

What is Product Planning: Benefits, Examples, Process
Home Blog Agile What is Product Planning: Benefits, Examples, Process
Product planning is the process of product development and management that involves defining and strategizing to create a successful product. It encompasses the activities and processes required to identify market needs, set product goals, prioritize features, and create a roadmap for product development.
The goal of product planning is to align business objectives with customer needs and market demand. It involves understanding the target market, conducting market research, and analyzing customer feedback and preferences. By gathering insights and data, product planners can identify opportunities, assess market trends, and make informed decisions about product features, pricing, and positioning.
What is Product Planning?
Product planning is a systematic approach taken to develop a successful product that meets customer needs and aligns with business goals. Product planning encompasses various activities, including market research, competitive analysis, customer segmentation, and defining product requirements.
The product planning and control phase involves key activities such as defining the product vision and goals, conducting market analysis, identifying target customers and much more. Product planners collaborate with various stakeholders, including product managers, designers, engineers, marketing teams, and sales teams, to gather input and ensure alignment.
Agile courses like Agile Methodology training offer you valuable insights and methodologies to enhance the product planning process by promoting adaptability, collaboration, and iterative development. Key components of product planning and control include:
- Market Analysis: Evaluating market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscape to identify market opportunities and potential challenges.
- Customer Research: Understanding the needs, behaviors, and pain points of target customers through surveys, interviews, user testing, and data analysis.
- Product Vision: Creating a compelling product vision that defines its purpose and aligns it with the overall business strategy.
- Product Goals: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that guide the product's development and success metrics.
- Product Roadmap: Creating a visual representation of the product's planned features, timelines, and priorities.
- Prioritization: Identifying and prioritizing the most valuable features and functionalities based on customer needs, market demand, and business objectives.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Collaborating with various teams, including product management, design, development, marketing, and sales, to gather input, align strategies, and ensure smooth execution.
- Iterative Development: Embracing iterative and agile development methodologies to incorporate feedback, adjust, and continuously improve the product.
Who is Responsible for Product Planning?
The product planning process is a collaborative effort that involves various stakeholders within an organization. While the specific roles and responsibilities may vary depending on the company structure and size, the following are key individuals typically involved in product planning:
Product Manager: Product managers are key players in an organization's product planning. They collaborate with cross-functional teams and stakeholders to ensure the product's triumph. Their pivotal role encompasses defining the product vision, conducting market research, gathering customer insights, prioritizing features, and aligning product strategy with business goals. Additionally, they are accountable for creating the product roadmap for development and release.
Product Owners: In Scrum, the product owner serves as the customer's voice, connecting the development team with stakeholders. They collaborate with the product manager to prioritize user stories, manage the product backlog, and communicate the product requirements to the development team. Certification like a certified Scrum Master course can enhance the understanding and application of Agile principles and practices, providing valuable skills for product planning and development.
Marketing Team: The marketing team plays a crucial role in product planning by conducting market research, competitive analysis, and identifying target customers. They contribute to defining the product positioning, messaging, and go-to-market strategy.
Development Team: The development team collaborates with the product manager and product owner to understand the product requirements. This collaboration helps the team develop the necessary features and functionalities.
Sales Team: The sales team provides valuable insights from the front lines, sharing customer feedback, market trends, and competitive information. They contribute to the product planning process by highlighting customer needs and market opportunities.
User Experience (UX) Designers: UX designers contribute to product planning by understanding user needs, creating user personas, and designing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
Executives and Stakeholders: Executives and key stakeholders provide guidance, strategic direction, and support throughout the product planning process. Their input and decision-making help shape the overall product strategy.
Product Plan Example
The first step of a successful product plan is identifying the target market. Conducting thorough market research gives you insights into the needs of your customers. These insights are of great use to the product development team.
Let us consider the example of Blue Hibiscus Beauty, an online retailer specializing in makeup, skincare products, and hair accessories. As part of their market research strategy, they distribute surveys to customers who make purchases from their online store. These surveys include demographic questions and an open-ended section where participants can provide feedback on desired products.
After analyzing the survey results, Blue Hibiscus Beauty discovers that their primary customer demographic, which consists of females aged 18 to 25, expresses a strong interest in sustainable and easy-to-apply eyeliner. With this knowledge, the company has decided to develop a new eyeliner product that meets these specifications.
Why is Product Planning Important?
Increased Chances of Success: Product planning helps to increase the chances of success for new products. Product planning helps in long-term business success.
Reduced Risk: Product planning can also help to reduce risk. By carefully analyzing the market and the competition, businesses can identify opportunities and avoid risks.
Improved Efficiency : Product planning can also help to improve efficiency. By creating a well-defined process businesses can streamline their operations and save time and money.
Better Decision-making: Product planning can also help businesses make better decisions by having a clear understanding of the market, the competition, and the company's goals,
Increased Customer Satisfaction: Product planning can also help to increase customer satisfaction. By creating products that meet the needs of the target market, businesses can improve customer loyalty and repeat business.
Certifications and KnowledgeHut Agile Methodology training can enhance the understanding and application of Agile principles and practices, providing valuable skills to support effective product planning and development processes.
The objectives of product planning are:
1. Customer Satisfaction: By understanding the target market and conducting thorough research, businesses can develop products that provide value and enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Market Competitiveness: Product planning aims to position the product in the market to gain a competitive advantage. The objective is to differentiate the product from competitors, identify unique selling points, and capture a significant market share.
3. Profitability: Product planning focuses on developing products that contribute to the financial success of the business. The objective is to create offerings that generate sufficient revenue, achieve profit margins, and contribute to overall business growth and sustainability.
4. Strategic Alignment: Product planning ensures that the development of new products aligns with the overall business strategy and objectives.
5. Innovation and Differentiation: Product planning aims to foster innovation and develop products that stand out in the market. The objective is to create offerings that introduce new features, technologies, or approaches, providing a unique value proposition and distinguishing the business from competitors.
6. Resource Optimization: Product planning focuses on optimizing resources, including time, budget, and personnel, to develop and launch products efficiently.
7. Risk Mitigation: Product planning aims to minimize risks associated with developing and launching new products. The objective is to conduct market research, feasibility assessments, and risk analyses to identify and mitigate potential challenges, ensuring the successful introduction of products in the market.
8. Customer Loyalty and Retention: Product planning seeks to build customer loyalty and promote repeat purchases.
9. Continuous Improvement: Product planning strives for continuous improvement of products based on customer feedback and market insights.
Core Elements of Successful Product Planning
Successful product planning encompasses several core elements that contribute to the development and launch of a product that meets customer needs and achieves business objectives. Here are the key elements:
Market Research: Thorough market research is essential to understand customer preferences, market trends, and the competitive landscape. It involves gathering insights on customer needs, pain points, and behaviors, as well as analyzing industry trends and competitor offerings.
Customer Segmentation: Identifying and segmenting the target market based on relevant characteristics such as demographics, psychographics, behaviors, and needs. This helps tailor the product to specific customer segments and create targeted marketing strategies.
Product Differentiation: Developing a unique value proposition that sets the product apart from competitors. This involves identifying and highlighting key features, benefits, and advantages that resonate with the target market and address their pain points.
Clear Objectives: Setting clear and measurable objectives for the product, such as sales targets, market share goals, or customer satisfaction metrics. Objectives provide direction, focus, and a benchmark for evaluating the success of the product.
Product Design and Development: The product planning and development process comprises transforming customer needs and preferences into a meticulously designed and developed product or service. This includes defining product features, specifications, functionalities, and user experience to meet customer expectations.
Pricing Strategy: Setting an optimal pricing strategy involves considering various factors such as production costs, perceived value, market positioning, etc. Pricing should align with customer perceptions of value while also supporting revenue and profitability goals.
Distribution Channels: Identifying the most effective distribution channels to reach the target market and make the product accessible to customers. This may include direct sales, e-commerce platforms, retail partnerships, or a combination of channels.
Marketing and Promotion: Creating a holistic marketing plan that encompasses various strategies and tactics to build brand awareness, generate customer interest, and boost sales. This includes defining marketing channels, messaging, branding, advertising, and promotional activities to effectively communicate the product's value to the target market.
Launch and Execution: Planning and executing the product launch, including production, distribution, marketing campaigns, and customer support. This involves coordinating cross-functional teams, monitoring performance, and making necessary adjustments based on market feedback.
Continuous Improvement: Monitoring the product's performance, gathering customer feedback, and making improvements or modifications as needed. Regular evaluation and analysis of market dynamics, competitor strategies, and customer needs help drive continuous product improvement and innovation.
Discover the leading Agile Category Courses
Stages of an Effective Product Planning
The following are the stages of product planning:
1. Ideation: In this stage, ideas for new product planning or enhancements to existing products are generated. Brainstorming sessions, customer feedback, competitive analysis, and technological advancements can all contribute to idea generation.
2. Research: Once ideas are generated, they need to be evaluated and screened to determine their viability. This includes researching the market, your target audience, and the competition.
3. Planning: At this stage, the selected ideas are further developed into tangible product concepts. This includes creating detailed product descriptions, outlining features and benefits, and considering potential target markets and pricing strategies.
4. Development: Once the product concept is deemed feasible and financially viable, the actual development process begins. This stage involves designing and engineering the product and creating prototypes.
5. Testing: Before a full-scale launch, the product is introduced to a specific market segment or geographic area to gather real-world feedback and assess market acceptance. This stage helps identify any issues, gather customer insights, and make necessary adjustments before the wider release.
6. Launch: The product is officially launched in the target market, accompanied by comprehensive marketing and sales activities. This stage involves executing the marketing plan, establishing distribution channels, training sales teams, and implementing promotional campaigns to create awareness and drive sales.
7. Post-launch: Once the product is on the market, ongoing monitoring and evaluation are crucial. This involves tracking sales performance, customer feedback, market trends, and competition. Regular evaluation helps identify opportunities for improvement, product extensions, or necessary adjustments to ensure ongoing success.
Mistakes in Product Planning
Product planning is a complex process, and various mistakes can occur if not carefully managed. Below are some common mistakes in product planning:
Insufficient Market Research: Thorough research and understanding of the market, target audience and competition is crucial before you start planning your product.
Poor Target Market Identification: Not accurately identifying and segmenting the target market can lead to ineffective product positioning and marketing efforts.
Ignoring Competitive Landscape: Neglecting to analyze competitors and their products can result in developing offerings that are not differentiated or fail to stand out in the market.
Overlooking Product-market Fit: Failing to ensure that the product aligns well with the target market's needs, preferences, and price sensitivity can lead to low adoption rates and poor sales.
Inadequate Planning and Resource Allocation: It is crucial to allocate sufficient time, budget, and resources to each stage of the product planning process.
Lack of Cross-functional Collaboration: Product planning involves various departments and stakeholders, including marketing, product development, finance, and sales.
Poor Pricing Strategy: Setting an inappropriate pricing strategy can lead to pricing that is too high or too low. Pricing should be based on factors such as production costs, value delivered, and customer perceptions.
Inadequate Marketing and Launch Execution: Poorly executed marketing strategies and product launches can lead to limited awareness, weak positioning, and slow market adoption.
Neglecting Post-Launch Evaluation: Failing to monitor and evaluate the performance of the product after its launch can hinder the ability to identify areas for improvement or necessary adjustments.
Lack of Flexibility and Adaptability: Product planning should be agile and adaptable to changing market conditions, customer feedback, and emerging trends. Failure to embrace flexibility can result in missed opportunities or the inability to respond effectively to evolving customer needs.
How to Avoid Product Planning Mistakes?
To avoid product planning mistakes and increase the chances of success, consider the following strategies:
- Conduct Thorough Market Research: Invest time and resources into comprehensive market research to understand customer needs, preferences, and market dynamics.
- Define a Clear Target Market: Develop a deep understanding of your target customers' pain points, aspirations, and preferences to tailor your product to their specific needs.
- Analyze the Competitive Landscape: Use competitive analysis information to differentiate your product and develop a unique value proposition that sets you apart in the market.
- Validate Product-market Fit: Conduct surveys, interviews, focus groups, or beta testing to ensure your product aligns with customer needs and provides value.
- Foster Cross-functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and communication between different departments and stakeholders involved in product planning, such as marketing, product development, finance, and sales.
- Execute Effective Marketing and Launch Strategies: Develop a comprehensive marketing plan that includes clear messaging, targeted marketing channels, and a well-orchestrated product launch.
- Monitor and Evaluate Continuously: Regularly review the product's performance, gather insights, and make data-driven adjustments to optimize your product planning strategies.
- Embrace Adaptability and Learn from Mistakes: Stay agile and be open to adapting your product planning strategies based on market feedback, emerging trends, and lessons learned from mistakes.
Product planning is crucial for businesses to create successful products, meet customer needs, and stay competitive. It involves understanding customers, aligning strategies, and optimizing resources to ensure well-designed products, differentiation from competitors, and customer satisfaction. By prioritizing product planning and incorporating customer insights, businesses increase their chances of success, adaptability, and innovation. It sets the foundation for long-term business growth and success in a dynamic and competitive marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some features of product planning are:
- Defining product goals and objectives.
- Generating product ideas and concepts.
- Developing a product roadmap and timeline.
- Monitoring and evaluating product performance.
In Agile methodologies, product planning involves creating a roadmap and backlog to guide iterative development. It entails collaboration among teams, product owners, and stakeholders to define the vision, prioritize features, and set release goals. Agile product planning emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and continuous feedback.
Steps to planning a product:
- Develop a product roadmap with key milestones and deliverables.
- Allocate resources and budget, and form a cross-functional team for product development.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate product performance, gathering feedback and making necessary adjustments for ongoing success.

Lindy Quick
Lindy Quick, SPCT, is a dynamic Transformation Architect and Senior Business Agility Consultant with a proven track record of success in driving agile transformations. With expertise in multiple agile frameworks, including SAFe, Scrum, and Kanban, Lindy has led impactful transformations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, defense, insurance/financial, and federal government. Lindy's exceptional communication, leadership, and problem-solving skills have earned her a reputation as a trusted advisor. Currently associated with KnowledgeHut and upGrad, Lindy fosters Lean-Agile principles and mindset through coaching, training, and successful execution of transformations. With a passion for effective value delivery, Lindy is a sought-after expert in the field.
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
Upcoming Agile Management Batches & Dates
- Product Management Tutorial
- What is Product Management
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Management Process
- General Availability
- Product Manager
- PM Interview Questions
- Courses & Certifications
- Project Management Tutorial
- Agile Methodology
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Software Development Tutorial
- Software Testing Tutorial
Product Planning | Introduction, Purpose, Importance and Steps
Product planning is a crucial aspect of product management, encompassing the strategic act involved in developing and bringing a product to market successfully. It involves a systematic approach to defining, refining, and aligning the product’s features and characteristics with the needs of the target market. This article explores the nuances of product planning, its purpose, steps involved, and the benefits it offers to organizations. Additionally, we’ll search into a comparison between product plans and go-to-market plans, strategies for effective product planning, and the importance of regular revision.

Product Planning
Table of Content
What is Product Planning?
Product plan vs go-to-market plan, purpose of product planning.
Importance of Product Planning
Steps of Product Planning
- Why One Should Regularly Revise Their Product Planning:
- Strategy for Best Product Planning:
- Benefits of Product Planning:
- Example of Product Planning:
- Conclusion:
- Product Planning: FAQs
Product planning, or product management planning, is the iterative process of establishing, refining, working toward, and measuring the key outcomes your product creates for your customers and business. Product planning includes every internally focused choice, action, and job required to create a successful product. Put another way, it includes all of the tasks you must complete that have an impact on the final outcome.

Before searching into the difficulties of product planning, it’s essential to understand the distinction between a product plan and a go-to-market plan. While a product plan focuses on the development and features of the product itself, a go-to-market plan outlines the strategy for bringing the product to market. The product plan details what the product will be, while the go-to-market plan explains how it will be introduced, promoted, and sold.
This table provides a clear comparison of the key aspects and differences between a Product Plan and a Go-to-Market Plan in product management.
The primary purpose of product planning is to align the product with market needs and organizational goals. It serves as a roadmap for product development, guiding teams through the entire life cycle of the product. Product planning ensures that the product not only meets trends customer requirements but also addresses market trends and competitive forces. We can also identify the Advantages and Drawbacks of the Product using Product Planning.
Product planning holds immense importance in the field of product management for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in establishing a clear vision for the product, enabling teams to work cohesively towards a common goal. Secondly, it ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, preventing unnecessary costs and delays. Thirdly, product planning facilitates risk management by identifying potential challenges and addressing them proactively.

- Profit Prediction : Estimates how much money a business expects to make.
- Ensures Profit : Makes sure the business is making enough money to be successful.
- Customer Satisfaction : Ensures customers are happy with the product or service.
- Marketing Program Initiator : Starts marketing activities and plans.
- Effects Marketing Actions : Impacts how well marketing efforts work to attract customers.
Here are the following Steps of Product Planning:
1. Market Research
Conduct deep market research to know customer needs, preferences, and trends. This forms the foundation for the product planning process. Producers and the market research industry use this method to analyse consumers and learn about their demands.
2. Define Goals and Objectives
An objective is a shorter term that specifies quantifiable steps to accomplish a larger goal, a goal is an achievable conclusion that is typically broad and longer term. Clearly deep market research to understand customer needs, preferences, and trends. This forms the foundation for the product planning process.
3. Target Audience Identification
Target audience refers to the specific group of consumers most likely to want your product or service, and therefore, the group of people who should see your advertisement campaigns. Define the target audience for the product. Understanding the demographics, behavior, and preferences of the audience is crucial for successful product planning.
4. Competitor Analysis
A competitor analysis, sometimes called a competitive analysis, is the process of locating rival companies in your market and learning about their various advertising approaches. This information helps in positioning the product effectively in the market.
5. Feature Prioritization
The process of prioritising and allocating features of a product according to customer value, business objectives, time and cost constraints, and technological viability is known as feature prioritisation in product management. Prioritize product features based on their importance to the target audience and the overall business strategy.
6. Development Roadmap
Create a development roadmap that outlines the timeline for different stages of product development. A product development roadmap is designed to track and communicate a product’s development enterprise and mileposts. This roadmap serves as a guide for the entire product team.
7. Testing and Feedback
Incorporate testing and feedback loops throughout the development process. This roadmap serves as a guide for the entire product team.
8. Go-to-Market(GTM) Strategy
Develop a comprehensive go-to-market strategy that includes pricing, distribution channels, marketing, and sales tactics. This strategy ensures a seamless product launch.The purpose of a GTM strategy is to provide a blueprint for delivering a product or service to the end customer, taking into account such factors as pricing and distribution.
Why One Should Regularly Revise Their Product Planning?
Regular revision of product planning is essential to adapt to changing market dynamics, technology advancements, and customer preferences. Markets are Continuously Changing, and what works today may not be effective tomorrow. By revising product plans regularly, organizations can stay agile and responsive, ensuring their products remain relevant and competitive.
Strategy for Best Product Planning
To achieve the best product planning, organizations should adopt a holistic strategy that involves cross-functional collaboration, customer-centricity, and flexibility. This strategy includes

1. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Encourage collaboration between different departments, including product development, marketing, sales, and customer support. This ensures a comprehensive and well-coordinated approach.
2. Customer-Centric Approach
Prioritize customer needs and preferences throughout the product planning process. This approach ensures that the final product resonates with the target audience.
3. Agile Methodology
Embrace an agile methodology that allows for iterative development and quick adaptation to changes. This flexibility is crucial in fast-paced and evolving markets.
4. Data-Driven Decision-Making
Based decisions on data and analytics. Regularly collect and analyze data to gain insights into user behavior, market trends, and the performance of existing products.
Benefits of Product Planning
Here are the following Benefits of Product Planning:

1. Strategic Alignment
Product planning ensures that the product aligns with the overall business strategy, contributing to the organization’s long-term goals.
2. Efficient Resource Allocation
By prioritizing features and setting a development roadmap, product planning helps allocate resources efficiently, preventing unnecessary costs and delays.
3. Risk Mitigation
Identifying potential challenges and addressing them during the planning stage minimizes risks associated with product development and market launch.
4. Customer Satisfaction
A well-planned product is more likely to meet customer needs, resulting in higher satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Competitive Advantage
Thorough market research and competitor analysis provide a competitive edge, allowing organizations to position their products effectively.
6. Clearly Defined and Measurable Outcomes
When you are in need of product discovery and design, it can be easy to lose sight of the outcomes in finding new initiatives, in that case product planning helps you stay on target.
Example of Product Planning
The example of a software company planning to launch a new project management tool. The product planning process involves:
1. Marketplace Studies
Analyzing the project management software market, understanding user preferences, and identifying features that are in high demand.
2. Define Goals and Targets
Setting goals such as becoming a top choice for small and medium-sized businesses, increasing market share by 20%, and achieving a user base of 100,000 within the first year.
Defining the target audience as project managers and teams in small and medium-sized businesses who require a user-friendly and feature-rich project management tool.
Studying competitors in the project management software space to identify unique selling points and areas where the new tool can outperform existing options.
Prioritizing features based on user needs and the identified unique selling points, ensuring a balance between core functionality and innovation.
Creating a development roadmap that includes key milestones such as alpha and beta releases, user testing phases, and the final product launch.
Incorporating user testing and feedback loops during the development process to refine features and address any usability issues.
8. Go-to-Market Strategy
Developing a comprehensive go-to-market strategy, including pricing models, marketing campaigns, partnerships with influencers, and a strategic rollout plan.
In conclusion, product planning is a fundamental aspect of product management that plays a pivotal role in the success of a product. By following a systematic approach, organizations can align their products with market needs, efficiently allocate resources, and gain a competitive advantage. Regular revision of product plans is crucial in adapting to changing market conditions, and important strategy involving cross-functional collaboration, customer-centricity, and agility enhances the effectiveness of product planning. Ultimately, effective product planning contributes not only to the success of individual products but also to the overall growth and sustainability of the organization.
Frequently Asked Questions on Product Planning: FAQ’s
What are the 4 p’s of product planning.
The 4 P’s of product planning, namely Product, Price, Place, and Promotion, form the foundation of marketing strategy
What are the 5 steps to production planning?
The five steps to production planning include forecasting demand, determining production objectives, planning production capacity, scheduling production activities, and monitoring and controlling production processes to ensure efficiency and meet customer demands effectively.
What are the 4 elements of planning?
The four elements of planning typically include setting objectives, identifying tasks, allocating resources, and establishing timelines to achieve desired goals efficiently and effectively. These elements are fundamental in guiding organizational efforts toward successful outcomes and strategic alignment.
What is the scope of PPC?
PPC, or Pay-Per-Click advertising, involves placing ads on search engines and websites where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It aims to drive targeted traffic to websites and increase conversions, making it a key strategy in digital marketing campaigns.
Similar Reads
- Geeks Premier League
- Product Management
- Geeks Premier League 2023
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Product Planning: What is it & How to do it? (Process & Steps)
There has never been a perfect recipe for managing and developing a successful product. Having a skilled product manager and the right resources are only the ingredients that help you make your product a great market dish.
But, product planning is like the process of cooking everything in a way, that you get the expected taste out of it!
In other words, product planning is the essence of product management that entails managing a product throughout its life, which contributes to a company’s growth with increased productivity.
“Proper planning and preparation prevents poor performance.” ― Stephen Keague
However, effective product planning is a complex process that covers thousands of factors transforming the initial idea and a wide range of activities to ensure suitable end results!
In this article, we will define the role of product planning in product management, its importance, best practices, and the process- step by step!
Let’s dig in!
What is Product Planning? (Definition)
Product planning is the process of identifying and creating a new product idea with all product-related requirements such as its features, price, promotion, distribution, etc.
Product planning aims to align the assets of the business and operational factors, to focus on product development, design, and engineering efforts.
Its purpose of it is to deliver the greatest probability of success in achieving business goals through effective product strategy.
The Importance of Product Planning:
Product planning is an indivisible part of every product’s implementation journey. It allows for secure product development as it helps to gauge possible risks and threats.
Project managers use the assumptions of product planning in their work to achieve best practices and outcomes.
Furthermore, product planning is beneficial for:

1. Better Customer Service
Product planning through work management and proper scheduling helps in providing better support to customers in terms of quality goods at reasonable costs as per the promised delivery timeline.
Proper product quality and delivery are an integral part of product planning that wins the confidence of customers, promotes profitable repeat orders, and improves relations with customers.
Read more: How to Create an Agile Product Roadmap?
2. Better Control on Inventory
A sound system of product planning and control helps in managing inventory at proper levels and, thereby, reduces investment in inventory.
It requires a minimum inventory of work-in-progress and lower finished stock to give efficient customer support. Product planning also helps in exercising better control over raw materials, which contributes to more effective purchases.
3. Optimum Resource Utilization
When a product is planned, it results in the effective and appropriate utilization of available resources and inputs which go into the production process.
Avoiding wastage of available resources and optimum use of required resources is one of the benefits of product planning.
4. Good brand Image
A good product makes a happy customer! And, happy customers and brand loyalty go hand in hand!
For a great product, companies need a proper system of product planning that helps in keeping everything systematized.
Such a company is in a position to meet its orders in time, making its customers happy. This leads to customer loyalty, increased profits, increased sales, industrial harmony, and ultimately a good brand image of the business.
Read more: What is Product Adoption & How to do it Right?
Step by Step Process of Product Planning:
Product planning presents a much larger view of the management and technical side of a product-based business which includes all of the moving parts from inception to exit.
Here are the key steps of product planning that you should go through when building out a new product:
1. Define the product concept
This is the most crucial step in your business that pivots and defines what you are trying to build as a product. Jot down this stage and ensure your idea for the product is a real idea.
Another part of the product concept is making sure you have a firm knowledge of the upcoming problems based on your strong understanding of the solutions needed.
2. Add details of your market research
Not all successful product ideas are successful business ideas. Once you have walked into the first step and have an idea or concept that solves a real problem, now it is time to do some market research.
During this stage of product planning, you need to prove that your idea has a market to sell.
This includes studying your competition, analyzing their weaknesses & strengths against yours, and finding out the niches where your product can have an advantage over your competitors.
3. Plan your product testing process
If your product planning has crossed step 1, step 2 of building a concept and confirming that there is a place in the market for your product, the next step is to build the MVP (Minimum Viable Product), so you can put a real-life product in front of customers or users for them to look at, test and provide feedback on the product.
4. Write product maturity details
After the launch, you need product maturity. This is where the product roadmap merges with the product planning.
A product roadmap will help you with smooth working on building out your product teams, pricing changes, and infrastructure, as you add more features and overall sales and marketing approaches.
5. Explain the product life cycle
The process of product planning does not stop with a product launch. It should also include managing the product throughout various stages of its product life-cycle.
During the initial growth phase, competition is usually low while sales are strong. However, with time, competitors will come up with their own products. So, having a constant life cycle in product planning will maintain the balance!
Read more: What is a Product Requirements Document & How to Create One Effectively?
3 Best Practices in Product Planning
As product planning is a very broad concept, there are a lot of ways as to how you can make it perfect:
Agile Product Planning
Easy product management methodologies can be applied to product planning and as we discussed above. There are three stages of agile product planning :
- Vision : This vision is what the goals and objectives represent, a common goal that all can work towards, and isn’t specifically about any particular product.
- Product Strategy: This is about how the objectives will be achieved, including identifying the target group, their demands, the benefits of the product offered to the target group, and to the business itself.
- Product Tactics : This level focuses on the basics of functionality, design, user interaction, and sprint goals.
Know your Audience
You can plan a product that design, management, and sales teams love. But if the customer or end-user is not pleased, the product will land with a thud.
That is why you need to be clear from the start on all customer demands. If you lack the opportunity to talk to them directly, ensure you work closely with your internal stakeholders who speak on their behalf.
This will help you to see different product plans that show relevant information from the audience’s point of view. You can then do product planning without worrying about results or customer acceptance.
Use a Product Management & Roadmapping Tool
Using software to plan out the product planning processes and their levels is an excellent way to make sure that everything is flowing in the right direction. In the past, product planning would be done on paper or on some generic software such as MS Word.
Today, however, there are multiple options for visual product mapping. These tools allow for a lot more customization, putting the product roadmap document right at the center of the business! In fact, over 50% of product managers will rely on product road mapping and management tools to improve communication and planning with IT and business stakeholders, by 2022.
One such product management software that is trusted by organizations and professionals in over 100+ countries is Bit.ai!
Why Create a Product plan in Bit.ai ?
It is the dream tool to help teams transform the planning process, by making it interactive and collaborative. Cool, right?
Here are some of the main benefits of using Bit:
- Organized workspaces and folders – Bit brings all your project management documents and details in one place by allowing you to organize information in workspaces and folders. Workspaces can be created around projects, operations, departments, and fields. Everyone added to a workspace can access and collaborate on its content. Inside each workspace, you can create an unlimited number of wikis and access your content library.
- Content library – Bit has a content library at the workspace level where you can store and share assets. You can save images, files, and content easily and can access it at any point.
- Rich embed options – Bit.ai integrates with over 100+ web applications (Ex: YouTube, PDFs, LucidChart, Google Drive, etc.) to help you weave information in their wikis beyond just text and images.
- Smart search – Bit has very robust search functionality that allows anyone to find information quickly. You can search for folders, files, documents, and content inside your documents across all of your workspaces.
- Interlink documents – Bit allows employees to create unlimited documents and interlink them to create wikis that expand the knowledge base. Simply highlight the words and you have the option to create a new document.
- Permission & sharing access – Bit supports features like document tracking, cloud upload, templates, document locking, document expiration, password protection, etc. Also, Bit docs can be shared in 3 different ways- Trackable links, Live embeds, and live state!
To make the process easier and fun, Bit offers a ready-made Product roadmap template for you! Check it out: Product Roadmap Template by Bit
Bottom line!
Good product planning lays the foundation for successful product management!
It exhibits the basis for cross-functional teams to plan, develop, and introduce their product in the market, and it ensures that product managers identify the appropriate target customers and niche industries prior to reaching the product planning stages.
Do you use a tool to optimize your product management plan? If yes, share your experience in the comments section below. Cheers!
Further reads:
Top SaaS Products for Small Businesses in 2022
Product Mix: Definition, Dimensions, Importance & Examples!
Software Product Development: Definition, Types, Methodologies & Process!
How To Create Product Launch Marketing Documentation
Product Development Process: Definition & Key Stages!
How to Create a Product Plan the Right Way?
How to Create an Effective Operational Plan for Your Business?

Client Portals: Communicate with Clients the Right Way!
Top 10 Benefits of Teamwork You Must Know!
Related posts
Portfolio: what is it & how to create an impressive one, 11 benefits of team building you need to know, 6 best talent management systems & software in 2023, what is google docs and how to use it, growth mindset: how to develop it for better future, best cloud document management systems in 2024.

About Bit.ai
Bit.ai is the essential next-gen workplace and document collaboration platform. that helps teams share knowledge by connecting any type of digital content. With this intuitive, cloud-based solution, anyone can work visually and collaborate in real-time while creating internal notes, team projects, knowledge bases, client-facing content, and more.
The smartest online Google Docs and Word alternative, Bit.ai is used in over 100 countries by professionals everywhere, from IT teams creating internal documentation and knowledge bases, to sales and marketing teams sharing client materials and client portals.
👉👉Click Here to Check out Bit.ai.
Recent Posts
The importance of documentation for business success, crafting engaging newsletters with the help of bit.ai, idea generation: how bit.ai sparks creativity, hospitality document template collection for efficient management process, healthcare document template collection: simplify your medical administration tasks, top 20 event management document templates for 2024.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- my-task icon Admin and security
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all use cases arrow-right icon

- Help Center
- Asana Academy
- Certifications
- Work management hub
- Customer stories
- Get support
- Developer support
- Customer Success
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Product development process: The 6 stag ...
Product development process: The 6 stages (with examples)

The product development process is a six-stage plan that involves taking a product from initial concept to final market launch. This process helps break down tasks and organize cross-departmental collaboration. Find out how to implement a process of your own.
Product development is both an exciting and difficult endeavor. From initial ideation to research and prototyping, no two product launches are the same. However, there’s a general process that can help you get started with the product development process.
The product development process describes the six steps needed to take a product from initial concept to final market launch. This includes identifying a market need, researching the competition, ideating a solution, developing a product roadmap, and building a minimum viable product (MVP).
The product development process has evolved in recent years and is now commonly used by dividing each step into six separate phases. This helps better organize the process and break individual deliverables into smaller tasks.

Effective sprint planning templates
Optimize your sprint planning process with Asana's customizable templates. Streamline task management, improve team collaboration, and deliver projects on time.
What is product development?
Is product development the same as product management.
Though they sound almost identical, there's an important difference between product development and product management. Product development describes the process of building a product, where product management is the overseeing of that work. It's a slight difference, but an important distinction. A product manager, who often oversees a team that is in the product development process, will lead product management.
The 6 stages of product development
Not only does the product development process help simplify a launch, but it also encourages cross-team collaboration with teamwork and communication at the forefront of the process.
Let’s dive into the product life cycle and define the six product phases. All of which can help you successfully launch your next product.
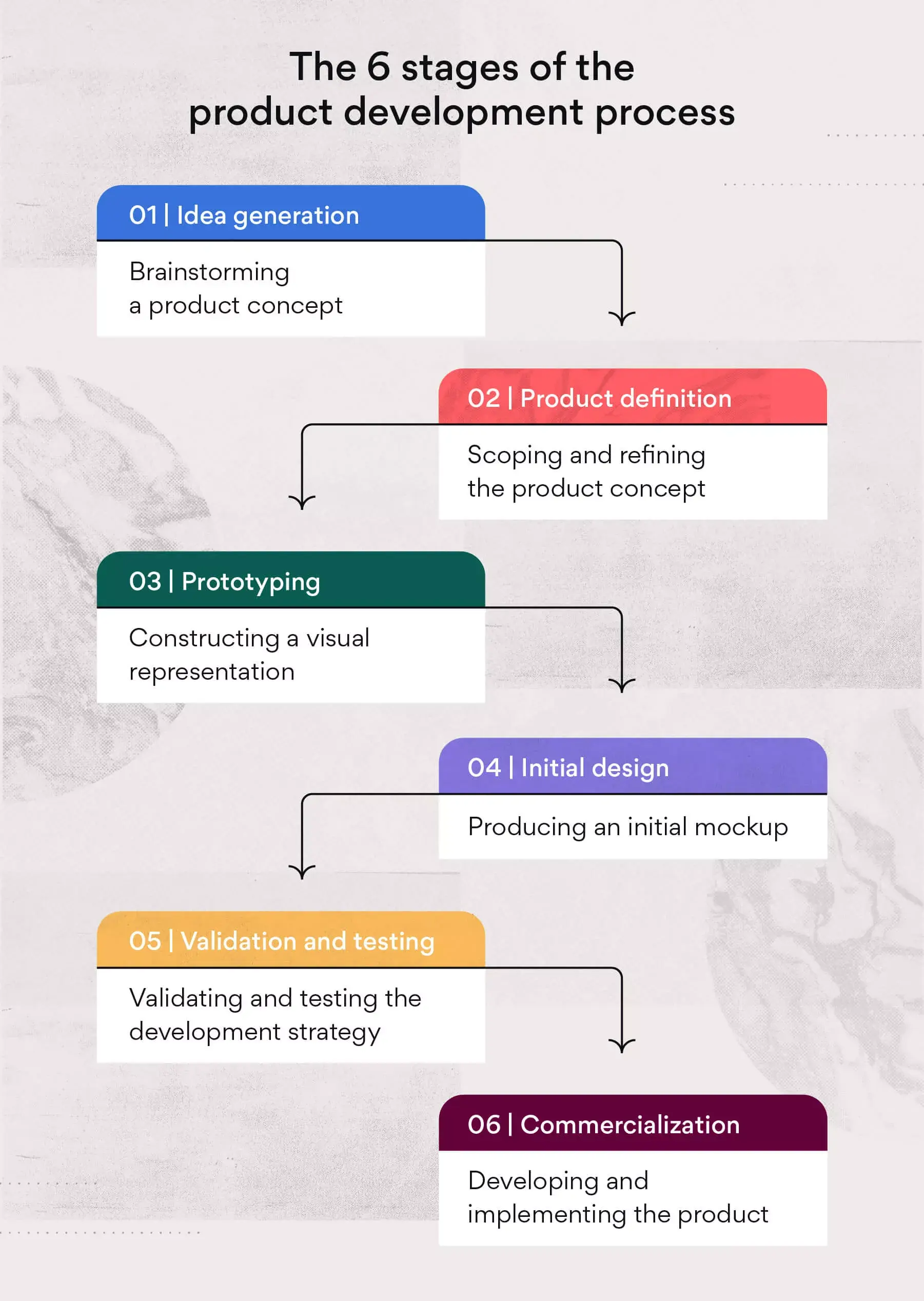
1. Idea generation (Ideation)
The initial stage of the product development process begins by generating new product ideas. This is the product innovation stage, where you brainstorm product concepts based on customer needs, concept testing, and market research.
It’s a good idea to consider the following factors when initiating a new product concept:
Target market: Your target market is the consumer profile you’re building your product for. These are your potential customers. This is important to identify in the beginning so you can build your product concept around your target market from the start.
Existing products: When you have a new product concept, it’s a good idea to evaluate your existing product portfolio. Are there existing products that solve a similar problem? Or does a competitor offer a product that doesn’t allow for market share? And if yes, is your new concept different enough to be viable? Answering these questions can ensure the success of your new concept.
Functionality: While you don’t need a detailed report of the product functionality just yet, you should have a general idea of what functions it will serve. Consider the look and feel of your product and why someone would be interested in purchasing it.
SWOT analysis : Analyzing your product strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats early in the process can help you build the best version of your new concept. This will ensure your product is different from competitors and solves a market gap.
SCAMPER method : To refine your idea, use brainstorming methods like SCAMPER , which involves substituting, combining, adapting, modifying, putting to another use, eliminating, or rearranging your product concept.
To validate a product concept, consider documenting ideas in the form of a business case . This will allow all team members to have a clear understanding of the initial product features and the objectives of the new product launch.
2. Product definition
Once you’ve completed the business case and discussed your target market and product functionality, it’s time to define the product. This is also referred to as scoping or concept development, and focuses on refining the product strategy.
During this stage, it’s important to define specifics including:
Business analysis: A business analysis consists of mapping out distribution strategy, ecommerce strategy, and a more in-depth competitor analysis. The purpose of this step is to begin building a clearly defined product roadmap.
Value proposition: The value proposition is what problem the product is solving. Consider how it differs from other products in the market. This value can be useful for market research and for developing your marketing strategy.
Success metrics: It’s essential to clarify success metrics early so you can evaluate and measure success once the product is launched. Are there key metrics you want to look out for? These could be basic KPIs like average order value, or something more specific like custom set goals relevant to your organization.
Marketing strategy: Once you’ve identified your value proposition and success metrics, begin brainstorming a marketing strategy that fits your needs. Consider which channels you want to promote your product on—such as social media or a blog post. While this strategy may need to be revised depending on the finished product, it’s a good idea to think about this when defining your product to begin planning ahead of time.
Once these ideas have been defined, it’s time to begin building your minimum viable product (MVP) with initial prototyping.
3. Prototyping
During the prototyping stage, your team will intensively research and document the product by creating a more detailed business plan and constructing the product.
These early-stage prototypes might be as simple as a drawing or a more complex computer render of the initial design. These prototypes help you identify areas of risk before you create the product.
During the prototyping phase, you will work on specifics like:
Feasibility analysis: The next step in the process is to evaluate your product strategy based on feasibility. Determine if the workload and estimated timeline are possible to achieve. If not, adjust your dates accordingly and request help from additional stakeholders.
Market risk research: It’s important to analyze any potential risks associated with the production of your product before it’s physically created. This will prevent the product launch from being derailed later on. It will also ensure you communicate risks to the team by documenting them in a risk register .
Development strategy: Next, you can begin working through your development plan. In other words, know how you’ll be assigning tasks and the timeline of these tasks. One way you can plan tasks and estimate timeline is by using the critical path method .
MVP: The final outcome of the prototyping stage is a minimum viable product. Think of your MVP as a product that has the features necessary to go to launch with and nothing above what’s necessary for it to function. For example, an MVP bike would include a frame, wheels, and a seat, but wouldn’t contain a basket or bell. Creating an MVP can help your team execute the product launch quicker than building all the desired features, which can drag launch timelines out. Desired features can be added down the road when bandwidth is available.
Now it’s time to begin designing the product for market launch.
4. Initial design
During the initial design phase, project stakeholders work together to produce a mockup of the product based on the MVP prototype. The design should be created with the target audience in mind and complement the key functions of your product.
A successful product design may take several iterations to get just right, and may involve communicating with distributors in order to source necessary materials.
To produce the initial design, you will:
Source materials: Sourcing materials plays an important role in designing the initial mockup. This may entail working with various vendors and ordering materials or creating your own. Since materials can come from various places, you should document material use in a shared space to reference later if needed.
Connect with stakeholders: It’s important to keep tight communication during the design phase to verify your initial design is on the right track. Share weekly or daily progress reports to share updates and get approvals as needed.
Receive initial feedback: When the design is complete, ask senior management and project stakeholders for initial feedback. You can then revise the product design as needed until the final design is ready to be developed and implemented.
Once the design is approved and ready to be handed off, move onto the validation phase for final testing before launching the product.
5. Validation and testing
To go live with a new product, you first need to validate and test it. This ensures that every part of the product—from development to marketing—is working effectively before it’s released to the public.
To ensure the quality of your product, complete the following:
Concept development and testing: You may have successfully designed your prototype, but you’ll still need to work through any issues that arise while developing the concept. This could involve software development or the physical production of the initial prototype. Test functionality by enlisting the help of team members and beta testers to quality assure the development.
Front-end testing: During this stage, test the front-end functionality for risks with development code or consumer-facing errors. This includes checking the ecommerce functionality and ensuring it’s stable for launch.
Test marketing: Before you begin producing your final product, test your marketing plan for functionality and errors. This is also a time to ensure that all campaigns are set up correctly and ready to launch.
Once your initial testing is complete, you’re ready to begin producing the final product concept and launch it to your customer base.

6. Commercialization
Now it’s time to commercialize your concept, which involves launching your product and implementing it on your website.
By now, you’ve finalized the design and quality tested your development and marketing strategy. You should feel confident in your final iteration and be ready to produce your final product.
In this stage you should be working on:
Product development: This is the physical creation of your product that will be released to your customers. This may require production or additional development for software concepts. Give your team the final prototype and MVP iterations to produce the product to the correct specifications.
Ecommerce implementation: Once the product has been developed and you’re ready to launch, your development team will transition your ecommerce materials to a live state. This may require additional testing to ensure your live product is functioning as it was intended during the previous front-end testing phase.
Your final product is now launched. All that’s left is to measure success with the initial success metrics you landed on.
Product development process examples
Now that you understand the six stages of the product life cycle, let’s look at real world examples of some of the most successful product development strategies of iconic startups to inspire your own.
Example 1: How Figma expanded their product features
Originally started in 2012, Figma was the first professional-grade UI design tool built entirely in the browser. Today, Figma has grown into the leading competitor for design web applications.
Their mission is to make design accessible to more people and help them bring their creativity to life. They’ve shown this by continuously adding new product features—like multiple flow capabilities, a brainstorming timer, and an interactive whiteboard—coordinating successful software releases, and building trust through transparency.
Read our case study to learn how Figma uses Asana to manage development backlogs.
Example 2: How Uber solved a market gap
While today we think of Uber as the biggest ride-sharing service, that wasn’t always the case. They too started with a compelling product strategy that made them into the innovative company they are today.
Uber’s strategy began by solving a gap in the existing taxi industry: creating an easier ride-hailing process with simplified payment processing. But they didn’t stop there: they continued to innovate their product portfolio by developing ride tiers ranging from luxury to budget-friendly.
While each situation varies slightly, with the right product strategy, you too can create an innovative portfolio.
Who is part of the product development team?
There are many stakeholders and various teams that assist with the product development process. The main leader is the product manager, who oversees all product tasks related to ideation, research, development, and product launch.

Additional important stakeholders include:
Product management: A product manager oversees all areas of the product life cycle and works to bridge communication gaps between various internal and external teams. The product manager works to initiate new product launches and initiates product ideation and market research.
Project management: A project manager may be involved in the product development process to assist with cross-departmental communication. They might also assist with task delegation and goal tracking.
Design: The design team helps during the prototyping and designing phase to support the visual product concept. It’s important to connect product designs with brand guidelines and UX best practices.
Development: The development team helps with the implementation of the product on your website. Most commonly, a team of developers will work together to build the new product offering depending on the complexity of the concept.
Marketing: The marketing team will assist with developing the marketing strategy and testing it before the product goes live. They will also measure the success of the marketing initiatives.
Sales: The product manager works with the sales team to come up with an effective strategy and report on success metrics after the product has been implemented.
Senior management: Senior stakeholders may need to give final approval before the product can go to launch.
In addition to these important roles, other teams that may be involved are finance, engineering, and any other related stakeholders. All of which can play a role in the process depending on the complexity of the concept.
The process that simplifies product development
The right product development process can help you streamline each step with organized tasks and team collaboration. The six stages outlined above will get your team through all steps of the process, from initial idea screening to the development phase.
But you might need help along the way. Coordinate tasks and organize your product development process with Asana for product management . Asana can help get your products to market faster by tracking workload and simplifying planning.
Related resources
What is a product backlog? (And how to create one)
User stories: 3 examples to drive user value

Everything you need to know about requirements management
Waterfall, Agile, Kanban, and Scrum: What’s the difference?
Product Management
What is Product Planning and How to Master It?
Created on:
September 9, 2024
Updated on:
September 4, 2024
10 mins read

Transform Insights into Impact
Build Products That Drive Revenue and Delight Customers!
Developing ideas into a successful product requires a great deal of effort. It is a journey that requires the right direction and involves teamwork. Product planning provides you with a framework to create a clear roadmap for taking a product from ideation to deployment.
Without a well-defined product plan, it gets difficult to channel product development. Eventually, brilliant ideas go bad and resources are wasted.
In this article, we'll go over what product planning is and how you can use it to ensure your product's success.
What is Product Planning?
Product planning is a systematic process of developing a product. It encompasses activities to guide every step of product development — from ideation to launch through market research, design, development, and pricing.
The purpose of product planning is to help you create successful products by making sure a product resonates with users and fulfills business objectives.
Product planning does not involve external processes of product development such as market launch and go-to-market plan. However, it is a continuous process involved in strategy decisions pertaining to product issues and requires careful thinking and dynamism.
Why is Product Planning Important?
46% of products fail as a result of poor product planning whereas a well-developed product plan increases the chances of success by 129% .
Here are the key points suggesting the importance of product planning:
- Understand the Market: By using planning, you can gain a deeper understanding of customer preferences, market demands, and competition dynamics. This knowledge enables the development of products that satisfy actual customer demands and stand out in the marketplace.
- Align Strategies: It ensures that the product aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization. This reduces wasted time , effort and resources.
- Manage Risks: You can create plans to reduce risks by recognizing potential risks and obstacles early in the planning stage. This proactive strategy decreases the likelihood of costly complications during development or launch.
- Set Clear Goals: Planning helps in developing a roadmap with clear goals and milestones. This clarity allows teams to stay focused, track progress, and make informed product decisions throughout the product's entire lifecycle. It also facilitates in directing available resources and efforts toward the most important tasks to manage risks.
- Optimize Resources: Well-thought-out planning makes it easier to distribute resources — like time, money, and talent — in a more effective manner. It also keeps resources from being wasted and makes sure they are put to use where they will yield the highest returns.
- Enhance Collaboration: A product plan creates a central source of truth to improve cross-team communication and collaboration, avoid conflicts in a team, and ensure product quality with standardized and transparent operations.
7 Strategic Phases Involved in the Project Planning Process
Product planning process is correspondence to the product development lifecycle. It comprises seven important phases designed to ensure the success of the product. Each phase is critical for moving your product from concept to completion.

1. Product Concept Development
This is the starting point for your product journey. The product concept development phase focuses on brainstorming and defining your idea. Begin by identifying market needs. What problem does your solution solve? Then you lay out the important aspects that will differentiate your product. Also, now is the ideal moment to clearly define your product's vision, laying the groundwork for all subsequent phases.
2. Competitive Analysis
After developing a concept, it's important to evaluate the competitive landscape. This involves investigating existing solutions to find out what's available. You need to identify market gaps and opportunities for differentiation. By framing your product uniquely, you can refine your value proposition and stand out in a congested market.
3. Market Research
After defining your concept and getting a competitive edge, you need to conduct market research to understand your target audience, market trends, and potential demand. This collected information helps you validate your product concept during the design and development phases.
4. Minimum Viable Product Development
Now is the time to bring your concept to life. Develop a basic version of your product that focuses on core features. This MVP lets you demonstrate the product's market viability. Collect customer feedback to iteratively enhance your product before launching.
5. Introduction and Launch
In the launch phase, you introduce your product to the world. Plan your launch strategy, including marketing, distribution, and rollout plans. The goal here is to create market awareness and promote initial adoption, thereby setting your product up for success.
6. Product Lifecycle Management
Product management begins after the initial development and includes what is done with a product after its release. You need to monitor performance, address issues, and make necessary changes. This ongoing phase keeps your product relevant in the market and offers solutions to customer's problems.
7. Sunset Phase
Nothing lasts forever and the same can be said for each and every product. The final stage consists of planning its discontinuance and the ending of its production, inventory management, and steering customers to the alternatives. The final phase also retains the loyalty of the customer even when the product is discontinued.
To create a comprehensive product plan, you need a tool which helps you gather your end-customers expectations and involve key stakeholders of the organization during planning.
Zeda.io is product planning software that helps you gather Voice of the Customer and create insights out of it to create an effective product plan. It pulls GTM data, user interviews, surveys, product analytics, and more into one dashboard to build roadmaps for success.
Sign up for free and start building impactful roadmaps that drive real business outcomes!
Common Challenges in Product Planning Process and How to Overcome
Product planning is not simple, especially when you're trying to handle multiple tasks and priorities. Here are some common challenges and how you can overcome them:

Aligning Stakeholder Expectations
When there are multiple stakeholders, it is difficult to avoid a situation when they have different visions of product development. You need to facilitate open communication among them and establish attainable shared goals. Also, update regularly and include the stakeholders in the important decisions to keep everyone on track.
Adapting to Market Changes
The market is ever-changing, and as such, your product plans need to change as well. You need to stay flexible, in addition to the monitoring of the market trends to pivot whenever necessary. Be ready to reassess and adjust your product strategy in order to compete with others.
Resource Allocation
Budgets and resources are often limited, so you need to manage them wisely. Set priority to tasks that offer the highest value and ensure your team is focused on what matters most. Effective planning and regular reviews can prevent resource bottlenecks.
Tips for Effective Product Planning
Effective product planning is essential for successful development of a product. Here are some tips to help you plan your product efficiently:
Leverage Agile Methodologies
Embrace agile methods like Scrum or Kanban to keep your product planning flexible and responsive. With an iterative approach, you can adapt to changes quickly and integrate feedback into your process efficiently. You can start by implementing sprints and reviewing the progress regularly.
Collaborate Across Teams
The cross-functional collaboration aligns everyone's efforts toward a common goal. Open communication and regular check-ins bridge gaps between team members. You can use collaboration tools like ProofHub to keep everyone on the same page.
Prioritize Features and Enhancements
Focus on what matters most by prioritizing features based on user feedback and business goals. You can use frameworks like MoSCoW or Kano to make informed decisions. This makes sure that you're building the right things at the right time.
Continuously Learn and Improve
Staying updated with industry trends allows you to refine your planning process. You can attend webinars, read industry blogs, and seek feedback from your team to keep improving.
Use Product Management Tools
Product management tools like Zeda.io let you streamline your planning process. From road mapping to task management, choose tools that can help you at each stage of development and ensure everything runs smoothly.
A well-defined product planning process lays the foundation for turning ideas into a viable and successful product. It creates the clear path for growth and innovation. Planning not only entails having a plan or a schedule that needs to be followed but also closely adapting to changes along the way.
Effective planning increases your chances of attaining your goals and minimizing risks. With a solid product plan, you can create something that will resonate with your customers and stand out in the market.
Author Bio:
Meet Sandeep Kashyap, the CEO of ProofHub who is transforming project management and team collaboration with his innovative solutions. With an unwavering passion for leading his team to success, Sandeep's mantra is simple - "keep growing, don't stop". When he's not busy at work, Sandeep loves to explore new destinations and challenge himself with trekking adventures.
Join Product Café Newsletter!
Sip on the freshest insights in Product Management, UX, and AI — straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, I agree to receive communications by Zeda.
What are the 4 P's of product planning?
The 4 P’s of product planning are product, price, place and promotion. These P’s focus on what a product is, determines its cost, how it will be distributed and how to create awareness and encourage sales.
What are the 4 A's of a product?
The 4 A's of a product influence its success in the market. These essential factors include acceptability, affordability, accessibility, and awareness.
What are the basic components of product planning?
The basic components of product planning are product innovation, product diversification, product standardization, and product elimination.
IN THIS ARTICLE:
Latest articles

Choosing the Best Product Discovery Tool: Top 5 Picks
Discover the perfect product discovery tool for your needs with our top 5 picks and maximize user feedback.

Product Adoption: Everything You Need to Know in 2024
This blod discusses the importance of product adoption, the various stages and processes involved, key metrics for measuring success, and effective strategies and tools to boost adoption rates.

Product Ideation Process & 8 Effective Techniques for Your Team
Discover 8 customer-centric product ideation techniques that will help your team always come up with ideas.
AI-powered product discovery for customer-focused teams
Product Planning: What It Is, Benefits, & Common Mistakes
Product planning is an iterative process to develop products. Here’s why it matters + mistakes to avoid.

Excellent products don’t appear out of thin air.
Even the simplest, most intuitive products were meticulously planned by a product manager and product team who developed an intimate understanding of their customers and the target market.
This guide walks you through what product planning is, why it’s important, common mistakes product teams make, and how to avoid them to create a better product. We also look at how Contentsquare’s tools help bring your product plan to life.
Product planning is an iterative process that involves establishing, refining, working towards, and measuring key outcomes for your customers and business
Product planning is essential to your team because it defines measurable outcomes, aligns teams, provides context to stakeholders, manages technical debt, and prioritizes research and analysis
Five core elements of product planning include
Knowing your customer
Understanding market opportunities
Analyzing the competitive landscape
Identifying product outcomes
Executing the product development process
Planning too far ahead is a common mistake when product planning. Other common product planning mistakes include planning in a silo, relying on assumptions, and focusing more on outputs than outcomes.
Your all-in-one platform for the right digital experience
Drive engagement, conversion, and retention across your digital assets with complete understanding of your customer experience.
- Get a demo Get a demo
What is product planning?
Product planning, or product management planning, is the iterative process of establishing, refining, working toward, and measuring the key outcomes your product creates for your target customers and business.
This includes
Conducting research to identify the outcomes that best define success for your customers and business goals
Discovering the elements, features, and functionality your product must contain to achieve these outcomes and
Identifying processes and measurements to take the product from ideation to execution
Remember : the goal of planning isn’t to produce a perfect plan, but to engage in continual learning that guides your team to create a product your customers will love.
What product planning isn’t
To truly understand what product planning is , you also need to understand what it is not .
Product planning isn’t
A meticulous roadmap outlining features, requirements, and deadlines
An excuse to constantly shift outcome goals or
A yearly or quarterly event to give your team a false sense of certainty
Product planning is often confused with project planning, but where project planning is all about outputs and deadlines, product planning is about outcomes and iteration.
Product planning can also be confused with product strategy and product discovery.
But while these terms and concepts are overlapping and connected, their purposes are distinct:
Note : product market research is a key activity that spans planning, strategy, and discovery. This is because understanding the customer’s needs is at the heart of the essential work of a product team. Contentsquare is a pivotal tool for product teams to turn learnings about customers into real product experience insights that can inform the product planning process.
Why is product planning essential for your product team?
Product planning is a mindset and a commitment to a way of working rather than something product teams occasionally do. Adopting this mindset aligns teams around key outcomes that define success for both the customer and the business.
Benefits of product planning
Clearly defined and measurable outcomes.
When you're in the thick of product discovery and design, it can be easy to lose sight of the outcomes in pursuit of shiny new initiatives—but continual product planning helps you stay on target.
A unified, outcomes-oriented product team
Every healthy team will have disagreements throughout the decision-making process when product planning. A commitment to continuously planning product improvements helps teams focus on key outcomes, creating alignment on team decisions.
Stakeholders who understand every decision
Product planning gives your team a powerful answer to why you’ve made certain decisions around product and feature development. By showing stakeholders exactly how users interact with your product, tools like Contentsquare’s Heatmaps give everyone involved a visual representation—and solid proof—of the improvements that need to be prioritized next.
Managing technical debt
Teams that continually engage in product planning will also continually measure progress against the most important outcomes instead of focusing solely on building new features.
Ongoing measurement of feature adoption and performance measurement creates space for managing technical debt—a buildup of low code quality that makes code difficult to modify for new features—and brilliantly prioritizing your product backlog .
Prioritizing research and analysis
A continual process of product management planning keeps your team focused on measurable outcomes that prioritize research and analysis. Tools like Contentsquare’s Session Replay give a clear picture of how your users feel and what they need, helping you build your case with user data.
Uncovering and fixing issues fast
Product bugs and blockers are easy to miss when your team isn't focused on product planning. In the planning stage, ongoing user behavior and experience insights—from tools like Contentsquare—help you understand the user experience and fix issues fast.
Avoiding recency bias
Recency bias is when teams divert their attention to solve a recently discovered (but less important) problem before solving more pressing issues.
This is one of the most distracting forms of bias and regular product planning prevents teams from focusing on the outcomes that matter most.
5 core elements of effective product planning
While product planning isn’t necessarily a linear process, certain elements will drive your team to success:
1. Knowing your customer
Every element in the product development process ultimately centers around your customer. Understanding the customer—their motivations, behavior, and goals—is absolutely necessary to provide them the most value. It’s also a critical part of establishing the right outcomes for your team.
Use Contentsquare’s Voice of Customer to collect feedback and create Surveys to give your team a constant source of customer feedback.
Capturing user feedback while they engage with your product is the best way to learn how they are (or aren’t) experiencing value.
2. Understanding the market opportunity
A constraint for many people in product is that, ultimately, products created for users also have to produce valuable outcomes for the business. That’s why product planning must involve identifying and creating a strong value exchange between the company and the user. A grasp of market dynamics, trends, and opportunities is essential to produce products and features that serve your customers and your business.
3. Analyzing the competitive landscape
Another constraint in identifying key outcomes is understanding how customers are currently solving their problems. Your solution must be significantly better than their current alternative for customers to adopt it. Your product planning process should also consider the value competitors offer and how your ideal outcomes will produce substantially greater value.
4. Identifying product outcomes
Once you have a solid grasp of your customers’ wants and needs, market trends, and the competitive landscape, you can focus on the outcomes that make both your customers and the business successful. Remember: outcomes are specific and measurable through metrics, so it must be clear how achieving them will result in success for the business.
Common outcomes for successful products include increased acquisition, retention , revenue, and a lower cost of acquisition.
5. Executing your product development process
Once you’ve identified the outcomes your team will aim for, you’re ready to execute your product development process and turn the product opportunity into a reality.
At this point, your plan is less a linear set of steps and more a process of continual learning and iteration to achieve your identified outcomes.
During this process, use tools like Contentsquare’s Surveys to collect continuous feedback and learn what users think about your latest plans before putting them into action. Designing surveys helps your team be proactive in asking customers about additional problems and discovering new opportunities.
5 common mistakes in product planning (and how to avoid them)
Product planning is a complex process with lots of moving parts and mistakes are inevitable. To set you on the right track from the start, here’s a list of the most common mistakes and tips on how to steer clear of them.
1. Treating planning as a single event rather than an ongoing process
The mistake : treating planning as an event prioritizes the plan over planning . A plan is just a snapshot of your understanding—of the product, market, and customer needs—at the time the plan was created, which means it becomes obsolete very quickly.
How to avoid it : schedule regular strategic planning sessions and continuously collect user feedback to emphasize the process over the snapshot.
2. Planning too far into the future
The mistake : sometimes teams plan months or years into the future, assuming their users, the market, and their competitive landscape will be the same forever (which is never the case).
How to avoid it : stick to a timeframe in which you can reasonably take action and deliver value. Instead of planning major changes for the future, focus on small, iterative changes with product analytics tools like Contentsquare that enable you to test changes and collect feedback in tandem.
3. Planning in a silo
The mistake : some product teams don’t work closely alongside other business units. But because product planning requires a broad understanding of customers, the market, and competitors, it’s impossible to succeed in a silo.
How to avoid it : have team members and key stakeholders participate in product planning discussions to get their unique insights and help them feel more invested in your direction and outcomes.
4. Relying on too many assumptions
The mistake : basing product decisions on assumptions and guesswork is a waste of your team's and users' time. Without an understanding of why users are interacting with your product in a certain way, teams risk prioritizing issues that don't exist (and neglecting those that do).
How to avoid it : put effort into learning about customers and the market to gain data-informed insights. Tools like Contentsquare minimize roadblocks later down the line, ultimately helping you reduce assumptions and prevent those pesky pitfalls we discussed earlier.
5. Focusing more on outputs than outcomes
The mistake : many product teams focus their planning on delivering outputs (i.e. new features) instead of achieving outcomes. But features alone don’t drive success; what drives success is how features meet market needs and produce business outcomes.
How to avoid it : don’t introduce unnecessary features and bombard users with information and options—the best products are usually the simplest. Every new feature should be geared toward improving the product experience for the user, and producing real business outcomes like increased revenue, acquisition, and adoption.
Ready to dive in?
Product planning doesn’t have to be scary or intimidating. The more you understand the purpose and benefits of product planning—and how to avoid common pitfalls—the better equipped you’ll be. And with Contentsquare’s insights to guide your decisions, you can be absolutely certain that every update is in line with what your customers want.
Product planning FAQs
The most critical part of the planning process is establishing outcomes that will drive business success based on data and product insights. Successful product planning can be as simple as setting the right milestones and regularly measuring your success in achieving them.
Product teams and other key stakeholders who are invested in the work that the product team is doing should be involved in the product planning process. Product managers lead the process, closely involving the entire product development team, communicating frequently, and seeking alignment from key stakeholders and leadership.
Product planning is often confused with building a product roadmap describing the features you will build over the next few months or years. But product planning is much more. It focuses on planning the processes and activities to work toward outcomes instead of creating a rigid, linear plan upfront. Product roadmaps can be helpful snapshots that represent a product team’s current thinking about the direction of the product. But the most effective roadmaps embrace the uncertainty of the future by being less detailed and more directional the further they go into the future.
Get insights that transform
- Start for free Start for free
- Book a demo Book a demo
- Integrations
- Learning Center
The 7 Strategic Phases of the Product Development Lifecycle
The only true consistent figure in this process is product management. Product managers take the reigns as early as product definition and concept vetting. They bring it to life, nurture its growth, and ultimately put it to bed one final time.
Before diving headfirst into any of the strategic phases of the product development lifecycle, it’s essential to understand all the steps. While mostly discrete activities, they do build on each other. A faulty foundation can result in a wobbly, flawed future.

1. Product Concept Development
This initial phase might be the most fun and creative stage in the product lifecycle, and it’s the most critical. Businesses come up with lots of ideas. So only the most promising projects must get the traction and resources they deserve.
So, once there’s an initial idea internal folks are excited about, it’s time to employ some of the available tools and techniques for some quick market validation . These tests give the team confidence they’re onto something with real promise.
A key step in this phase is product discovery. This process gives the product team a much deeper understanding of the problems potential customers face and the user personas the solution can target. Without a solid foundation of who the product is for and which of their pain points it solves, there’s little hope of finding product-market fit.
Armed with a good idea and a solid understanding of the key problem, the concept is then fleshed out while gathering additional information.
hbspt.cta.load(3434168, 'a00f7861-658a-4ef3-829a-60fc115c8a11', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
2. competitive analysis.
If a company has stumbled onto a great idea, it’s likely they’re not the only ones to have this epiphany. That’s why the next step is surveying the landscape. You do this to see how the product concept compares to what’s already available or under development.
The goal here is to understand the other options potential customers already have. Sometimes there will be a direct competitor with a relatively similar offering. There may be broader solutions that include similar functionality to the product in question. An effective competitive analysis must include completely unexpected, less-than-elegant workaround solutions potential customers use to solve their pain points.
This includes using spreadsheets for building product roadmaps , authoring code in a plain text editor, or building animations in PowerPoint. People often use the tools they already have at their disposal. Changing those behaviors may be just as important and challenging as taking on direct competitors.
3. Market Research
Still not done with homework! Now that the business has a handle on how its solution fits into the scene, it’s time to see if its differentiated approach to solving user problems holds up.
Market research typically involves both qualitative and quantitative research. Surveys and aggregated data can indicate trends, help calculate the total addressable market, and serve as valuable input to the prioritization process.
Meanwhile, qualitative research can help product teams get to the “why” at the heart of the solution. Using focus groups, interviews, and other in-depth research methods. These methods add both color and a sense of humanity to the research and development process. An added benefit is that they challenge assumptions.

4. Minimum Viable Product Development
The tail end of the market research phase may also entail developing a Minimum Viable Product. An MVP is functional for gauging the reaction and interest of likely buyers. It only includes the most vital features and functionality based on the business’s understanding of which user stories customers need most. It is laser-focused on solving core problems.
During MVP definition and development, the team may begin employing prioritization frameworks . MVPs determine which items would deliver the most “bang for the buck” and must be in place for the initial product offering. Frameworks focused on core functionality versus product line expansion are a good fit at this time. Examples include the jobs-to-be-done framework , which ensures the business is building products customers actually want and use.
By getting something to the market quickly, the company can validate its concept and generate user feedback. This is crucial during these early stages. It serves to inform for adjustments to perform key tasks at launch, and the value proposition and messaging matches the offering.
5. Introduction and Launch
With “Version 1.0” about to become a reality, it’s time to take this idea to market. Even if it still bears a “beta” label . The hard work of generating awareness and demand often starts well before the “download” link goes live.
The product marketing team should be generating demand and building some buzz for the offering in anticipation of the release.
Using A/B testing on different messaging and price points to build up a list of interested parties and validate the value proposition’s efficacy. Press and analysts are briefed in advance and given product demos. This seeds the media market with coverage when the grand unveiling occurs.
A robust mechanism for soliciting, collecting, aggregating, and analyzing user feedback must be in place at launch. Asses the first impressions and the efficacy of different campaign messages and tactics. The results inform plans and how to allocate resources for wider promotion and growth.
Employing product analytics and customer research, product teams can begin measuring product-market fit. If gaps are identified, they can be added to the product backlog in preparation for future prioritization and product roadmapping activities.
6. Product Lifecycle
Mature products enter a new phase of existence. Typically, this is a cycle of iterative improvements and modifications. Interspersed with more significant expansions (or removal) of functionality and capabilities.
At this point, the product roadmap becomes indispensable. As processes mature, release cadences are established, and the focus shifts to enhancements and growth. KPIs, goals, outcomes, and objectives will evolve throughout the product lifecycle. It will shift based on both the success and struggles of the product as well as the organization.
While rarely boring, this is the most predictable and routine phase of the product lifecycle. Suppose the product continues to find traction and adequate growth while establishing profitability. This phase may last for years, if not decades assuming the product remains viable and there’s a persistent market for it.
To synchronize strategic objectives with resource allocation and development priorities, structure a product roadmap using themes . Themes are excellent to ensure efforts remain focused on what matters most. This method still gives the implementation team some latitude in an Agile development framework.
All things must end. For some lucky product management professionals, this never happens on their watch. However, statistically, there’s a pretty good chance they’ll have to say goodbye to an entire product or major component at some point during their career.
This isn’t always a bad thing. In fact, it’s just an inevitable part of the strategic phases of the product planning process. It’s a phase in which you are retiring a product due to a superior offering’s arrival. Another reason is a dwindling need for a particular solution. This is because the problem is no longer acute enough to warrant a product.
But wrapping up a longstanding offering has many implications. Using a checklist can ensure all the aspects are properly addressed during the wind-down period.

3 Reasons for Product Manager Turnover (and How to Prevent It)
When an employee leaves a company, there’s more walking out the door than a salary and a nameplate. They take...

Going Overboard on a Data-Driven Approach (How to Avoid the Trap)
These days, product management and a data-driven approach are unshakeably tied together. Most want decisions based on a solid foundation...

The Art of Communication: 7 Tiny Tweaks That Deliver Big Impact
Are your product management communication skills up to snuff? Here are seven adjustments you can make to deliver a significant...
Continue exploring
You can search or explore specific categories.
Product Updates
Company news and updates, templates and workbooks, remote product management, product metrics and analytics, product strategy example, product managers, prioritization and backlog, tools and resources, customer-centricity, product leadership, product management, roadmap and roadmap management, product strategy, agile & product development, career and interviews, subscribe to our newsletter, share on mastodon.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Product planning is the process of product development and management that involves defining and strategizing to create a successful product. It encompasses the activities and processes required to identify market needs, set product goals, prioritize features, and create a roadmap for product development. The goal of product planning is to ...
Product planning is a crucial aspect of product management, encompassing the strategic act involved in developing and bringing a product to market successfully. It involves a systematic approach to defining, refining, and aligning the product's features and characteristics with the needs of the target market.
Here are the key steps of product planning that you should go through when building out a new product: 1. Define the product concept. This is the most crucial step in your business that pivots and defines what you are trying to build as a product. Jot down this stage and ensure your idea for the product is a real idea.
Looking at 50+ conversations each day and deciding to keep some of them unread so you can look at them later was a major pain in the past. Slack's user-centric product planning, however, resulted in a Tinder-like swipe experience that lets you go over all of your unreads in mere minutes. 2. Adaptability and Agility.
Product planning involves all of the internally focused decisions, steps, and tasks necessary to develop a successful product. In other words, it involves everything you'll need to do that will affect the product itself. By contrast, go-to-market planning involves all of the external-facing steps. These are the things you'll do to introduce ...
Asana can help get your products to market faster by tracking workload and simplifying planning. Create a product development template. The six stages of the product development process are 1. ideation, 2. definition, 3. prototype, 4. design, 5. testing, and 6. commercialization. Read more.
Product planning involves all of the internally focused decisions, steps, and tasks necessary to develop a successful product. In other words, it involves everything you must do that affects the product itself. By contrast, go-to-market planning involves all external-facing steps to introduce and market your product to the public.
Product planning is a systematic process of developing a product. It encompasses activities to guide every step of product development — from ideation to launch through market research, design, development, and pricing. The purpose of product planning is to help you create successful products by making sure a product resonates with users and ...
1. Treating planning as a single event rather than an ongoing process. The mistake: treating planning as an event prioritizes the plan over planning. A plan is just a snapshot of your understanding—of the product, market, and customer needs—at the time the plan was created, which means it becomes obsolete very quickly.
1. Product Concept Development. This initial phase might be the most fun and creative stage in the product lifecycle, and it's the most critical. Businesses come up with lots of ideas. So only the most promising projects must get the traction and resources they deserve. So, once there's an initial idea internal folks are excited about, it ...