation has been a key driver of its success. The company is well-positioned to continue pushing the boundaries in areas like artificial intelligence , internet of things (IoT) technology, and 5G connectivity . This will allow them to cater to evolving consumer needs and stay ahead of the curve.
- Expansion into New Markets and Demographics: Xiaomi has a strong presence in emerging markets but can further expand its reach by targeting new demographics and regions. This might involve tailoring products and marketing strategies to appeal to specific customer segments, such as budget-conscious consumers in developed markets or young adults in new geographic regions.
- Increased Investment in Research and Development: To maintain its competitive edge, Xiaomi will likely increase investment in research and development (R&D). This will allow them to develop next-generation technologies and ensure a steady stream of innovative products that meet the demands of a global audience.
If Xiaomi can stay ahead of the curve by addressing potential roadblocks and embracing these exciting new directions , their global strategy can take them even further. Their talent for adapting, constantly innovating, and meeting the needs of all kinds of customers will be crucial for their continued success in the ever-changing world of technology.
Xiaomi’s global strategy offers valuable insights for anyone interested in the dynamics of the technology industry and the challenges and opportunities of international expansion. Here are the key takeaways from our analysis :
- A Winning Formula: Xiaomi’s success hinges on a carefully crafted global strategy that prioritizes affordability, innovation, and a strong brand image. Their focus on delivering high-quality products at competitive prices, particularly in emerging markets, has resonated with consumers worldwide.
- Beyond Smartphones: Xiaomi’s vision extends beyond just smartphones. The company’s strategy of building an ecosystem of interconnected devices similar to Apple’s model positions them for future growth and caters to a wider range of customer needs.
- The Power of Localization: Understanding and catering to local preferences is crucial for success in a global marketplace. Xiaomi’s global strategy emphasizes localization, ensuring their products and marketing messages resonate with diverse cultural contexts.
- The Importance of Translation Services: Language translation services are an often-overlooked yet vital component of Xiaomi’s global strategy. By ensuring clear and culturally-sensitive communication across international markets, translation services empower Xiaomi to build trust and expand their reach.
The significance of Xiaomi’s global strategy transcends the smartphone market. It serves as a case study for companies aiming to achieve international success . Xiaomi’s ability to adapt, innovate, and cater to diverse customer needs on a global scale offers valuable lessons for businesses of all sizes looking to expand their reach beyond their home markets.
Cracking the code of Xiaomi’s global strategy isn’t just about understanding what they do well. It’s also about seeing the roadblocks and opportunities they face. With this knowledge in hand, businesses can craft their own winning formulas to navigate the ever-changing global market .
Xiaomi’s global strategy offers a wealth of practical guidance for businesses aiming to replicate its success in the international marketplace. Here, we explore actionable insights that go beyond the core elements already discussed :
Localization goes beyond just words. Xiaomi adapts product features, user manuals, packaging, and even website layouts to suit different regions. For instance, they might modify measurement units, adapt to local payment methods, and include warranty information in the local language.
Not necessarily. While Xiaomi might have a preferred partner for core projects, they may collaborate with various translation companies with expertise in specific regions or languages. This ensures a nuanced understanding of local dialects and cultural contexts.
Reputable translation agencies use a multi-step process to guarantee quality. This typically involves professional translators , editors familiar with the target market, and potentially even native speakers who review the final product for accuracy and cultural appropriateness.
Translation timelines can vary depending on the volume of content and the target languages. However, experienced language services providers have efficient workflows to ensure timely delivery. Xiaomi likely factors localization into their product development cycle to avoid delays.
Market research plays a crucial role. Xiaomi prioritizes languages spoken in regions with a high potential customer base or significant market growth. Additionally, factors like cultural similarities between regions might influence their translation choices.
Xiaomi’s global strategy emphasizes innovation, affordability, strong branding, and localization. They focus on high-quality products at competitive prices, particularly in emerging markets. Their distribution network combines online and offline channels, supported by strong partnerships. Localization, including culturally sensitive translations, is key to their success. Future challenges include increased competition and geopolitical tensions, but Xiaomi aims to maintain growth through continued innovation and expansion into new markets. 🌍📱
Thank you for your insights, Tanisha! Much appreciated! You’ve highlighted several key aspects of Xiaomi’s strategy, especially their commitment to affordability and innovation, which have indeed been instrumental in their rapid global expansion. I agree that their focus on localization and culturally sensitive translations has helped them resonate with diverse audiences, particularly in emerging markets.
It will be interesting to see how Xiaomi navigates the growing competition and geopolitical challenges in the coming years. Their ability to innovate while adapting to local market needs will be critical. I’m curious to hear your thoughts on how they might handle these challenges, especially as they expand into newer markets.
Thanks again for sharing your perspective!

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.

All You Need to Know about Xiaomi - The Popular Chinese Electronics Company

Himaya Presthitha , Chayanika Goswami
Company Profile is an initiative by StartupTalky to publish verified information on different startups and organizations. The content in this post has been approved by Xiaomi.
‘Quality products at honest pricing’ is almost everyone’s need. Xiaomi has a separate fan base for its high-grade products built with cutting-edge technology at reasonable prices. Xiaomi is a Chinese company that has its major ground in electronics. The company has its presence in over 100 countries and regions and has been hailed as the world's most valued tech startup already in 2014. Xiaomi currently ranks in the 70th position on the Top 100 Most Valuable Global Brands in 2021 by Kantar BrandZ.
Xiaomi Mobiles have also gained much popularity in India, which has only seen growth year on year. The company tops the list of the best-selling phones in India. Xiaomi India even made it to the ‘GUINNESS WORLD RECORDS’ by building the largest light mosaic (logo) in the world. It was set by placing 9,690 bulbs and this momentous work is found on the terrace of Xiaomi’s head office in Bengaluru. Here are some more interesting facts and figures about Xiaomi.
Xiaomi – Company Highlights
About Xiaomi Xiaomi - Founders/Owners Xiaomi - History Xiaomi - Name, Tagline & Logo Xiaomi - Funding & Investors Xiaomi - Competitors Xiaomi - Revenue Model Xiaomi - Growth & Revenue Xiaomi - Future Plans
About Xiaomi
Xiaomi is an electronics company based in Beijing, China. It was founded by Lei Jun in April 2010, and in 2014, Xiaomi was the largest smartphone company in China. Today, Xiaomi is one of the top five smartphone vendors in the world. The smartphone commodities of Xiaomi include different series such as Mi Series, Mi Note Series, Mi Max Series, Mi Mix Series, Mi NoteBook Series, Redmi Series, Blackshark, and Pocophone. Xiaomi has around 291.6 million active users for its MIUI updates. Besides, the company also offers laptops, mobile apps, mobile accessories, wearables, home appliances, and smart-home devices.
From 2019, Xiaomi even started selling accessories such as caps, bags, glasses, backpacks, and also lunchboxes, pillows, cups, filters, umbrellas, and screwdrivers.
In 2018, Xiaomi launched Mi Credit in India for easy accessibility of personal loans. The company also offers various value-added-internet services like 'Mi Music', 'Mi Video' and 'Mi Game'.
Xiaomi - Founders/Owners
Lei Jun is the founder, CEO, and President of Xiaomi. The other co-founders are, Lin Bin, Dr. Zhou Guangping, Liu De, Li Wanqiang, Wong Kong-Kat, Hong Feng and Chuan Wang.
Lei Jun is a graduate in computer science from Wuhan University. In 1992, Lei Jun joined Kingsoft, a Chinese software company as an engineer. In 1998, Lei Jun became the CEO of Kingsoft. In December 2007, he resigned from Kingsoft for health-related issues. While he was still working with Kingsoft, Lei Jun founded an online bookstore named Joyo.com. Joyo.com was acquired by Amazon.com in 2004.
After resigning from Kingsoft, Lei Jun became an angel investor and invested in over 20 companies. He still invests in various companies through Shunwei Capital. In 2008, he joined UC Web as Chairman, and in 2010 Lei Jun founded Xiaomi.
Xiaomi co-founder & President Lin Bin is a graduate in radio electronics and holds a rich experience of working with companies like ADP, Microsoft, and Google. Lin Bin is also a member of the board of advisors of Tufts University School of Engineering located in Boston (USA).
Dr. Zhou Guangping , who is a Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering, worked with Motorola and held various pivotal positions in the company before joining Xiaomi. Currently, Dr. Zhou leads the hardware and BSP teams at Xiaomi.
Liu De is an M.S. and an expert in Industrial design. He established the Industrial Design Department at the University of Science and Technology Beijing. In 2003, Liu De founded 'New Edge', an Industrial Design Company. Mr. Liu currently looks after the industrial design and Ecosystem Development teams at Xiaomi.
Li Wanqiang is known as one of the earliest UI and HCI experts in China. After completing his graduation in Industrial Engineering in 2000, Mr. Wanqiang joined Kingsoft, where he was leading many important and well-known software projects. In 2010 Wanqiang joined Xiaomi as a co-founder.
Wong Kong-Kat graduated in computer science in 1997 and joined Microsoft, where he worked till 2010. Mr. Wong is now in charge of the Mi wifi and Mi Cloud teams.
Hong Feng holds a post-graduate degree in computer science. He started his career with Siebel System as a Lead Software Engineer. In 2006, Mr. Hong joined Google as a Senior Software Engineer. Later he also looked after the development of the various localized products of Google (in China) like Google Music and Google Pinyin Input as a Senior Product Manager at Google China. Mr. Hong now looks after the MIUI division at Xiaomi.
Xiaomi co-founder Chuan Wang is a seasoned entrepreneur. In 1997, Mr. Wang founded Thunderstone Technology, which grew to be the largest VOD (Video on Demand) system provider in China. In 2007 Chuan Wang founded a digital book company named Beijing Duokan Technology of which he is currently the CEO. In 2012, Mr. Wang joined Xiaomi as the co-founder and Vice President. Presently he manages the Mi TV and Mi Box teams at Xiaomi.

Flaunt your startup with StartupTalky
800+ stories, thousands of founders, and millions of visitors. Want to be the next?
StartupTalky is where founders, entrepreneurs, startups and businesses hang out and look up to for inspiration. If you have the means, we have the medium! Inviting founders and startups who are building sustainable solutions from ground zero! Startups who run the show, StartupTalky will let the world know!
Xiaomi - History
Lei Jun founded Xiaomi in 2010, as a software company and created MIUI ROM based on Google's Android. The idea behind developing MIUI was to offer more functionalities and a better UI than Android. MIUI indeed got the popularity it deserved. As per reports in March 2020, the MAU ( Monthly Active Users) of MIUI increased to 330.7 million worldwide.
In 2011 Xiaomi entered the hardware segment by launching the Mi One phone. The Xiaomi team's focus has been on creating quality hardware devices and sell them at comparatively lower costs than those available in the market while they intended to make revenue through their services and content. The company today not only sells mobile phones but much more like mobile apps, wearables, home appliances, and smart home devices.

Xiaomi - Name, Tagline & Logo
The meaning of the word ‘Xiaomi’ is ‘Millet’ and few reports show that it also means ‘Rice’. Lei Jun relates the word ‘Xiao’ to the Buddhist concept that, a single grain of rice is as great as a mountain’, indicating the company’s endurance. “Only for fans” was its tagline before.

The logo of the company shows the word ‘MI’- written in white placed inside an orange rectangle. ‘MI’ is the abbreviation for “Mobile Internet”, but Xiaomi has mentioned that it can also be read as “Mission Impossible”, representing all the challenges the company has faced so far.
Xiaomi - Funding & Investors
Xiaomi has raised funding worth approx. $7.4 Billion over 15 different funding rounds. Xiaomi went public in 2018.
Xiaomi - Competitors
Top competitors of Xiaomi include Samsung Electronics, Apple , Huawei , Samsung , OnePlus, and Oppo . Xiaomi sustains its paramount position with constant updates and optimization along with marketing at reasonable prices. Apple and Samsung provide good quality phones but have high prices. Whereas Xiaomi provides a number of features at reasonable prices.
Redmi smartphones are priced for as low as 6000 rupees on Amazon, and Xiaomi continues to have the highest market share for smartphone shipments in India. One of Xiaomi's strongest competitors is Realme. Realme is a daughter brand of Oppo also coming up with equally great phones like Xiaomi. And thus there is strong competition between Realme and Xiaomi. Motorola and Samsung are increasing the competition. Samsung released the M series where they actually did focus on value for money without compromising necessary specs.

Xiaomi - Revenue Model
Xiaomi’s primary source of revenue is from smartphones, the Internet of Things (IoT) and lifestyle products, internet services, and other miscellaneous products and services that the company offers.
A major portion of Xiaomi's revenue comes from the sale of smartphones. In 2018, the company is reported to have sold 119 million smartphones. Around 25% of Xiaomi's revenue comes from IoT and Lifestyle products. The company deals in a wide variety of IoT-enabled products like smart TVs, electric scooters, vacuum cleaners, cameras, rearview mirrors, etc. As regards the internet-based services provided by the company, pre-loaded apps and services form a good part of Xiaomi's revenue. Besides the company offers monthly subscriptions to its TV shows, games, and movies, and also earns by providing advertisement services.
Xiaomi - Growth & Revenue
Xiaomi has grown in sales and product ranges. The company reportedly has around 22,074 employees worldwide.
However, due to the Coronavirus pandemic, the smartphone company saw a decline in the Q1 of 2020. However, Xiaomi has also been declared as the only brand among the top five smartphone sellers , to achieve comparatively sound sales in the first quarter of 2020. It saw a 1.4% YoY from 2019, during the first quarter of 2020.
In 2019, Xiaomi’s total revenue was approximately RMB 205.84 Billion, and gross profit was nearly RMB 28.55 Billion. In the Q4 of 2019, the company’s total revenue grew by 27.1% to RMB 56.5 Billion with an attuned net profit of RMB 2.3 Billion and a 26.5% YoY increase.
“Despite headwinds from the Sino-US trade war and global economic downturn, Xiaomi stood out in 2019 with a commendable set of results as our revenue exceeded RMB 200 billion for the first time. We also celebrated several key milestones, ranging from the successful launch of our dual-brand strategy as Xiaomi and Redmi are spun-off and independently operated, the affirmation of ‘5G+AIoT’ as our strategic roadmap, to our inaugural entries into the prestigious ranks of the Fortune Global 500 and BrandZ’s Top 100 Most Valuable Global Brands” says, Mr. Lei Jun, Founder, Chairman, and CEO of Xiaomi.
According to reports dated September 1, 2021, Xiaomi has revealed that it would not be launching any more of its products with the Mi brand. The Chinese tech giant has decided to withdraw the "MI" name from all their future products.

Xiaomi - Future Plans
Xiaomi’s vision is to make quality technology accessible to everyone, i.e., “Innovation for everyone”. The company makes this possible with its high-quality products and remarkable services.
In 2020, Xiaomi intends to keep its focus on the development of 5G smartphones, and thus improve its position in the premium smartphone segment. The company also has plans to invest big in AIoT.

In the current scenario, where the Indian Government and the public at large are opposing China-made goods, Xiaomi India Head Manu Jain is quite optimistic about the company's position in India.
"We act like an Indian company since we have local productions. Data is stored in India as well. We have been trying to build a truly local company" - quotes Manu Jain
According to reports, Xiaomi has 7 factories in India, four of which are in Andhra Pradesh, two in Tamil Nadu and one in Noida. As claimed by the company about 99% of Xiaomi phones are produced in India. As said by Manu Jain, the company has also started a pilot project whereby the company is exporting Xiaomi phones made in India to Bangladesh and Nepal. Besides smartphones, the company claims that almost 100% of smartphone chargers, USB cables and batteries are made in India. Xiaomi also has a smart TV manufacturing plant in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh.
With an aim to expand its business in India, MI increased its production capacities in the country by establishing 2 more factories to manufacture smartphones in India, and 1 factory dedicated entirely for the Smart TV division of the brand, as of February 2021.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
- International Money transfer- XE Money Transfer
Former Ola CBO Sidharth Shakdher Becomes CMO and Business Head at Paytm
According to reports, Sidharth Shakdher has been named the new Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) and Business Head of Paytm, a fintech company. Within nine months of joining the company run by Bhavish Aggarwal, Shakdher left Ola. Among other accomplishments, he was instrumental in the establishment of the consumer loans section,
Blinkit Launches Seller Hub to Facilitate Vendors' and Brands' Onboarding
In a LinkedIn post, Blinkit Chief Technology Officer Sajal Gupta announced the debut of Seller Hub, the seller programme for Zomato's rapid commerce platform, on October 23, 2024. This business structure is based on Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA), which is an e-commerce service offered by Amazon. Brands and
Uber Will Soon Test its Bus Service in Hyderabad and Mumbai
After Delhi and Kolkata, the ride-hailing app Uber plans to test its bus (shuttle) service in Hyderabad and Mumbai. The company is currently negotiating with a number of local stakeholders to obtain approval to launch in the nation's IT hub. In an interview with the media, Prabhjeet Singh,
Infosys and Meta Deepen Their Strategic Partnership to Promote Generative AI Innovation
The multinational technology company Meta and Infosys, a pioneer in next-generation digital services and consulting, bolstered their partnership on October 23, 2024, to promote generative AI innovation through open-source projects. Infosys is a firm believer in democratising AI and is a major supporter of open-source software. By utilising Meta'
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Xiaomi Redefined What It Means to Be a Platform
- Tony W. Tong,
- Yanting Guo,

Three factors enabled the electronics giant’s unique business model.
Traditional platform businesses generally fall into one of two categories: Ecosystems, such as Apple’s App Store, which offer limited resources to a wide array of independently-run firms; and Corporate Venture Capital (CVC) companies, such as Intel Capital, which invest heavily into a small number of ventures that promise either financial or strategic returns. However, new research into Xiaomi’s growth strategy suggests that the Beijing-based electronics giant has developed a blended approach, borrowing elements of both traditional ecosystem and CVC firms to create a broad ecosystem of strongly-supported partner ventures. Based on a series of in-depth interviews with executives from both Xiaomi and its partner companies, the authors identify three factors that have enabled this novel business model: Xiaomi structures its investments to incentivize innovation and build trust while still ensuring alignment, proactively fosters an ecosystem mindset throughout its organization, and takes a deliberate, measured approach to expanding the scope of its ecosystem over time.
From Apple to Amazon, Google to WeChat, digital platform-based ecosystems have become increasingly dominant in the last decade. However, while these businesses may all seem to follow similar models, there are in fact major differences between different types of platform companies.
- TT Tony W. Tong is a Professor of Strategy & Entrepreneurship and currently the Senior Associate Dean for Faculty and Research in the Leeds School of Business at the University of Colorado. He studies firm strategy, innovation management, and international business. He has published numerous top journal papers in these areas as well as multiple bestseller case studies in Harvard Business Publishing .
- YG Yanting Guo is an Assistant Professor in the School of Management at Xiamen University, China. Her research interests lie in technological catch-up, organizational capabilities, and innovation management. She has published articles in journals including Technological Forecasting and Social Change and IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management ; as well as several case studies in Harvard Business Publishing.
- LC Liang Chen is an Associate Professor of Strategic Management at the University of Melbourne. He is an expert on platform ecosystems and studies how firms engage in competition, innovation, and globalization in the digital economy. His research appears in Strategic Management Journal , Journal of Management , Journal of International Business Studies , and Harvard Business Review .
Partner Center
How Xiaomi is Dominating the Global Smartphone Market?
Just have a look around yourself, there must be at least 5 people around you who would be using a Xiaomi phone. Today, we will be talking about the leading smartphone brand who has been able to establish trust among users worldwide.
Let us first deep dive into Xiaomi’s journey-
Xiaomi Corporation is a Chinese electronic company founded in April 2010. The company began its operations as a software company by ex-Kingsoft CEO Lei Jun, by creating a new custom ROM based on Google’s Android, MIUI. The company launched Mi 1 and Mi 2 smartphones in August 2011 in and 2012 respectively in Asia and East Asia Markets.
In 2015, Xiaomi Corporation decided to expand its business in India through major e-commerce sites and offline retailers. Xiaomi was a ground-breaking smartphone at the time in budget and was well received by Indian customers. Since then, the company has expanded in Pakistan, Spain, UK, Ireland, Austria, Denmark, Sweden, Paris, Milan and the USA.
Besides smartphones, the corporation has also launched various smart home products, fitness products, TVs, laptops, drones, Wi-Fi routers, cloud services and instant messenger services.
Xiaomi Business Model
With the main aim of providing quality technology at affordable prices to everyone, Xiaomi has captured third place in the global smartphone market. Xiaomi’s Chief Executive Officer Lei Jun fragmented the source of revenue-generation into four segments of the market:
- Internet of Things (IoT) and lifestyle products
- Smartphones
- Internet services
- Miscellaneous services and products
As the years of success passed, the revenue generation process became faster and enterprise value touched $100 Billion during the initial public offering. The company began to compete with tech giants such as Apple and Samsung.
When Xiaomi was struggling to gain profit in 2016, the CEO decided to sell products other than smartphones. They generated substantial revenue that was enough to make a strong base for a large company. Besides selling smartphones, the company also provides services like air purifiers, suitcases, televisions and much more. Xiaomi also provides paid cloud storage. Services offered by Xiaomi also include online games and TV shows. Xiaomi is also producing AI-engines which can impact the business model positively in future.
Now, let’s have a look at different categories in which Xiaomi is ruling the technology market:
- Xiaomi’s Global Smartphone Market: In the present day, the smartphones of Xiaomi are responsible for 65% of the total revenue. According to a survey, Xiaomi sold 119 million smartphones in 2018. It is the highest number for any brand to date.
- Internet of Things and Lifestyle Products: Xiaomi has always focused on making people’s life simpler with its innovative technologies. Xiaomi’s IoT and lifestyle products roughly made 25 percent of revenue generation in 2018. It produced around $6.4 billion approximately. The products include internet cables, Bluetooth Speakers, Smart TV, Electric Scooters, Vacuum Cleaner, Cameras, Smart Home systems and much more.
- Internet Services: The business model of Xiaomi also includes internet service business. These businesses include preloaded apps and apps in the Mi store. Around 9.1 per cent of the total revenue comes from these services. They also provide cloud storage which is again a paid service. Xiaomi always focused on its internet services. Its efficient internet services are for start-ups. Start-ups play a crucial role in Xiaomi’s success in terms of business.
Xiaomi’s Revenue Generation Model:
With ensuring better productivity at an affordable price, Xiaomi focuses on its customer acquisition and advertising strategy. The business model of Xiaomi includes a variety of electronic gadgets and internet services that are innovative and attractive. Miscellaneous additional services and products of Xiaomi also have their fair share in helping the company generate good revenues.
Customer reliability is one of the critical strengths of Xiaomi. Xiaomi always produces affordable products. This thing still fascinates the customer towards the brand. Xiaomi provides its users with an unforgettable experience which also helps them to retain their customer base. This lets the company have more subscribers for its proprietary services such as Mi Store, Music, MI Cloud and so on. All this helps the company make good money.
Marketing Approach adopted by Xiaomi:
Xiaomi has kept its marketing strategy minimalistic due to the cost leadership business strategy. Unlike other recent competitors like Oppo and Vivo, the mobile internet company didn’t adopt traditional marketing and utilised social media marketing to save on advertising costs.
Xiaomi adopted hunger marketing as an integral part of their digital marketing strategies. The company operated according to the emotional needs of their target customer segment by creating a shortage of supply in purpose, creating a buzz in the market and evoking desire in customers to own an MI smartphone.
Xiaomi focused primarily on the price element of the marketing mix compared to other elements of the 7P’s of marketing. Let us check out those 7Ps of marketing: Product: The mobile internet company offered high-quality phones with latest features at unbelievable prices. The product consisted of high-quality hardware components and the final price was very low when compared to other brands.
- Pricing: The product was sold on its cost price through online platforms without involvement of any mediator.
- Place: After the huge success in China, Xiaomi launched its products internationally. They hired Hugo Barra (Ex-Google android Executive) to discover new opportunities for expansion.
- Promotion by Social Media: Xiaomi leveraged social media platforms beautifully to enhance their online presence. Engineers engaged with consumers and gathered feedback to refine the software and remove the bugs.
- Promotion by Brand Promoters: Xiaomi actively participates in the discussion on social media has succeeded in generating a dedicated fan base of millions of users. Promotion by Word of Mouth: The Flash sales created a buzz and everyone was talking about it. It helped Xiaomi to gather huge popularity.
- Promotion by CEO: Xiaomi’s head, Lei Jun, did a great job in making his brand look cool. He put a face to the brand. Lei Jen’s is quite similar to Steve Jobs in the way he talks about the brand.
Social Media Strategy adopted by Xiaomi
Leveraging the power of social media marketing, the Chinese mobile internet company didn’t invest a single penny in traditional advertising. The company employed 2000 people over social media and online forums to manage its online community. Xiaomi followed a well-strategized plan to expand its online presence:
- Building a strong tech fan base: Starting the company with a single product that was MIUI operating system, Lei Jun was not in the mood to spend money on advertising and marketing in the beginning phase. To create brand awareness, he with his team started to promote his product on online forums. They all worked very hard and spent a lot of time on forums, making comments, sending posts and advertising. They used the above method to do marketing with zero budget, they set up MIUI mobile phone forum, which became the base camp of “mi fan” with over 1 million registered users.
- Gaining the trust of the fan base: Xiaomi started to collect feedback from its users every week and implement it in the next release. Every week, a new version of MIUI was released which was again then analysed by a few hundred thousand hardcore users. Some of the users participated in product research, development, test, spread, marketing and public relation. Fans also organized offline city gatherings.
- Selling directly to your fans and Promote your brand’s name: Naturally, the 1 million “mi fan” users became the first buyers of MIUI smartphones. People bought the phones, liked it and recommended it to other users. The company now uses Flipkart, Amazon and offline stores as Point of Sale.
Campaigns by Xiaomi
Social media marketing is a very effective and reliable source for any brand, product which is going to be launched. If social media marketing is used with a proper plan and strategy then we can see a huge difference in traffic and terms of revenue. To connect with the customers, attract engagement and build the presence of the brand online, Xiaomi developed various social media campaigns. Let’s have a look into them.
#MiIndia – A Social Media Campaign on Twitter by Mi India To attract new buyers for Mi 3 (the newly launched Smartphone by Mi India in July 2014), the brand connected with people on Twitter use the hashtag #MiIndia. Users were asked to show their interest in the Smartphone and register themselves on the official website. One lucky winner would win a power bank from Mi India.
#GuessTheCup- A Social Media Campaign on Facebook by Mi India To promote the Mi Bands, the brand connected with people across Facebook with a contest. The users were asked to guess the cup under which the band was present in a video uploaded. The lucky winners would get a chance to win bands from Mi India.
Redmi Note– A Social Media Campaign through Twitter by Mi India Mi India connected with people on Twitter to promote their new Redmi Note phone and convinced them to participate in the contest. The users were asked to follow the brand and re-tweet the official launch tweet for Redmi Note. 10 lucky winners would win priority passes for the grand launch of the Smartphone.To amplify the effect, Xiaomi debuted television with its first ever TVC for the Indian market in 2015. The ad film promoted its newest offering- Redmi Note 3.
#Shot on RedmiNote7s On Instagram, the camera quality of the Mi phones was explored and promoted in the best way. Xiaomi relied on Social media to engage with Mi fans, consumers and used the platform to share thoughts, converse with like-minded people and generate high-quality content.#ShotOnRedmi helped communicate the value of a phone for a potential consumer and also helped in retaining followers for the brand.
Note Kiya Jaye – #RedmiNote7Pro With the launch of Note 7 Pro, Xiaomi launched a new campaign “Note Kiya Jaye” that featured their new brand endorser, Ranveer Singh who had the power to play multiple characters with his strong comical tone. Note Kiya Jaye effortlessly played out humorous scenarios while showcasing the features of the phone and innovative technology for customers.Xiaomi left no stone unturned to promote its product. They used 360 degree marketing strategy slowly and steadily. They have also conducted several influencer marketing campaigns to promote its product among the youth.
- DurSeDekho- Redmi Note 7 Pro In the classroom scene, the Father (Ranveer Singh) while casually inspecting the classroom environment uses the double-tap double-zoom feature on Redmi Note 7 Pro’s 48MP camera to zoom into the student’s desk to find that he is reading a comic book instead of a textbook.
Key Takeaways from Xiaomi’s Business Strategy
Xiaomi’s business strategy depends upon time and trends. Here are some key-takeaways from the strategy that we must study and implement to further growth:
- Assembling and Employing a fan base: Since 2012, the brand has created a huge fan base that involves millions of people across the world. Fans spend countless hours online discussing Xiaomi products on various forums which increased the level of brand awareness at no extra cost to the company. Just like Apple, every mobile company enjoys a hardcore following.
- Manufacturing Exceptional Products at Pocket-friendly services: With the aim of providing people with exceptional products at pocket-friendly prices, Xiaomi with MIUI interface created a practical design with their latest technology, By providing exceptional technology, they have also targeted the lower-income group. They can buy these smartphones easily. Xiaomi mainly competes with the market on providing cheap products and services.
- Regular Optimizing of Products and Services: The mobile company is actively developing the ecosystem for its products and services. Xiaomi’s business strategy attracts business from 55 companies of which 29 companies were originally started by Xiaomi itself. Besides manufacturing smartphones, Xiaomi also deals in various products ranging from gaming laptops to homemaking products.
- Large Community and Social Media Engagement: With more than 1 Million monthly users, MI community has become a strong platform to interact with the Mi users. When compared to other brands, some of the biggest tech giants do not provide a common platform to share their views. The tech giant also invites its fans for its launch of any new product. Xiaomi also does its engaging part with the users on the other social media platforms and remains active with them.
- Flash Sales: Xiaomi builds its market by creating a demand for its newly launched product. People get the Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and eventually end up discussing when the next sale goes on. This leads to curiosity and free promotion. This type of marketing strategy is called hunger marketing.
- Beta Access to Gadgets: To create a hype in the market, Xiaomi chooses a limited number of beta users which can be up to 500. They can buy gadgets for less selling price and loyalty points before its ahead of the official launch. Xiaomi teased its MiPad in May, selected Xiaomi fans got hold of the Android-based tablet a few weeks before it hit Xiaomi’s online sales.The strategy used created hype and enhanced word-of-mouth advertising. It’s usually a period when newly-revealed gadgets drop off the radars of most gadget enthusiasts.
Conclusion Truly, Xiaomi is a perfect example of a start-up business. It has been a unique blend of business strategies, digital marketing strategies and social media marketing strategies which has transformed the business in just 5 years of its inception. Cost competitive strategies have been boon for the brand. There are opportunities for Xiaomi to become the world’s No. 1 smartphone company as the company is already giving a tough competition to other competitors.

Experential

What marketing strategy helped Xiaomi lead the Indian smartphone market
The smartphone market in India is one of the most competitive markets in the country. Both local and international brands fight hard to position themselves in India, as the country is still developing and has a comparatively lower smartphone penetration than developed countries like the US, UK, or the European market.
The number of smartphone users in India is expected to be over 760 million in 2021 according to Statista, depicting the importance of these devices in our daily lives. From Mukesh Ambani down to your nearest chai-wala, everyone can be seen flaunting one. This number is fuelled further by the penetration of the internet in the rural areas, and the coronavirus pandemic shifting business meetings and classes online.

When we talk about buying smartphones in India, one brand that definitely comes to mind is Xiaomi. Almost every second person would be using a Xiaomi phone so much so that in a crowded space, when a phone rings, one would not be able to distinguish their phones from others, because of the familiar Xiaomi ringtone. We have all seen the famous “Kiska baja” ads by the company.
The Chinese player, which has led the Indian smartphone market for three consecutive years, has a whopping 26% of market share as of Q1 of 2021, compared to the 20% market share captured by its long-rival, Samsung. That’s a steep rise for a company that had just 3% of the market in 2015. All thanks to the innovative marketing strategy of Xiaomi that stimulated this growth.
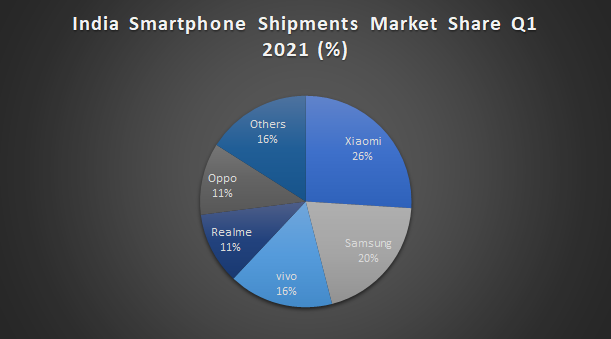
Regulatory filing access by AltInfo showed that Xiaomi posted a profit of Rs 401 crore in FY20 after sustaining Rs 148 crore loss a year earlier. In FY20 Xiaomi India clocked revenue of 38,196 crore which is roughly 13.5% of its global revenue of 2,82,000 crore .
Fun Fact: It’s a very famous fact that Xiaomi owns Mi and Redmi but do you know that there is an unknown Chinese company that owns OPPO, VIVO. OnePlus, Realme- BBK Electronics. If we combine their market share it’s actually BBK Electronics that rules the Indian smartphone market. What strategy did BBK Electronics use to rule the Indian smartphone market?
In this article, we will explore the marketing strategies that Xiaomi deployed to get to the top of the table
Understanding the demand of customers.
The consumer needs in India are different from that of their western counterparts. What works in global markets, may not work in India. Xiaomi sells about 200+ products in China, while in India, the count is about 20+ products. The company has established a dedicated R&D center in Bangalore to specifically cater to Indian consumers.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Xiaomi India (@xiaomiindia)
The price elasticity of demand is high which means that consumers here are sensitive to pricing. Smartphones had not been able to reach the masses due to their high prices before the entry of affordable smartphones. Mr. Manu Kumar Jain , the CEO of Xiaomi India, identified this as a potential and aimed to make its foot stronger in the Indian market by targeting people who have been untouched by the telecom revolution, amidst the explosion of the Internet .
The tech giant’s mission statement, thus, came to be-
“At Xiaomi, we strive to create the highest quality products at the lowest possible prices to provide people with access to the necessary tools and services that connect them to the world and, ultimately, their dreams.”
Ever used a smartphone for more than 2 years? I don’t think so.
Over 52% of the smartphone users in India changed their primary smartphones after at least 2 years of use. 26.9% upgraded their phones within 1-2 years of use. The primary reason is to own the latest or a better smartphone. Xiaomi capitalized on this fickle behavior by frequently launching new products with new features.
Understanding the market and competition
Xiaomi surveyed the Indian market and carefully analyzed the competitive strategies used by Apple and Samsung. It concluded that both the brands had a loyal fan base and a robust operating system-iOS and Android, respectively. It picked up on these conclusions and started designing its own custom UI known as MIUI-based on Android.
In order to compete with the likes of Samsung, Apple, OnePlus, Xiaomi had to constantly work on improving its product. This was done by collecting feedback from users and incorporating it in the next higher version.
Mi fans, calling out all our #RedmiNote8Pro , #RedmiNote7Pro , #RedmiNote7 & #RedmiNote7S users to become a part of pilot testing of #MIUI12 . Let us come together & make #MIUI better for everyone. Apply now: https://t.co/xjWP1qECOJ RT to spread the word. pic.twitter.com/THs8e4jWJg — MIUI India (@MIUI_India) June 12, 2020
Once, Xiaomi was through with its OS, the next big task was to acquire early users. However, it didn’t want to spend huge amounts of money on advertising. Rather, the company wanted to build brand awareness by creating a loyal fan base.
So how did Xiaomi do it?
The company employed people to manage its social media and online forums. This team began engaging with the community. Their efforts proved fruitful the day Xiaomi launched the Mi 3 and the Flipkart website crashed in a matter of seconds!
Apart from this, Xiaomi also runs a lot of campaigns on social media to promote its smartphones and made effective use of word-of-mouth advertising.
#MiFans , Celebrate this friendship day with #Mi . 👬 Here's your favorite #Mi11XSeries at an amazing price. Now save up to ₹13,000. Come celebrate this friendship day with us at: https://t.co/xDxXUdlTnZ pic.twitter.com/Kbw9l2Ge7Q — Mi India (@XiaomiIndia) July 31, 2021
#MiFans , get the best deals on your favourite #Mi Smartphones Up to ₹4,000 off on exchange and ₹3,000 Instant Discount and more 🤩 Head now to https://t.co/D3b3QtmvaT , @amazonIN and shop yours today! pic.twitter.com/WopVPbFR8C — Mi India (@XiaomiIndia) July 29, 2021
Another reason for Xiaomi’s success was the slow collapse of India’s home-grown mobile brands due to the lack of 4G capability. There was a time when we saw Indian players like Micromax leading the market, but things took a drastic turn around 2016-17 when 4G was introduced in India.
By the time 4G had arrived in India, Chinese companies had already managed to successfully outfit cheap phones with 4G technology and were selling them back home! This made it easier for Xiaomi to transition phones from 3G to 4G overnight in India, ultimately killing the Indian brands that failed to adapt quickly.

Quality products at affordable prices
Xiaomi phones rate high on the value-for-money factor that they provide. They come power-packed with features and hardware that make Indians feel that they were getting more bang for their buck. Its flagship Redmi range of phones, for instance, typically start at Rs. 9,999/- rupees and goes up to Rs. 19,999/-.
Penetration pricing is a pricing strategy where the price of a product is initially set low to rapidly reach a wide fraction of the market and initiate word of mouth. The strategy works on the expectation that customers will switch to the new brand because of the lower price.
The way the company used penetration pricing helps explain their popularity in India-consumers were getting better features than before at rock bottom prices. In order to further cut costs, the company started to assemble its products locally in India to take advantage of the Make in India duty benefits.
Here is a review article by Gadgets 360 that has rated Xiaomi’s Redmi Note 10 an overall 9 out of 10 for value for money.
Xiaomi is basically an e-commerce company
Xiaomi largely sells its phones online and does not invest a lot in building an offline presence in the form of a traditional brick and motor retail store. In the Indian context, although it operates its own website to sell its products, Xiaomi also partnered with the biggest e-commerce platforms-Flipkart and Amazon to tap into their strong distribution channels.
This way, the company did not have to incur unnecessary capital expenditure and at the same time, making sure that their products reached the maximum number of smartphone lovers. A simple, yet effective move!
Creating Scarcity
Xiaomi’s flash sales help it reduce inventory costs and overproduction disasters. It is an exciting marketing strategy where Xiaomi uses discounts, time limits, and limited stocks as tactics to fascinate the customers.
While that makes it harder to get your hands on a new Xiaomi device, the company has managed to spin that into a positive, creating periodic hype as flash sales of a limited number of devices open up every week. Although the scarcity of a product results in disappointment, it nevertheless increases the value of the product by enticing the customers to buy it by invoking a feeling of FOMO.
We heard you! India's all-rounder Redmi Note 5 will go on sale at noon on https://t.co/cwYEXdVQIo & @Flipkart . #GiveMe5 pic.twitter.com/Yfqpp1CCS7 — Redmi India – #RedmiBook Super Start Life (@RedmiIndia) March 16, 2018
Once a flash sale is completed, Xiaomi makes use of the quick sell-out in further social media postings, to grab more eyeballs. This is known as hunger marketing. Competitors including OnePlus and Realme have also started using flash sales.
Hunger marketing is a marketing strategy especially focusing on the emotions of human beings. Hunger marketing is a psychological strategy that focuses on the desire of consumers, making them hungry thus having a strong desire to buy products that other people also want to buy.
The Way Forward
Xiaomi’s share of the market has not been able to grow much beyond the 26-27% mark, signaling a plateau. The Korean tech company, Samsung is inching close behind; and newer brands like Realme have started to gain the limelight.
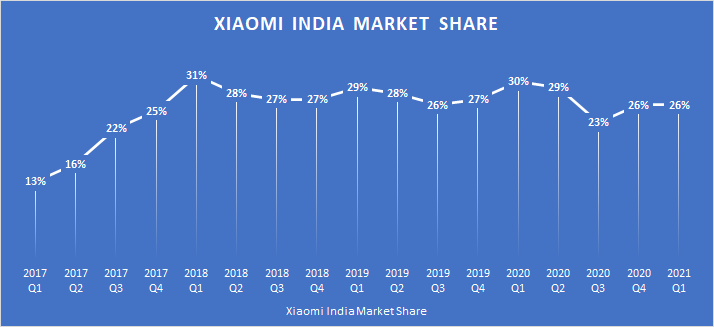
This could explain why Xiaomi is testing waters in the premium smartphone market, with the launch of a new range of phones called the K-20 series.
“A few years ago, the premium market was about three to four percent of the Indian smartphone market. This has now grown.” Xiaomi India’s director, Manu Jain, said in an interview with the Hindu newspaper. He also added that the company had set its sights beyond the affordable smartphone market.
Most recently the Mi 11 series graced this list with much hue and cry. In the advertisement below you will notice a premium feel. Xiaomi has customized its marketing strategy and market positioning for the premium market.
Xiaomi will need to keep pushing its limits and continuously evolve its marketing strategy in India, given that the competition remains fierce and no company has dominated it for too long.
#Mi11 Series: An outstanding ‘Trend-setter’ 😍 1 year ago many didn't believe when we started our premium journey. Today #Mi11Series is ~25% more searched than biggest competition. 🙏 #Mi11Ultra , #Mi11XPro , #Mi11X , #Mi11Lite : all huge success!✌️ Thank you all. I ❤️ #Mi #Xiaomi pic.twitter.com/9mlmMCpNRD — Manu Kumar Jain (@manukumarjain) July 30, 2021
-AMAZONPOLLY-ONLYWORDS-START-
Also, check out our most loved stories below

Why did Michelin, a tire company, decide to rate restaurants?
Is ‘Michelin Star’ by the same Michelin that sells tires, yes, it is! But Why? How a tire company evaluations became most coveted in the culinary industry?

Starbucks prices products on value not cost. Why?
In value-based pricing, products are price based on the perceived value instead of cost. Starbucks has mastered the art of value-based pricing. How?

Nike doesn’t sell shoes. It sells an idea!!
Nike has built one of the most powerful brands in the world through its benefit-based marketing strategy. What is this strategy and how Nike has used it?

Domino’s is not a pizza delivery company. What is it then?
How one step towards digital transformation completely changed the brand perception of Domino’s from a pizza delivery company to a technology company?

Why does Tesla’s Zero Dollar Budget Marketing Strategy work?
Touted as the most valuable car company in the world, Tesla firmly sticks to its zero dollar marketing. Then what is Tesla’s marketing strategy?

Yahoo! The story of strategic mistakes
Yahoo’s story or case study is full of strategic mistakes. From wrong to missed acquisitions, wrong CEOs, the list is endless. No matter how great the product was!!

Apple – A Unique Take on Social Media Strategy
Apple’s social media strategy is extremely unusual. In this piece, we connect Apple’s unique and successful take on social media to its core values.
-AMAZONPOLLY-ONLYWORDS-END-

Ai Ling is currently a semi-qualified CA and a graduate of St. Xavier's College, Kolkata. She has done her articleship from Garv & Affiliates and also briefly interned with Nestle in their operational finance team.
Related Posts

Dior Marketing Strategy: Redefining Luxury

Dunkin-licious marketing mix and Strategy of Dunkin Donuts

Healthy business model & marketing strategy of HelloFresh

Twist, Lick, and Dunk- Oreo’s Marketing Strategy

The Inclusive Marketing Strategy of ICICI Bank

Nestle’s Marketing Strategy of Expertise in Nutrition

How does Vinted make money by selling Pre-Owned clothes?

N26 Business Model: Changing banking for the better

Sprinklr Business Model: Managing Unified Customer Experience

How does OpenTable make money | Business model
How does Paytm make money | Business Model

How does DoorDash make money | Business Model

Innovation focused business strategy of Godrej

How does Robinhood make money | Business Model
How does Venmo work & make money | Business Model

How does Etsy make money | Business Model & Marketing Strategy
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Advanced Strategies
- Brand Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Luxury Business
- Startup Strategies
- 1 Minute Strategy Stories
- Business Or Revenue Model
- Forward Thinking Strategies
- Infographics
- Publish & Promote Your Article
- Write Article
- Testimonials
- TSS Programs
- Fight Against Covid
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and condition
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Master Sessions
- Live Courses
- Playbook & Guides
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Xiaomi invades the smartphone market in India
- Published: 27 May 2020
- Volume 47 , pages 215–228, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- Rahela Tabassum 1 &
- Shehbaz Ahmed 1
50k Accesses
7 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The case study is based on Xiaomi Corporation, a Chinese Public company, headquartered in Beijing, China. Xiaomi (the word Xiaomi means millet which means a “grain” that is a staple diet in various parts of the world) is the world’s fourth largest smartphone (a smartphone is a mobile phone with various functions of a computer) company based on total shipments. It produces low-cost but high specification smartphones. Xiaomi which has emerged as the top smartphone brand in India also manufactures consumer electronics and mobile apps. Currently, Xiaomi revenue comes from the sale of products like smartphones, Iot, lifestyle products, advertising services and internet value-added services (which include online games). According to IDC India, Xiaomi has 29.7% of market share at the end of Q218. The organization has achieved an astounding growth. Xiaomi’s India revenue jumped 175% in 2017–2018 to Rs. 230.6 billion year on year. The firm that sells smartphones under the brand Redmi and Mi had a net profit of Rs. 2.93 bn in 2017–2018 (according to IDC, Counterpoint Research). Xiaomi Corporation which was founded in April 2010 was listed in the Hong Kong stock exchange on July 9, 2018. Xiaomi being the “Coolest Company” in the heart of its users is committed to continuous innovation. Xiaomi has launched its first smartphone in August 2011 and became the largest smartphone company in China by 2014. Xiaomi the Bengaluru headquartered firm has entered the Indian market on July 15, 2014, in partnership with Flipkart to sell its smartphone with a concept of Flash sales. It has become a global player from a startup company in smartphone market in a span of not even a decade. Samsung of South Korea and Xiaomi of China are expected to continue their fight for top slot in 2019. The study aims to analyse the Indian smartphone market with the business model, marketing mix and innovative strategies of Xiaomi in order to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and challenges. The finding indicates that the company needs to focus on improving its product quality, advertising and distribution network to face fierce competition. Through the innovative strategies of Xiaomi, it is likely to become a game changer in the near future.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Xiaomi’s Mission Statement:
At Xiaomi, we strive to create the highest quality products at the lowest possible prices to provide people with access to the necessary tools and services that connect them to the world and, ultimately, their dreams.
Introduction
The use of smartphones has seen spectacular growth in the recent past. Most users have shifted from simple phones to smartphones. IBM was the first company to introduce smartphones in the year 1990. Later, it was followed by Nokia, Ericsson, Apple, Blackberry, Samsung and others. The smartphone market has plenty of new players who manufacture and sell smartphones. Xiaomi popularly known as “Apple of China” was founded 7 years ago on April 6, 2010, by a serial Entrepreneur Lei Jun in Beijing and became the leading smartphone brand in the first largest market China and the second largest market India. Later, it expanded its business in other countries like Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines and South Africa. It has entered the Western market but couldn’t catch enough attention. The founder of Xiaomi has an estimated net worth of US$ 12.5 billion which makes him the 11th richest person of China and 118th richest person of the world. The market valuation of Xiaomi is more than the US $ 46 billion.
Initially, Xiaomi was a startup technology-based company and in a span of fewer than 5 years has become a global player in the smartphone market. Xiaomi has launched its first smartphone in August 2011 and became the largest smartphone company in China by 2014. It is the world’s fourth largest smartphone manufacturer after Samsung, Huawei and Apple. Its target market is the price-sensitive lower middle-income group of customers and millennials who prefer smartphones in a lower price range.
The serial entrepreneur Lei Jun has founded Xiaomi in 2010 based on the vision “Innovation for everyone”. According to the Wall Street Journal, Xiaomi awarded the founder and CEO Lei Jun about $1.5 billion in stock. In July 2019, Xiaomi was listed in Fortune Global 500 companies and became the youngest Global 500 companies of 2019. It ranks 468th among all categories and ranks 7th in the internet services and retail category (Xiaomi Team-Aug 20, 2019).
It entered the Indian market on July 15, 2014, in partnership with Flipkart to sell its smartphone Mi 3 whose price was Rs. 13,999. It was an exclusive sales tie-up with Flipkart, and the Mi phones were sold within 30 min on the very first day. Xiaomi India’s focus is to design high-quality products and make it available at accessible prices to the world.
To understand the business strategies and competitiveness of Xiaomi India in the smartphone segment.
To evaluate the marketing mix model which provides guidelines to Xiaomi India to put the right product in the right place at the right time and price.
To analyse the major challenges faced by Xiaomi India in the arena of smartphones.
To conduct a SWOT analysis to assess Xiaomi India’s current position and how the company capitalizes its opportunities in the Indian market
Xiaomi: an overview
Xiaomi Corporation which was founded in April 2010 was listed in the Hong Kong stock exchange on July 9, 2018. Xiaomi being the “Coolest Company” in the heart of its users is committed to continuous innovation.
Xiaomi has launched its first smartphone in August 2011 and became the largest smartphone company in China by 2014. Xiaomi India the Bengaluru headquartered firm has entered the Indian market on July 15, 2014, in partnership with Flipkart to sell its smartphone with a concept of Flash sales. It has become a global player from a startup company in the smartphone market in a span of not even a decade. Samsung of South Korea and Xiaomi of China are expected to continue their fight for the top slot in 2020.
In a developing economy like India, the smartphones are unable to reach the masses due to its high prices. Mr Manu Jain, the CEO of Xiaomi India who acts like a nimble startup, maverick Footnote 1 in risk taking, nimble in decision-making but aggressive in execution is aiming to make its foot stronger in the Indian market by targeting people who have been untouched by the telecom revolution. Xiaomi popularly known as “Apple of China” entered the Indian market with an exclusive sales tie-up with Flipkart. In a very short span, the company has acquired the number one position in the Indian smartphone market surpassing even the Korean giant Samsung (Fig. 1 ).
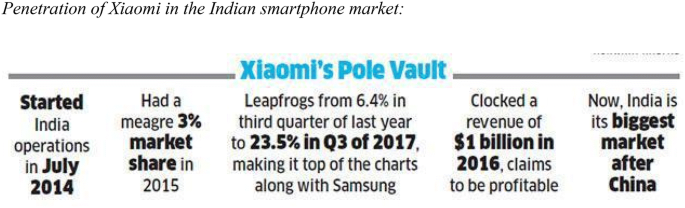
Source : Economic Times, Mar 17, 2019
Journey of Xiaomi India from the time of its inception.
Penetration of Xiaomi in the Indian smartphone market
Xiaomi India has started its operations in India in 2014 and had a meagre share of 3% in 2015.
However, in 2016 it has clocked a revenue of $1 billion and became profitable (Fig. 2 ).
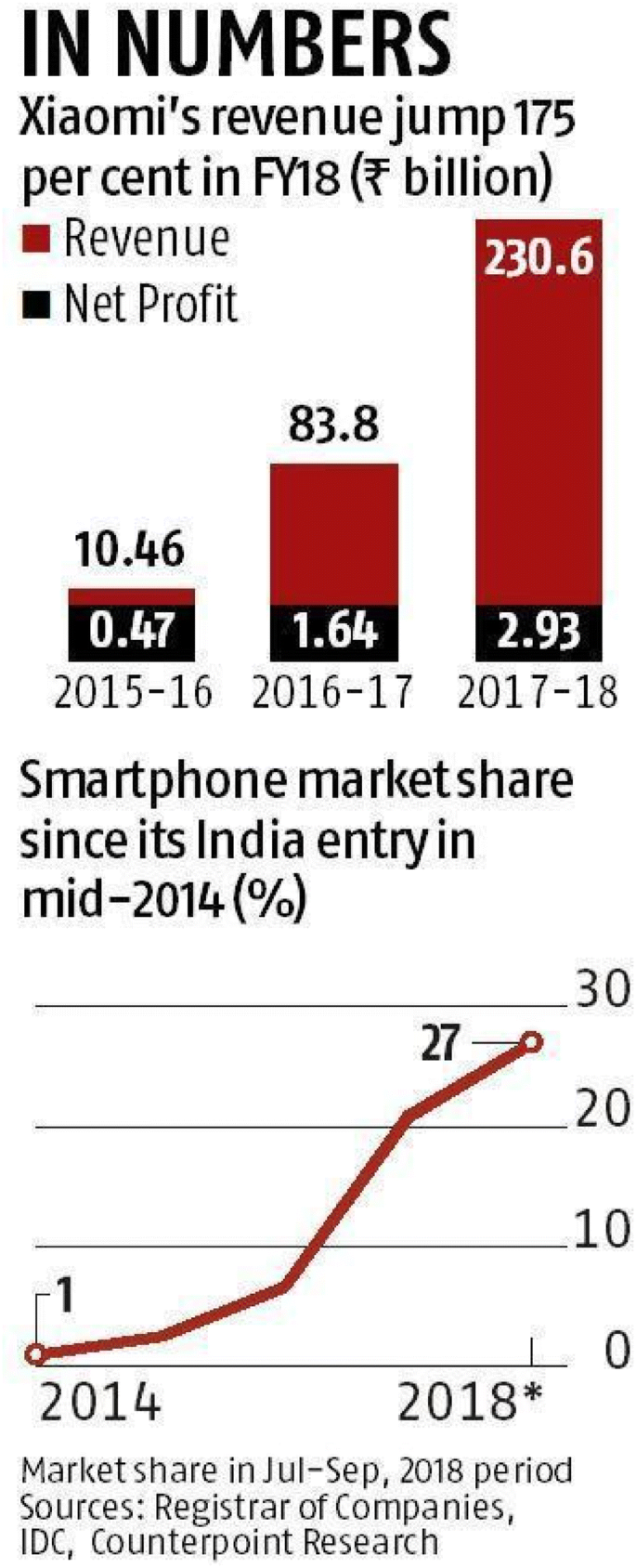
Source : IDC Counterpoint Research
Xiaomi revenue and net profit (in Billion Rs) in recent years.
Xiaomi India’s revenue jumped 175% in 2017–2018 to Rs. 230.6 billion year on year. The firm that sells smartphones under the brand Redmi and Mi had a net profit of Rs. 2.93 bn in 2017–2018 (according to IDC, Counterpoint Research).
The documents available at the Registrar of Companies show that in 2016–2017, Xiaomi India had a net profit of Rs. 1.64 bn and sales of Rs. 83.8 bn. According to Canalys (research agency), Xiaomi smartphones continued to experience high growth in the Indian smartphone market and ranked first in terms of market share by shipments in the second quarter of 2018.
India is an emerging market for smartphones. According to Counterpoint Technology Market Research and Cyber Media Research, although the global annual sales of smartphones have declined, the Indian smartphone market has grown by 12% approximately from about 134 million to 150 million in 2017.
According to International Data Corporation (IDC), in 2018, Xiaomi shipped 11.7 mn smartphones and became the top brand in the Indian market with 27.3% in the third quarter of 2018. Xiaomi India was able to grow to a new height with its successful Redmi 5A and Redmi Note 5 Pro series. It also has refreshed it Redmi 6/A/Pro portfolio.
The smartphone segment is the major growth driver in India. According to the ET report, Xiaomi’s smartphone shipments in India are going to register a 22% CAGR Footnote 2 in 2018-20E with market share gradually rising to 34% in 2020E from 30% in 2018. Among the emerging markets, India enjoyed the strongest growth of 14% YoY in 2017 to 8% of global market share, up from 7% in 2016 (Fig. 3 ).
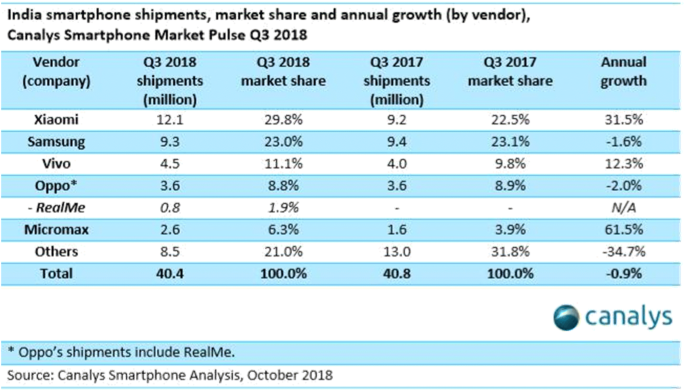
Annual growth and market share of smartphone manufacturers in the Indian smartphone market in 2017–2018
According to Canalys research report, in the Q3, 2018, Xiaomi’s market share was 29.8% with an annual growth of 31.5%. Samsung market share was 23% with a negative annual growth of 1.6%. The market shares of Vivo and Oppo were 11.1 and 8.8%, respectively. The annual growth rate was 12.3% and − 2.0%, respectively (Fig. 4 ).
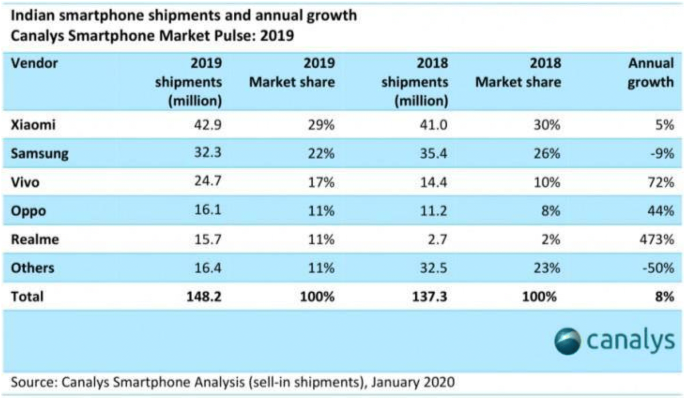
Source : Canalys smartphone analysis, Jan 2020
Annual growth and market share of smartphone manufacturers in the Indian smartphone market in 2018–2019.
According to Canalys Smartphone Analysis, Jan 2020 Xiaomi India was able to maintain its top position in 2019 with an annual growth of 5% and a market share of 29%.
Xiaomi’s smartphone shipments across the globe
According to Macquarie Research, July 2018, Company model has 15% CAGR for unit smartphone shipments in India in 2018-20E, driven by rising population and smartphone penetration rates. When compared to the rest of the globe, Xiaomi’s popularity is incredibly high in India (Figs. 5 , 6 ).
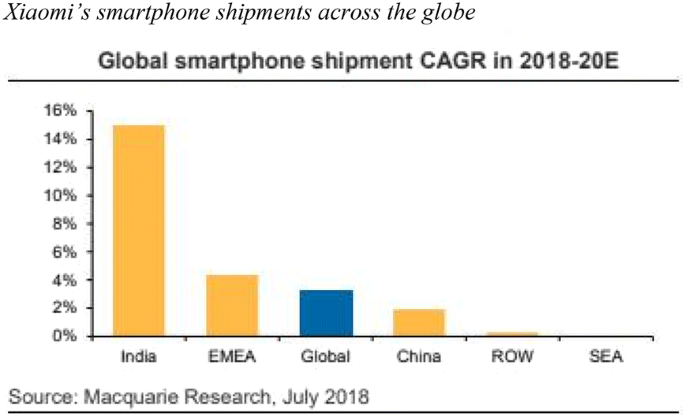
Source : Macquarie Research, July 2018
Xiaomi’s Global smartphone shipment.
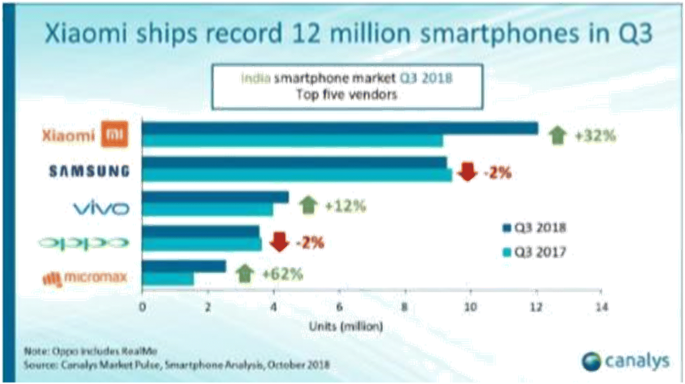
Source : Canalys Research
India’s smartphone market Q3 2018-top 5 vendors.
The performance streaks of Xiaomi have shown no signs of abating. The company has cemented its lead in the country by shipping more than 12 million smartphones in Q3 2018. Samsung was able to ship 9.3 million smartphones in Q3 2018. Vivo and Oppo came the third and fourth with 4.5 million and 3.6 million shipments, respectively.
SWOT analysis of Xiaomi
Growing market Growing market for smartphones in developing countries is a major strength of Xiaomi, especially in the Asian market. India, China and Pakistan are the largest consumers in the Asian market. Currently, Xiaomi products are available in more than 80 countries around the world and have a leading foothold in many of them.
Pricing strategy The pricing strategy adopted by Xiaomi is penetrative pricing. It prices its product very reasonably. It offers the right quality at the right price to its customers.
Quality products At a very low price, the company sells good quality products on the e-commerce portal. The smartphones of Xiaomi are regularly rated very high on quality.
Consistent strong revenues and profit The Company has seen a consistent increase in the annual growth for the last 4 years which enabled innovations in the smartphone segment.
Advance technology The smartphones of Xiaomi are technologically advanced and are well known for its cameras which are very high in resolution. Xiaomi is often at the leading edge of new technology as it offers innovative and featured products.
Increased brand awareness The increase in brand awareness of Xiaomi smartphones has resulted in higher sales across the Asian market.
Online marketing The Flash sales of Xiaomi smartphones on e-commerce portal have made consumers go crazy, and the company was able to sell the smartphones at very reasonable prices in a limited time.
Investment in R&D The Company invests heavily in R&D. Its major R&D expense is towards cost advantage Footnote 3 rather than on differential advantage. Footnote 4
Operating advantage Its low production cost is an operating advantage with excellence in engineering and innovative designs.
Brick-and-mortar store Xiaomi was able to sell its smartphone through click stores. (Flash sales). But offline sales were not so attractive. Lack of significant retail presence is a weakness.
Advertising and marketing The company has spent very less on marketing and advertising. Its advertisements are not very consistent. The company spends on advertising only during a new product launch.
Poor service and weak after sales Service centres of Xiaomi India are limited and provide very little after-sales support when compared to the competitors.
Brand image and equity Because of being a Chinese manufacturer, the company’s brand image is not as good as Samsung and Apple.
Opportunities
Growing urban income The per capita income is the indicator of the prosperity of an economy. According to the Ministry of statistics and programme implementation (MOSPI), the per capita income has shown a rise of 8.6% (FY Footnote 5 2017-18). However, it was slower than in the previous year growth pattern.
Increase in urban population According to U.N. World Urbanization prospects 2018 report, 34% of India’s population lives in urban areas. It shows an increase of 3% urban population since the 2011 census.
FDI norms The relaxation in FDI norms has a positive impact on the smartphone industry.
Growing Educated youth preferring smartphones The shopping trend of this growing educated youth has shown a preference for smartphones which are available at reasonable prices. According to the IMF, India’s population mostly comprises of young people, with 41% of people in the age group of 25–40.
Emerging market India as an emerging market for the smartphone segment provides an opportunity to increase revenue.
Government regulation As the government is serious about the security of phones and user data, the company has to respond to India’s data security and privacy concerns. It can be a destabilizing factor.
Health concern As the customers are showing a lot of concern towards health, an awareness about the dangerous effects of using mobile phones can have an impact on consumer behaviour which can in turn have a negative impact on the smartphone industry.
Uncertainties in share market Due to sudden fluctuation in stock prices, Xiaomi sinks after billions of shares are unlocked for sale. This will have an impact on the market share of Xiaomi India.
The imposition of Tax The implementation of GST has increased the prices of goods. But Xiaomi products are still priced cheaper than its competitors. However, when the government has cut the GST rates, the company has reduced its prices of smartphones to pass the benefits to its customers.
Increase in competition The market for smartphone makers in India is saturated as many other Chinese manufacturers (like Oppo and Vivo) are coming up with affordable products with handsome specs.
Business model and innovative strategies of Xiaomi India
The Flash sale model has worked wonderfully for Xiaomi. In Flash sales, the product is generally made available only in limited quantities. The model has made the customers go crazy. The CEO of Xiaomi India Mr Manu Jain has defined himself as a Maverick. He is the one who challenged the status quo by doing exactly the opposite of what other mobile brands were doing in India. People have labelled him Crazy as the rivals were entrenched in brick-and-mortar stores across the country; he has adopted the online route to sell its products in a country like India. The company has got huge orders within that limited time, and Xiaomi India was able to reach its target sales in that short span (Fig. 7 ).
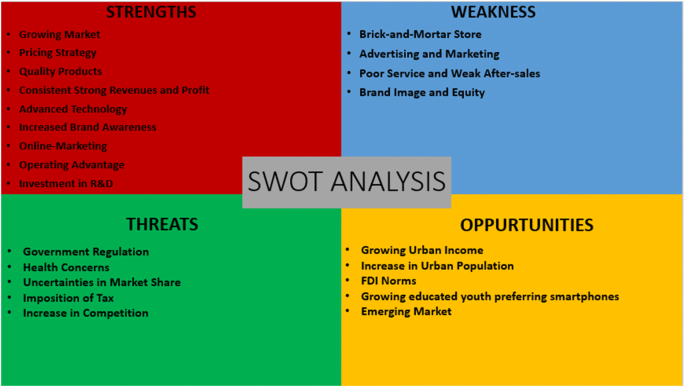
SWOT analysis of Xiaomi India
The pricing strategy of Xiaomi India is that its products are 30–50% cheaper than the top brands like Samsung and L.G. The company’s strategy is to keep just 5% margin for itself. It assembles its products locally to take advantage of Make in India duty benefits. The Company has plans to follow the same pricing strategy for its smart appliances. Moreover, the Flash sales model concept shall also be extended to white goods.
The company focuses on a triathlon model. This creates synergies by cross-selling services and products to users, through its innovative retail concept which involves direct online sales to maximize efficiency and create a long-term direct digital relationship with the users. With its astounding growth, the company has challenged the leading smartphone makers Samsung and Apple in the Indian market (as per the Xiaomi Team report published on Aug 20, 2019).
Xiaomi India’s adopts a line modernization strategy as it intends to expand its smartphone line by refreshing the portfolio and expanding the range. It also wants to expand its product category and has plans to enter the white goods market in India. All the electronic appliances which are going to be launched in India are going to be based on IoT. All these appliances are going to be launched online first and then will be available in exclusive brand stores. The most innovative strategy of the company is its keen focus to create new revenue drivers.
Financial highlights of Xiaomi India
Total revenue was approximately RMB51.951 billion, up 14.8% YoY;
Gross profit was approximately RMB7.26billion, up 28.4% YoY;
Net profit was approximately RMB1.96 billion;
Non-IFRS adjusted net profit was approximately RMB3.64 billion, up 71.7% YoY;
Earnings per share were RMB0.082.
Marketing strategies
The product portfolio of xiaomi india.
The product portfolio of Xiaomi India can be categorized into Smartphones, Smart TV’s and Ecosystem Accessories. The detailed items are listed below:
Smartphones
Redmi Note 6 Pro
Redmi Note 5 Pro
Redmi 6 Pro
Other products sold by Xiaomi India
Power banks
Selfie sticks
Chargers and cables
Bands and fitness trackers
Cases and protectors
Air purifiers
VR headsets
Xiaomi offers high cost-to-performance products. The company adopts a penetration pricing strategy. It offers competitively priced smartphones to its consumers. Indian customers are price sensitive and cannot afford expensive smartphones. According to Xiaomi, its success comes from consistently focusing on price and features. Xiaomi had a tough time in India because of its competitors Samsung, Oppo and Vivo. But because of its penetrative pricing strategy, Xiaomi was able to win its battle in India. However, the company for its Premium models displays aggressive specifications that might create avenues to lift Xiaomi’s brand image and support premium pricing.
Chinese smartphone giant Xiaomi India has kicked off its No.1 Mi Flash sale on Mi.com and Amazon India. Xiaomi Smartphones were up for sale online for a limited period until Friday in the month of December 2014. Xiaomi India has also partnered with Paytm, Google pay and MobiKwik to offer cashback and rewards to its customers during the Flash sales on Mi.com. The Amazon partner has offered an instant discount to its HDFC Bank Users.
Xiaomi India has taken the online route to enter into Indian market while its rivals were deeply entrenched in brick-and-mortar stores across the country. According to Manu Jain, the India head of Xiaomi as told to ET (Mar 2018), the competitors of Xiaomi were splurging millions of dollars on advertising and hiring bollywood biggies like Khans; the company was betting on word of mouth. The company believed in their blockbuster fans, i.e. their customers.
The Flash sale offered the 4 GB RAM variant of Redmi Note % pro at a discounted price of Rs. 12,999, while Redmi Note % Pro 6 GB RAM model was available at Rs. 11,999. The company offered huge discounts and rewards to its customers during the Flash Sales.
Chinese smartphone manufacturer Xiaomi has toppled the leading smartphone maker Samsung in India (Canalys report 2018). Xiaomi which was once considered as a cheap copycat is now able to rub shoulders with the South Korean market leader. It has set up 500 Mi stores in rural areas and has plans to ramp up to 5000 stores in 2019 to increase its offline sales (ET 2018). The company also wants to penetrate the rural market through its offline sales. It also wants to enter into a franchise agreement with its local vendor to reach out to the masses. The size of Mi stores is on average not more than 300 Sq ft. These Mi stores are likely to generate employment opportunities to over 15,000 employees in these regions.
The key factor that supports smartphones sales in India is the rising rate of internet penetration which drives online purchase. However, the internet users in Indian cities rose 10% in 2017, but the overall internet users stayed low at around 480 m in 2017. It is only 35% of the total population which shows a rich upside to grow. The online channel sales of smartphones in India rose from 34% in the fourth quarter of 2017 to 36% in the first quarter of 2018. The rising 4G coverage due to operator investments in 4G networks and 4G service price cuts (e.g. Reliance Jio) have accelerated smartphone market growth (Fig. 8 ).
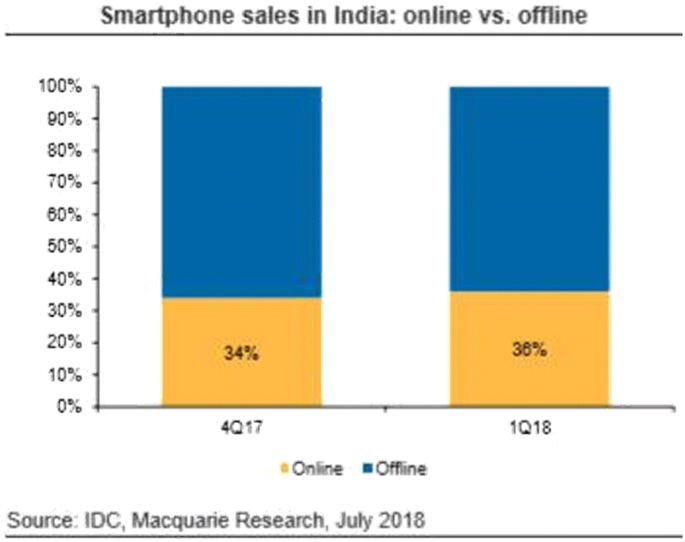
Smartphone sales in India: online versus offline.
Xiaomi’s high cost-to-performance smartphone models have contributed to its largest market share in India. Another major factor for its rising market share is the comprehensive distribution channels which include both online and offline. Online channels contribute to 70% of Xiaomi’s smartphone sales. According to IDC, riding on the growing online channel market trend (up from 34% in 4Q17 to 36% in 1Q18), Xiaomi also gained market share in e-Tailer shipments, to 53% in 1Q18 from 32% in 1Q17. In May 2017, Xiaomi started its first offline channel in India by establishing “Mi Home”. By 2018, Xiaomi has 17 Mi Home stores. The company increased it to 100 stores by mid-2019.
Although the entry of Xiaomi into the Indian market can be inspiring for many, the company was in the spotlight when the Xiaomi Redmi Note 7s exploded and the company refused to take the blame as it clarified that the damage to the phone was "customer induced" (Report of Times of India). Similar cases have been reported in the products under the Redmi brand as many phones exploded while charging. The Chinese tech company is facing criticism for its faulty batteries and manufacturing defects which caused the explosion threatening the lives of the users. However, the company’s CEO Mr. Manu Jain has made a statement that the damage is caused due to external forces (Business Today Nov 2019).
Moreover, Sweden’s Ericsson smartphone maker got an interim injunction against the sale of Xiaomi’s smartphones claiming that Xiaomi infringed 4 of its patents which deal with GSM, GPRS, EDGE and WCDMA technologies. This caused a ban on all Xiaomi smartphones selling in India, but later on smartphones based on Qualcomm chipsets were only allowed. Ericsson later claimed that Xiaomi was selling its non-Qualcomm products through a website called www.xiaomishop.com violating its interim order. Xiaomi India defended the claim by stating that they had no stake on the website and their name was being misused (The Indian Express Nov 2017 ).
In another case, Coolpad a Chinese smartphone maker has filed to Indian court against its rival Xiaomi over patent infringement as India has a good reputation in protecting Intellectual Property Rights (Economic Times Jun 2018).
Though the Xiaomi smartphones are famous for their design, affordable price, high-resolution cameras and good performance, it has faced a backlash on its ad ridden MIUI. Many customers hold back from buying a Xiaomi handset because of the ads being a part of its user interface.
Moving ahead
Xiaomi India has plans to invite more of its suppliers of the component to investing in India. The Chief Marketing Officer of Xiaomi India Mr. Anuj Sharma in an interview with ET said that 95% of smartphones are made in India. One of the suppliers “Holitech Technology” has signed an MoU with the Government of A.P to start its manufacturing facility. Economic Times 2018 report says that Xiaomi India has six factories in India. The company has plans to increase its manufacturing capacity of existing plants and also opening up new plants in India to cater to the local demand of customers. Presently, Foxconn Corporation India Unit makes the company’s phone locally. Foxconn and HiPad are producing Mi and Redmi devices in India. The company has plans to invest heavily in other manufacturers to build an ecosystem of IoT to extend its reach beyond smartphones.
To meet its growing demand for handsets, the company has partnered it with an original equipment maker FLEX to manufacture smartphones in Tamilnadu. This new plant at Tamilnadu is the seventh plant of Xiaomi India. Xiaomi India’s partner Holitech Technology which supplies components to top companies except for Apple sets up a plant in Greater Noida, to invest $200 mn. The new plan has started its operations in the third quarter of 2019. It is also estimated to generate 6000 jobs in the coming 3 years. It has plans to make compact camera modules, screen modules, fingerprint modules, thin-film transistors, capacitive touch and flexible printed circuits.
To boost its growth in the smartphone segment, Xiaomi India has plans to enter India’s rural market as it believes that the urban market has greater potential for the online market, but in rural India, the offline segment provides significant growth. It has launched Mi stores in the Tier 3 market of rural India to cater to the needs of India’s rural smartphone user. The Chief Operating Officer of Xiaomi India Mr Murali Krishna has said in an interview with ET that they have launched 500 stores in the rural market across India.
Out of 48% of market share, 20% of the sales of Xiaomi India are offline and the rest are online. The companies plan to open their own operated and branded stores is still pending with the Government. It has plans to open around 200 retail stores in the next 2 years to increase its target market.
Xiaomi India has plans to enter the white goods market in India which will make the country’s largest smartphone maker the full-fledged consumer electronics company in India. The Company has plans to make its electronic goods as smart appliances based on IoT. These smart appliances can connect to the internet and other devices and can be operated remotely. Xiaomi India’s potential electronic appliance category includes air conditioners, washing machines, refrigerators, laptops, vacuum cleaners and water purifiers.
The CEO of Xiaomi India as reported to Business Today has plans to launch various product categories in India, and their only concern is to customize the products to suit Indian customers. Xiaomi India would like to foray in areas where stringent rules and regulations don’t apply. Rather than bringing products like Drones which are subjected to strict rules and regulations, the company would like to focus on flexible sectors like electric cycles and vehicles.
The company at present caters to 50 markets in the country and has plans to enter 500 markets. To expand its business, it shall make offline presence through exclusive brand stores with a range of smartphones, smart televisions and other electronic appliances. The Chinese handset maker Xiaomi is all set to install its vending machines to sell its smartphone and accessories in major Indian cities (ET May 2019). These vending machines are called “Mi Express Kiosk “and will allow its consumers to purchase smartphones and accessories. The customers can pay through credit or debit cards, cash and UPI (ET 2019).
Xiaomi India has plans to launch in the high-end range of smartphone market competing for the toe to toe with the likes of Samsung, Oneplus and Apple which currently rule the segment in 2020.
Conclusion and inferences
The handset market has witnessed stiff competition, as the bigger players are getting even bigger and marginalizing the smaller players. Samsung of South Korea and Xiaomi of China are expected to continue their fight for the top slot in 2020. The other rivals for the top five positions will be from Oppo, Vivo, Realme, HMD Global(Nokia) and Huawei/Honor. Through the innovative strategies of Xiaomi, it is likely to become a game changer in the near future. The category expansion strategy of Xiaomi has made it a global player from just a startup firm.
Xiaomi has 190 million MAUs Footnote 6 on the MIUI.MIUI (Mi User Interface) is the proprietary operating system built on the android operating system which allows users to download mobile apps from the android ecosystem. The company has 38 apps with more than 10 million MAUs and 18 apps with more than 50 million MAUs. This app includes Mi App Store, Mi Browser, Mi Music, Mi Video Apps. (ET March 2018). With such innovative strategies, Xiaomi India is building a growing tribe of fans (Xiaomi tribe). They mostly target millennials who are tech savvy and innovators of products.
The most important move of Xiaomi India about offline expansion, especially in the rural market, is the significant factor for its growth and success. Moreover, the promise to get innovative designs like foldable smartphones and bezel-less smartphones at an affordable price shall make Xiaomi India sustain the top position in the long run.
Xiaomi plans to expand its product category (entering the white goods space in Indian market) shall open newer avenues of growth in the Indian market. The appliances based on IoT will contribute to the growing revenue. Xiaomi’s investment in various channels, innovative business models, growing ecosystem across devices and internet services is likely to drive market share gains in the future.
According to IDC 2018, Xiaomi has already acquired 30.6% market share in the first quarter 2019; the company’s future rests on how it capitalizes the strengths and minimizes its weaknesses to create sustainable competitive advantages. Currently, the company should concentrate on improving its manufacturing facility, advertising, product quality and distribution network. The company should come up with more such innovative business practices to deal with increasing uncertainties. The case study is based on secondary data from corporate websites relevant reports, news and articles from business magazines and newspapers. The study is useful to learn about the smartphone segment in India, its growth potential and challenges, future trends. To the best of the author’s knowledge, no such study was made in the past which attempts to investigate the marketing mix strategies, business models and challenges faced by smartphone maker Xiaomi India with the detailed analysis. The study infers that case study of Xiaomi is a lesson for all marketer’s as uncertainties and challenges can appear any time, and a combination of market research and innovative strategies is necessary to face such situations.
Maverick—one who doesn’t go along with group or party.
CAGR—Compounded Annual growth rate
Is something where the focus of the company is on reducing the cost.
Is something where the focus is on developing different features.
FY starts from 1st April and ends on 31st March in India
MAUs—Monthly Active Users.
“Behind the fall and rise of China’s Xiaomi”, 22 December 2017. Wired.com. https://www.wired.com/story/behind-the-fall-and-rise-of-china-xiaomi/
Buisness Today Nov 21, 2019, Xiaomi Redmi Note 7S allegedly explodes. https://www.google.com/amp/s/m.businesstoday.in/lite/story/xiaomi-redmi-note-7s-allegedly-explodes-company-says-fire-customer-induced/1/390793.html
Business standard, Oct 24 2018, Xiaomi India revenue rises 175% in FY18, Mi posts net profit of Rs. 2.93 bn. https://www.business-standard.com/article/technology/xiaomi-india-revenue-rises-175-in-fy18-mi-posts-net-profit-of-2-93-bn-118102301482_1.html
Business today, December 21, 2018, Xiaomi’s Redmi Go handset could soon be launched in India. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomis-redmi-go-handset-could-soon-be-launched-in-india/story/302990.html
Business Today, December 20, 2018, Xiaomi No. 1 Mi Fan Sale: Here are all the deals and discounts you need to know about. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-no1-mi-fan-sale-here-are-all-the-deals-and-discounts-you-need-to-know-about/story/302592.html
Business Today, Mar 20, 2019, Xiaomi makes its largest investment in India so far. https://www.businessinsider.in/xiaomi-investment-india-new-products-launch-expected/articleshow/68460618.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
Business Today Nov 15, 2018, Xiaomi is the leader of the pack in India with a market share of 27.3% in Q3. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-is-the-leader-of-the-pack-in-india-with-market-share-of-27.3-in-q3/story/291275.html
Business Today, November 20, 2018, Xiaomi plans to set up 5000 stores in rural India by the end of 2019. https://www.businesstoday.in/current/economy-politics/xiaomi-plans-to-set-up-5000-stores-in-rural-india-by-end-of-2019/story/292820.html
China’s Xiaomi raises 1.1 billion from investor at 45 billion valuation, Dec 9 2014. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-xiaomi-fundraising/chinas-xiaomi-raises-1-1-billion-from-investors-at-45-billion-valuation-idUSKBN0K70FQ20141229
CNBC, Jan 25 2019, Here’s why Apple lags behind Samsung and Xiaomi in India. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/xiaomi-corporation-hkg-1810-financial-011724304.html . 13 Jan 2019
CNBC Markets, 22 June 2018, Xiaomi reportedly awards founder $1.5 billion in stock ahead of IPO. https://www.cnbc.com/2018/06/22/xiaomi-reportedly-awards-founder-1-point-5-billion-in-stock-ahead-of-ipo.html
First post, Jan 02, 2020, Like Xiaomi, Realme phones are now spammed with ads, but they can be disabled. https://www.firstpost.com/tech/news-analysis/like-xiaomi-realme-phones-are-now-spammed-with-ads-but-they-can-be-disabled-7849991.html
Gadgets Now Oct 3, 2018, Xiaomi Mi A1 smartphone ‘explodes’ while charging. https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.gadgetsnow.com/mobiles/xiaomi-mi-a1-smartphone-explodes-while-charging/amp_articleshow/66049991.cms&ved=2ahUKEwju-JXgrMznAhXYxDgGHUUsDdoQFjACegQIDxAL&usg=AOvVaw2mEcinXILls3L7VOkLdPjD&cf=1
Gsm arena 30 Jan 2020, Xiaomi leads in Indian smartphone sales, while Realme grows exponentially. https://www.gsmarena.com/xiaomi_leads_in_india_smartphone_sales_while_realme_grows_exponentially_-news-41277.php
“Inside Xiaomi: The perks and perils of startups that join its ecosystem”, March 2018. Tech in Asia. https://www.techinasia.com/xiaomi-ecosystem
INC 42, India Contributed 32% of Xiaomi’s Total Global Revenue of $18 Bn in 2017. https://inc42.com/buzz/india-contributed-32-of-xiaomis-total-global-revenue/
KGI research Jun 25, 2018. https://www.kgieworld.sg/securities/resources/ck/files/sgreport/Xiaomi_IPO%20Note_KGI%20Securities%20180625.pdf
“Lei Jun says Xiaomi is a retail business and the goal is to be another MUJI”, 12 Sept 2017, Medium.com. https://medium.com/@pandaily/lei-jun-says-xiaomi-is-a-retail-business-and-the-goal-is-to-be-another-muji-86636b388923
Macquarie Research, Jul 8, 2018. http://www.macquarie.com/research/disclosures
Samsung to launch India-first smartphones to counter Chinese rivals. https://www.investing.com/news/stock-market-news/samsung-to-launch-indiafirst-smartphones-to-counter-chinese-rivals-1745537
The Business Standard, Oct 23, 2018, Smartphone shipment hits all-time high of 44 mn units in Q2. Xiaomi leads. https://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/smartphone-shipment-hits-all-time-high-of-44-mn-units-in-q2-xiaomi-leads-118102300540_1.html
The Business Today, Apr 02, 2019, Xiaomi India bets on internet services to increase revenue. https://www.businesstoday.in/buzztop/buzztop-technology/xiaomi-india-bets-on-internet-services-to-increase-revenue/story/333225.html
The Business Today Apr 25 2019, Xiaomi bets big on offline as online sales saturate. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-bets-big-on-offline-as-online-sales-saturate/story/340430.html
The Business Today, Aug 27, 2018, Xiaomi eyes rural market in India, to open 500 Mi stores. https://www.businesstoday.in/current/economy-politics/xiaomi-eyes-rural-market-in-india-to-open-500-mi-stores/story/281674.html
The Business Today, Jun 19, 2019, Xiaomi Redmi Note 7 Pro is on sale today on Flipkart, Mi.com; check price, specifications. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-redmi-note-7-pro-sale-today-on-flipkart-micom-price-specifications/story/357244.html
The Business Today, Mar 18, 2019, Xiaomi bets big on India, invests Rs 3,500 crore in two tranches. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-bets-big-on-india-invests-rs-3500-crore-in-two-tranches/story/328741.html
The Business Today, Mar 20,2019Xiaomi enters the digital payments market, expands handset manufacturing. https://www.business-standard.com/article/companies/xiaomi-enters-digital-payments-market-expands-handset-manufacturing-119032000049_1.html
The Business Today, Nov 15, 2018, Xiaomi is the leader of the pack in India with a market share. https://www.businesstoday.in/technology/news/xiaomi-is-the-leader-of-the-pack-in-india-with-market-share-of-27.3-in-q3/story/291275.html
The Economic Times Apr 1, 2019, Xiaomi looks to monetise internet services in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/68666216.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times, Apr 26, 2019, Xiaomi slips but retains top spot in the Indian market. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/69054617.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times, Aug 23 2018, Xiaomi Q2 revenue soared 152% on strong growth in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/65504336.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Dec 20, 2018, Xiaomi to invite more component suppliers to invest in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67147023.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst . Accessed 3 Jan 2019
The Economic Times Dec 4, 2018, Xiaomi eyes India’s rural market to fuel growth. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/66941007.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Dec 6, 2018, Xiaomi leads India wearables market in Q3 2018. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/66969493.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Dec 21, 2018, Xiaomi to enter white goods space in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67184592.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Jan 3, 2018, Smartphone sales will grow only in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67200234.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Jan 9, 2019, Xiaomi sinks after billions of shares are unlocked for sale. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67450375.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Jan 2, 2019, Xiaomi TVs cheaper by up to Rs 2000. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67343214.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Jan 4, 2019, Xiaomi, Redmi split to become different brands: report. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/67378086.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Jun 01, 2018, Coolpad open to taking Xiaomi to court in India. https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://m.economictimes.com/tech/hardware/coolpad-open-to-taking-xiaomi-to-court-in-india/amp_articleshow/64408739.cms&ved=2ahUKEwjZkLqFq8znAhV-yTgGHZYDAlkQFjAAegQIBhAB&usg=AOvVaw17Pd8MSFWpYBjfEdQgCB00&cf=1
The Economic Times Jun 8, 2019, Samsung, Vivo & Oppo intensify offline battle to take on Xiaomi. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/hardware/top-brands-like-samsung-oppo-take-the-phone-battle-offline/articleshow/69698361.cms
The Economic Times, Mar 17, 2018, Unboxing Xiaomi: how this Chinese company does what it does in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/63342269.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times May 13, 2019, Xiaomi to sell phones via vending machines in India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/69311072.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times, Nov 26, 2017, China’s handset maker Xiaomi came first in India. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/hardware/how-chinas-handset-maker-xiaomi-came-first-in-india/articleshow/61798368.cms?from=mdr
The Economic Times Nov 29, 2019, Xiaomi touches $5 billion milestone in 2018–2019. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/hardware/xiaomi-touches-5-billion-revenue-milestone-in-india-in-2018-19/articleshow/72299318.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Economic Times Sep 6, 2017, Chinese smartphone maker Xiaomi open to moving servers to India. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/articleshow/60382698.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Hindu, Apr 09, 2019, Xiaomi set up new manufacturing units in India for smartphones, PCBs. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/mobiles-tablets/xiaomi-sets-up-new-manufacturing-units-in-india-for-smartphones-pcbs/article23479556.ece
The Hindu Apr 24, 2019, Xiaomi eyes 10,000 retail stores in India. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/info-tech/xiaomi-eyes-10000-retail-stores-in-india/article26931067.ece
The Hindu, May 18, 2018, Urbanization on the rise in India. https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/growth-in-urbanisation/article23925543.ece
The India Today, May 13, 2019, Mi Express Kiosk launched in India, allows buyers to purchase Xiaomi products instantly. https://www.indiatoday.in/technology/news/story/mi-express-kiosk-launched-in-india-allows-buyers-to-purchase-xiaomi-products-instantly-1523687-2019-05-13
The Indian Express Nov 24, 2017, Xiaomi violating order selling non-Qualcomm smartphones. https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/mobile-tabs/xiaomi-ericsson-xiaomi-mi4/
The Times of India, May 31, 2018, India’s per capita income grows by 8.6% to Rs 1.13 lakh in FY. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/64403580.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst
The Week Magazine, Dec 10, 2018, Ringing in change: the rise and rise of Xiaomi Xiaomi’s popularity has spread far and beyond China, especially in India. https://www.theweek.in/news/sci-tech/2018/11/12/ringing-in-change-the-rise-and-rise-of-xiaomi.html
“The dramatic rise and fall of Xiaomi”, 11 June 2016. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/ckgsb/2016/07/11/the-dramatic-rise-and-fall-of-xiaomi/#e5f93ad33da4
www.Canalys.com , Palo Alto, Shanghai, Singapore and Reading (UK)—Tuesday, 30 October 2018 India struggles to grow in Q3 despite Xiaomi’s record sell-in of 12 million smartphones https://www.canalys.com/static/press_release/2018/India-struggles-to-grow-in-Q3-despite-Xiaomis-record-sell-in-of-12-million-smartphones.pdf
Xiaomi Corporation—Prospectus. http://www.hkexnews.hk/APP/SEHK/2018/2018050202/Documents/SEHK201805030005.pdf
“Xiaomi’s Ecosystem”, 18 April 2018. CMS Research. http://img3.gelonghui.com/pdf201804/pdf20180419133513809.pdf
“Xiaomi’s Growth Path”, May 2018. ChinaLabs. http://t.cj.sina.com.cn/articles/view/6418632331/17e948e8b00100f6fn
Xiaomi posts 71.7% jump in 2Q2019 net profit, beating consensus. http://blog.mi.com/en/2019/08/20/xiaomi-posts-71-7-jump-in-2q2019-net-profit-beating-consensus/#targetText=In%20June%202019%2C%20MAU%20of,22.6%20million%20in%20June%202019
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Amjad Ali Khan College of Business Administration, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Rahela Tabassum & Shehbaz Ahmed
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rahela Tabassum .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tabassum, R., Ahmed, S. Xiaomi invades the smartphone market in India. Decision 47 , 215–228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40622-020-00242-w
Download citation
Published : 27 May 2020
Issue Date : June 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40622-020-00242-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Global player
- Serial entrepreneur
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Localization & Translation
- BLEND Voice
- Data for AI
- Transcription
- Technologies
- Integrations & Partnerships
- Spotlight Integrations
- By Industry
- Freelancers i Translators, voice actors, linguistic experts, content writers -apply here

How BLEND transforms Xiaomi’s Global Presence Powering Local Sales
Xiaomi is one of the world’s biggest names in consumer electronics, dominating the Chinese smartphone market and shipping over 125 million units a year. Despite being a relatively young company, founded in 2010, Xiaomi has rapidly expanded throughout Southeast Asia, Europe, and around the world, winning an ever-increasing loyal customer base thanks to a combination of premium-level features, low prices, and the close relationship the company nurtures with a global community of active users. Of course, with global expansion comes linguistic expansion: software, user agreements, privacy policies, and more, all require seamless, rapid localization. For Xiaomi it quickly became clear that they needed a partner who could provide not only professional native communication but also an in-depth understanding of each market’s needs and culture – and with a fast turnaround. BLEND became their ideal localization partner, offering a comprehensive suite of solutions: reliably excellent translation services to 45 languages, full Crowdin integration, expert centralized management, and much more. This enhanced local appeal had immediate and long-lasting benefits for the Xiaomi brand, driving significant growth in multiple markets with minimal operational hassle.
The Challenge:
Finding the Consistency in Infinite Diversity For Xiaomi customers, their phones, laptops, and other electronics are at the very core of their daily lives, from work and studies to entertainment and communication. This means that being able to use Xiaomi technology in users’ native languages is key to Xiaomi’s marketing and sales strategy as it expands to new territories. When Xiaomi approached BLEND with this challenge back in 2015, there were already several major issues that had to be resolved. Firstly, there were 18 different languages to deal with, ranging from major global languages to much smaller niche ones like Maltese, Basque, Galician, and Catalan. Secondly, due to Xiaomi’s unprecedented expansion speed, the Xiaomi community had been pitching in to help with translations – an amazing stop-gap effort, but one that led to many pre-existing consistency issues and required correction of previous material while simultaneously handling new texts. Finally, as the world of mobile communication never pauses for breath, Xiaomi needed a way to get translations almost in real-time for their daily software updates and any other sales, marketing, or legal language requests that might pop up at any minute, for any language.
The Process: Smooth, Seamless & Xiaomi
The advantages of working with BLEND became abundantly clear the moment the relationship began, all the way back in 2015 (just five years, but Xiaomi has covered a whole lot of ground in that period of time). Santi Guan, Xiaomi’s Software Localization Manager, explained that the company had gone from just a few languages to 18 almost overnight, and the localization strategy had to match up with the broader market penetration strategy. “When we’re entering the biggest markets, like those in Europe, distributors insist on having sales and marketing materials in local languages.”
The Xiaomi team recognized the importance of multi-market localization to drive sales and partnered with BLEND to power their efforts. It was a big step up from relying on an ad-hoc approach where each territory did its own thing.
BLEND’s full integration with the Crowdin localization management platform made the process much smoother for both sides. Instead of manually uploading each text to both the Xiaomi and BLEND platforms and then notifying BLEND for each and every translation, Xiaomi can simply submit documents, screenshots, or even specific strings (anything from ten to 10,000 words), and they are allocated to the right translators automatically. For Xiaomi, the question of the “right” translators is about so much more than ensuring texts are sent to translators who deal with the necessary language – English, Swedish, Hungarian, Hebrew, Lithuanian, and more. Quality is crucial, as the software and online documentation is the public face of the company worldwide, shaping the user experience for millions of people every minute of the day.
“For clients like Xiaomi that are submitting so much, reliable quality and consistency are crucial. That’s why we provide a huge pool of exclusive, pre-approved translators – so we can cover every eventuality with the assurance that Xiaomi is always getting premium quality.” Corina Apostoiu, BLEND’s Project Manager
Since 2015, the BLEND-Xiaomi relationship has gone from strength to strength, with BLEND’s global community of localization experts always on hand to accommodate Xiaomi’s evolving needs. No matter which territory becomes the next focal point for the Xiaomi sales team, full and ongoing localization is always available, with quick turnaround and impeccable cultural knowledge.
“Sometimes I get unusual language requests from our sales team,” Santi said, “and I assume we’ll have to take the risk of going local and hiring a translator who we don’t know, and who doesn’t know our system. But no matter what language we need, BLEND always has it!” Santi Guan, Xiaomi Software Localization Manager
Another major issue – Xiaomi’s struggle with consistency and quality control throughout older community-translated texts – has also been resolved thanks to the full integration between the BLEND and Xiaomi platforms via Crowdin, which enables smooth editing and revisions and direct communication with the translators who are on the job. Translators can also receive the kind of specific training that is only possible through long-term ongoing relationships, minimizing the chances of glitches or misunderstandings. BLEND has become a hub for all Xiaomi’s language projects, taking the weight off the shoulders of local marketing managers and coding teams. Instead of multiple uncoordinated translation efforts, Xiaomi is able to run every request and concern through a single dedicated account manager. This creates a completely hassle-free workflow for Xiaomi, freeing up sales, marketing, and software development specialists to focus on what they do best: growing the business.
Bonus: Coming to a Pocket Near You
Xiaomi entered its first non-Chinese market (Singapore) in 2014 and established a fruitful relationship with BLEND in 2015. The rest is history… and the future. Backed by BLEND’s powerful localization capabilities, Xiaomi has now launched in upwards of 80 global markets, with big ambitions for continued expansion.
“We’re really growing quickly in Europe – not just our phones, but the whole MiOT Ecosystem, like smartwatches and smart bands,” Santi enthused. “The whole brand is becoming very popular. Having software in the local languages is a huge part of that, especially where we don’t have local marketing teams. It’s a vital tool for sales.” Santi Guan, Xiaomi Software Localization Manager
This support for sales teams, as well as legal and other departments, is hugely significant for a company straddling cultures as diverse as Japan, Spain, and just about everywhere in between. Xiaomi’s phones, laptops, smartwatches, and other devices aim to feel perfectly at home on any desk or in any purse or pocket, and BLEND is able to offer that broad cultural appeal. When consumers and distributors prefer that local touch, BLEND provides native nuance and flair, enhancing brand affinity and reach all the way around the globe.

You may also enjoy

Red Games Expands Gaming Titles to Global Player Base with BLEND

Teva Brings Vital Medication to New Markets with BLEND

Cambridge Health Alliance Strengthens Community Ties Through BLEND Localization

International YouTube Star Nuseir Yassin, Owner of Nas Daily, Grows Russian Language YouTube Channel 35% with BLEND

Simply Increases App Conversion Rate by 10% with BLEND Localization Services
Get in Touch
Brought to you by:

Xiaomi: Entering International Markets
By: Miao Cui, Yan Zhao, Sitara Aziz, Mimi Xiao
After recognizing numerous opportunities in the global market, Xiaomi Technology Corporation Ltd. (Xiaomi), based in Beijing, charted its overseas market strategy in 2013. However, opportunities came…
- Length: 12 page(s)
- Publication Date: Apr 27, 2017
- Discipline: Entrepreneurship
- Product #: W17235-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Same page, Teaching Note
- Same page, Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
After recognizing numerous opportunities in the global market, Xiaomi Technology Corporation Ltd. (Xiaomi), based in Beijing, charted its overseas market strategy in 2013. However, opportunities came with challenges, and during the internationalization process, Xiaomi encountered many problems. By 2016, after three years of hard work, Xiaomi had gained more experience than profits. Compared with Xiaomi's domestic success, Xiaomi's internationalization strategy was unsatisfactory. How could Xiaomi meet its international goals? Should it establish international strategic alliances, develop its firmware operating system, or consider other options?
Miao Cui is affiliated with Dalian University of Technology.
Learning Objectives
The case is suitable for MBA and executive courses in international business. It provides students with an opportunity to establish a basic and structured way of analyzing the internationalization of enterprises, using theories regarding the motivation for internationalization, selection of overseas markets, and modes of overseas market entrance. After working through the case and assignment questions, students will be able to develop the ability to analyze companies' motivations for internationalization; analyze the rationale for choosing target markets; and identify different entry modes and how they may be improved.
Apr 27, 2017
Discipline:
Entrepreneurship
Geographies:
China, Chinese Taipei, Hong Kong SAR, India
Industries:
Ivey Publishing
W17235-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about Xiaomi's history, business strategy, and growth in the Indian market. Find out how Xiaomi uses web-based business, social media, and customer feedback to compete with Apple and Samsung.
When Xiaomi launched in 2010, it only offered a free Android-based OS. But within seven years, it became one of the world's largest smartphone makers, reaching $15 billion in revenue.
By 2016 it had started to expand internationally, and this case lays out the company's globalization strategies and challenges moving forward. Hugo Barra, a top Android executive, had left Google a few years earlier to lead Xiaomi's international growth. Xiaomi's founder and CEO, Lei Jun, said the company's ultimate goal was "making ...
Secondly, Xiaomi has capitalized on the power of the internet by establishing a robust online sales strategy. This approach has allowed them to bypass traditional retail markups, further reducing costs for consumers. ... It serves as a case study for companies aiming to achieve international success. Xiaomi's ability to adapt, innovate, and ...
Xiaomi Case Study | Secret Behind Xiaomi's Success In India. Xiaomi Corporation is a Chinese gadget manufacturer established by Lei Jun in2010 and headquartered in Beijing. Xiaomi makes and puts resources into cellphones, versatile applications, trimmers, headphones, television, and numerousother products. Ranked 468th, Xiaomi was the most ...
He has published numerous top journal papers in these areas as well as multiple bestseller case studies in Harvard Business Publishing. YG Yanting Guo is an Assistant Professor in the School of ...
Xiaomi, the Chinese smartphone company founded in 2010, had quickly become an industry leader in the Chinese market. By 2016 it had started to expand internationally, and this case lays out the company's globalization strategies and challenges moving forward. Hugo Barra, a top Android executive, had left Google a few years earlier to lead Xiaomi's international growth. Xiaomi's founder and CEO ...
In June 2021, a global smartphone sales report marked an unusual tipping point. According to Counterpoint Research, Xiaomi, with a 17.1 percent share of global sales, surpassed both Apple and Samsung and became the #1 smartphone brand in the world for the first time.More interestingly, Xiaomi did it without entering one of the largest smartphone markets - the United States - due to ...
Key Takeaways from Xiaomi's Business Strategy. Xiaomi's business strategy depends upon time and trends. Here are some key-takeaways from the strategy that we must study and implement to further growth: Assembling and Employing a fan base: Since 2012, the brand has created a huge fan base that involves millions of people across the world.
After breaking into China's smartphone market, where it becomes a leading brand, Xiaomi sees sales stagnate and then decline as the disruption strategy that empowered its rise loses momentum. As competitors counter every move, targeting its core consumer segment, the company urgently needs to reignite growth and develop a sustainable competitive advantage. The case describes the changing ...
In. 2021, we generated RMB163.6 billion in revenue from abroad markets, a 33.7% year-over-year. increase and 49.8% of our overall revenue. The market share of smartphones shipp ed by Xiaomi in ...
A Case Study on Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi. Ashok Panigrahi. Associat e Professor, NMIMS Univers ity, Shirpur, Maharasht ra. E- mail: [email protected]. ABSTRACT. With t he int ens e de ...
That's a steep rise for a company that had just 3% of the market in 2015. All thanks to the innovative marketing strategy of Xiaomi that stimulated this growth. Source. Regulatory filing access by AltInfo showed that Xiaomi posted a profit of Rs 401 crore in FY20 after sustaining Rs 148 crore loss a year earlier.
The case study is based on Xiaomi Corporation, a Chinese Public company, headquartered in Beijing, China. Xiaomi (the word Xiaomi means millet which means a "grain" that is a staple diet in various parts of the world) is the world's fourth largest smartphone (a smartphone is a mobile phone with various functions of a computer) company based on total shipments. It produces low-cost but ...
Download Case Study. Santi Guan, Senior Localization Manager. Xiaomi is one of the world's biggest names in consumer electronics, dominating the Chinese smartphone market and shipping over 125 million units a year. Despite being a relatively young company, founded in 2010, Xiaomi has rapidly expanded throughout Southeast Asia, Europe, and ...
This paper will use business management models from PEST, Porter's five forces and SWOT to analyze the internal and external environment of Xiaomi, and evaluates whether Xiaomi has a strategic model of sustainable development, strategic flaws and recommend some suggestions to overcome them. Over the past six years, (between the period 2014 -2019), China's electronic information industry and ...
After recognizing numerous opportunities in the global market, Xiaomi Technology Corporation Ltd. (Xiaomi), based in Beijing, charted its overseas market strategy in 2013. However, opportunities came with challenges, and during the internationalization process, Xiaomi encountered many problems. By 2016, after three years of hard work, Xiaomi had gained more experience than profits. Compared ...
A CASE STUDY OF XIAOMI TECHNOLOGY COMPANY Aibolat Yesentemirov, Almaty Management University Gulziya Aldashova, Zhubanov Aktobe Regional State University ... The study aim is to understand Xiaomi success from its strategic management perspective. The purpose of this article is to get an insight into Xiaomi success and how it has
The Xiaomi Smart Band 9's case is made of an aluminum alloy and has no buttons or openings. The 1.62-inch display is the same size as its predecessor and is as long as it is narrow.